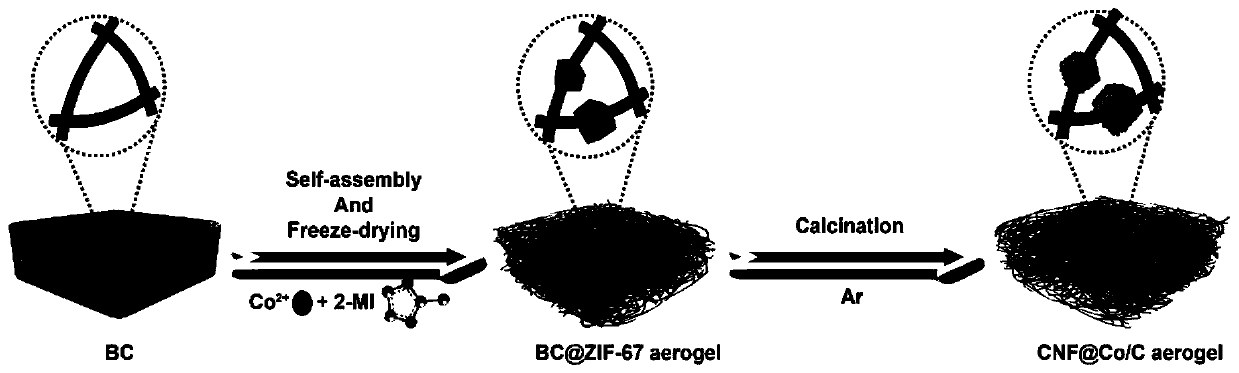
Ultra-light efficient electromagnetic shielding composite material and preparation method thereof
A composite material and raw material technology, applied in shielding materials, magnetic field/electric field shielding, carbon preparation/purification, etc., can solve the problems of secondary pollution of electromagnetic waves, high reflectivity, etc., and achieves less cellulose addition and excellent shielding performance. , the effect of low cellulose addition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1 Preparation of electromagnetic shielding airgel of the present invention
[0045] Raw material bacterial cellulose (BC) was purchased from Guilin Qihong Technology Co., Ltd.; 2-methylimidazole (2-MI, 98%), cobalt nitrate hexahydrate (Co(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O, 98%) and potassium hydroxide (KOH, >85%) were purchased from Aladdin.
[0046] 1. Synthesis of BC@ZIF-67 airgel
[0047] Pretreatment of bacterial cellulose (BC): BC (1.601 g) was soaked in 1% (mg / mL) KOH aqueous solution at 70°C for 5 hours, and then washed with deionized water.
[0048] Self-assembly: Add the pretreated BC to 40mL containing 2mmol (0.582g) Co(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O aqueous solution, stirred at 25 ° C for 6h. Then, 60 mL of an aqueous solution containing 1.64 g of 2-MI was added dropwise under stirring, and mixed well. After continuing to stir for 2 hours, it was allowed to stand at 25 °C for 18 hours for undisturbed aging. Then the liquid was removed, the remaining system was washed 3 ...
experiment example 1
[0056] Experimental Example 1 Structural Characterization
[0057] 1. Experimental method
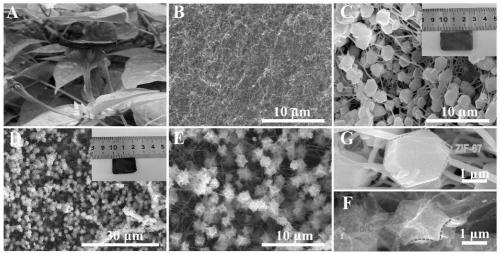
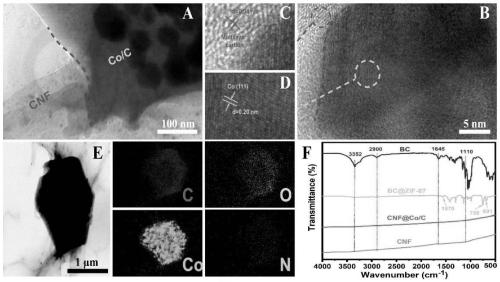
[0058] The CNF@Co / C airgel prepared in Example 1 was tested; the raw material bacterial cellulose (BC), the CNF airgel prepared in Comparative Example 1, and the metal-organic framework material ZIF- 67. The intermediate product BC@ZIF-67 airgel prepared in Example 1 was used as a control.
[0059] Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), transmission electron microscopy-energy spectroscopy (TEM-EDS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction were performed on the samples respectively. (XRD) test to characterize the sample structure.
[0060] 2. Experimental results
[0061] SEM results such as figure 2 As shown in B~G, the TEM results are as follows image 3 As shown in A, the HRTEM results are as follows image 3 As shown in B~3D, the TEM-EDS results are as f...
experiment example 2
[0064] Experimental Example 2 Thermal Stability Characterization
[0065] 1. Experimental method
[0066] The CNF@Co / C airgel prepared in Example 1 was taken for testing; the CNF airgel prepared in Comparative Example 1 was used as a control.
[0067] The samples were subjected to thermogravimetric analysis (TG) with a thermogravimetric analyzer (TG 209F1, NETZSCH, Germany). The test conditions were nitrogen atmosphere, the test temperature range was 30-800°C, and the heating rate was 10°C / min.
[0068] 2. Experimental results
[0069] Such as Figure 5 As shown, it can be seen that the CNF@Co / C airgel prepared in the present invention has excellent thermal stability.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com