Composition for inhibiting or dissolving calcium oxalate stones as well as preparation method and application of composition
A composition, the technology of calcium oxalate, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of very large irritation of the urothelium, irritation of the urinary tract mucosa, and susceptibility to infection, and achieve the effects of increasing catalytic efficiency, preventing stone recurrence, and high safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Preparation of immobilized oxalate decarboxylase magnetic particles by physical method
[0037] In the present invention, polyacrylamide, protein, cellulose, chitosan, alginic acid, polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer and other macromolecular materials that can undergo cross-linking reactions can be used to prepare immobilized oxalate decarboxylase. Example Taking microcrystalline cellulose as the carrier of magnetic particles, the preparation process of immobilized oxalate decarboxylase magnetic particles by adsorption method is illustrated to illustrate the preparation process of immobilized oxalate decarboxylase.
[0038] 1. Preparation process
[0039] Disperse 5 g of microcrystalline cellulose in 120 g of N,N-dimethylacetamide, place the mixture in an oil bath and heat to 150°C with constant stirring, and disperse for 30 min. Subsequently, the temperature of the mixture was lowered to 100° C., 8 g of LiCl was added and mixed uniformly, and stirred f...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Preparation of immobilized oxalate decarboxylase magnetic particles by chemical method
[0046] In the present invention, magnetic beads containing amino groups, carboxyl groups, N-hydroxysuccinimide groups, aldehyde groups, epoxy groups, maleimide groups, etc. that can be covalently bonded to proteins can be used to immobilize oxalic acid The preparation of decarboxylase magnetic particles, this embodiment uses the carboxyl-coupled Fe 3 0 4 Taking the immobilization of oxalate decarboxylase on magnetic beads as an example, the preparation process of immobilized oxalate decarboxylase is described.
[0047] 1. Immobilize oxalate decarboxylase on the surface of carboxyl group magnetic beads
[0048] 1.1 Preparation process
[0049] (1) Select carboxyl group magnetic beads with a particle size of 0.2-2 μm and remove the storage solution; wash with deionized water and reaction buffer (100mM MES, pH6.0) respectively, and remove the supernatant through magnetic ...
Embodiment 3
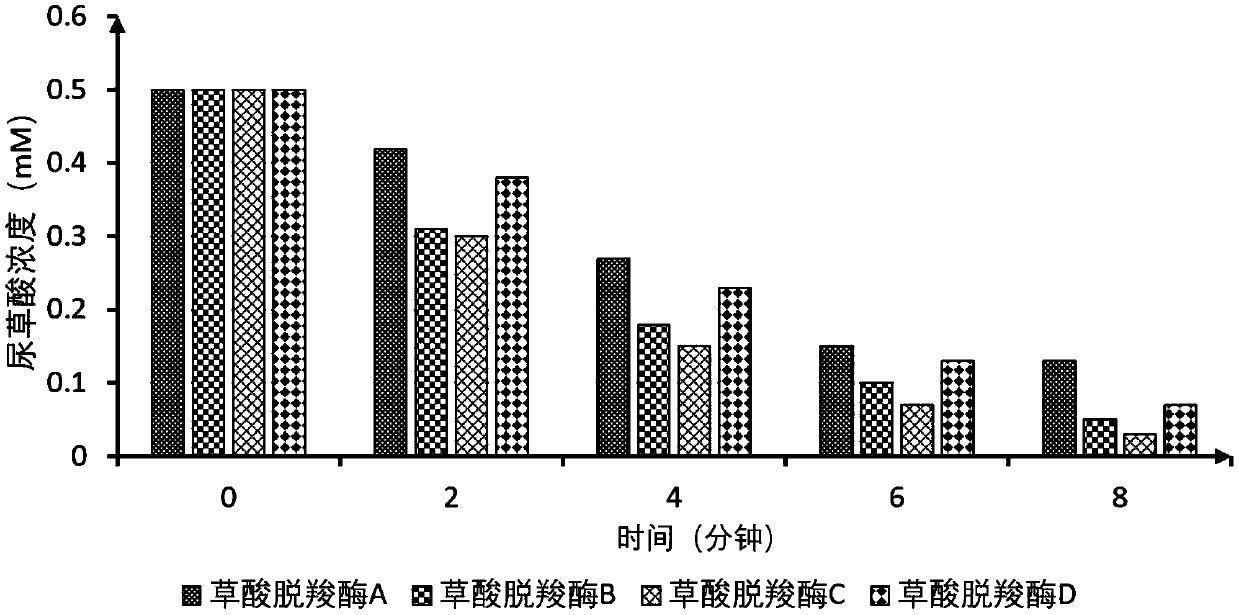
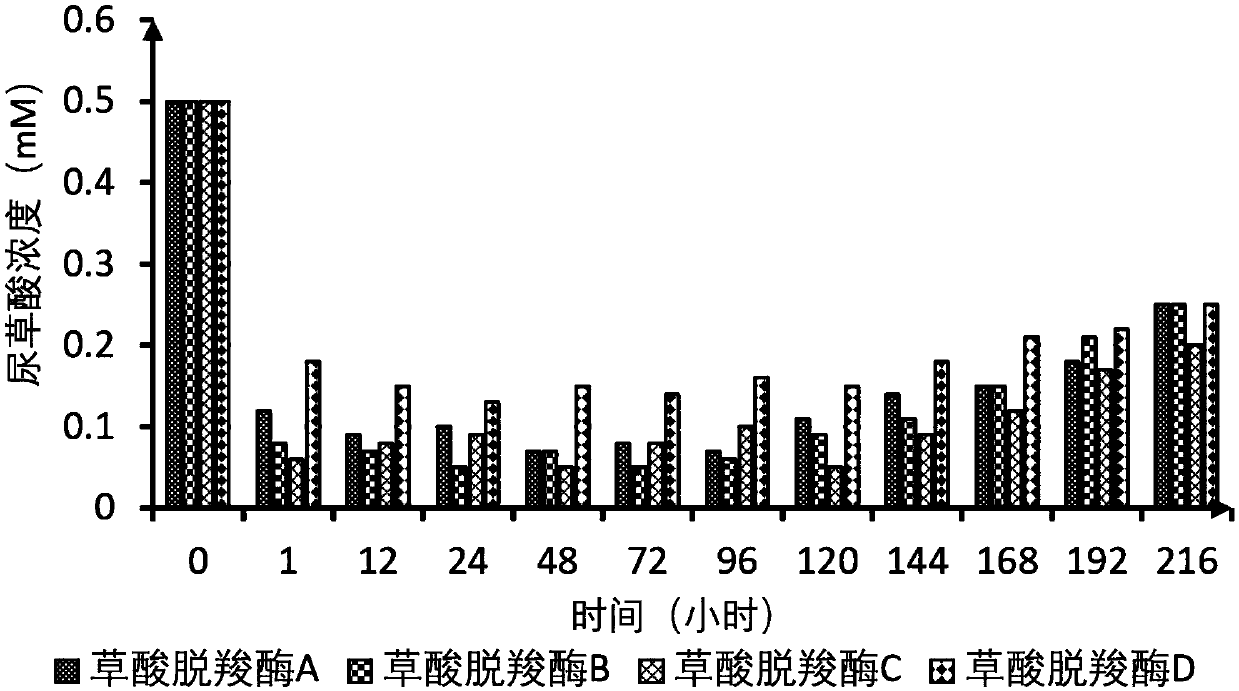
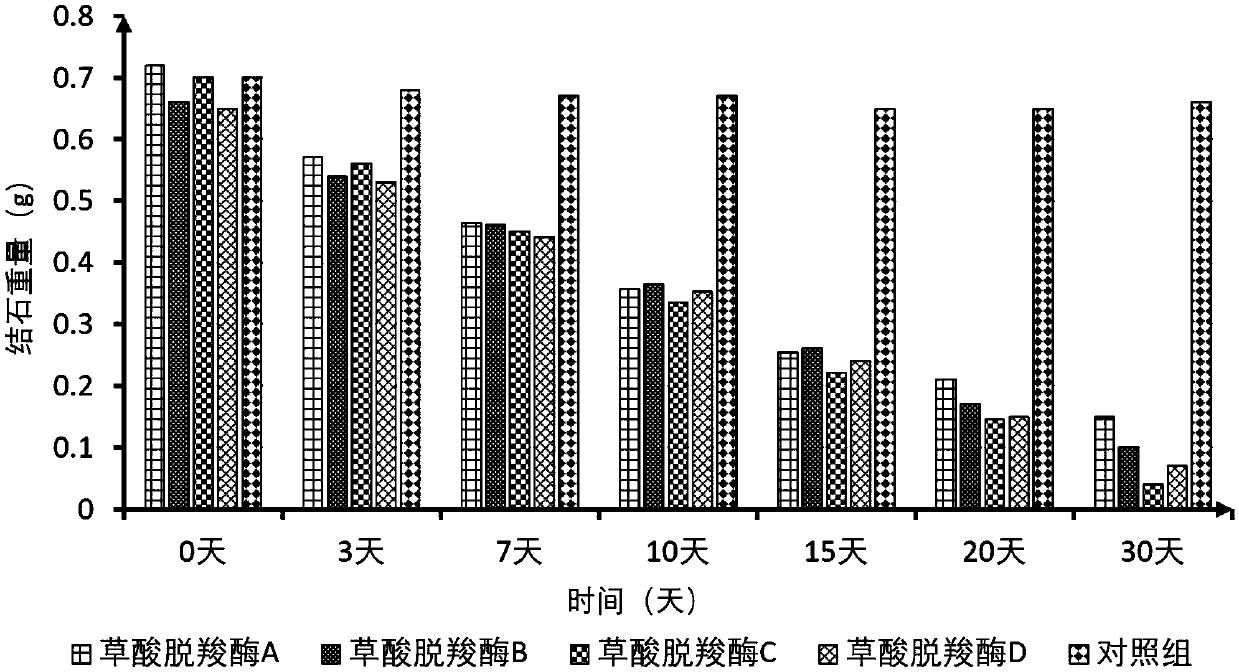
[0064] Example 3: Tolerance urine inhibition test of oxalate degrading enzyme
[0065] The action environment of the composition of the present invention is the urine in the human urinary system, therefore, the anti-inhibition performance of the immobilized oxalate decarboxylase is the key to whether the composition can function efficiently. In this embodiment, the main inhibitory factors (chloride ion, urea, and pH) in human urine are used as screening conditions, and four kinds of oxalate decarboxylases immobilized by physical adsorption method in Example 1 and carboxylated magnetic beads in Example 2 to filter. The specific conditions are: the activity of the immobilized oxalate decarboxylase under 200mM NaCl; 50mM urea; pH3.5-pH7.5.
[0066] Table 4 Tolerance test of different oxalate decarboxylases (physical adsorption) to urine inhibitory components
[0067]
[0068]
[0069] Note: Oxalate decarboxylase A is from Bacillus subtilis, oxalate decarboxylase B is from...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com