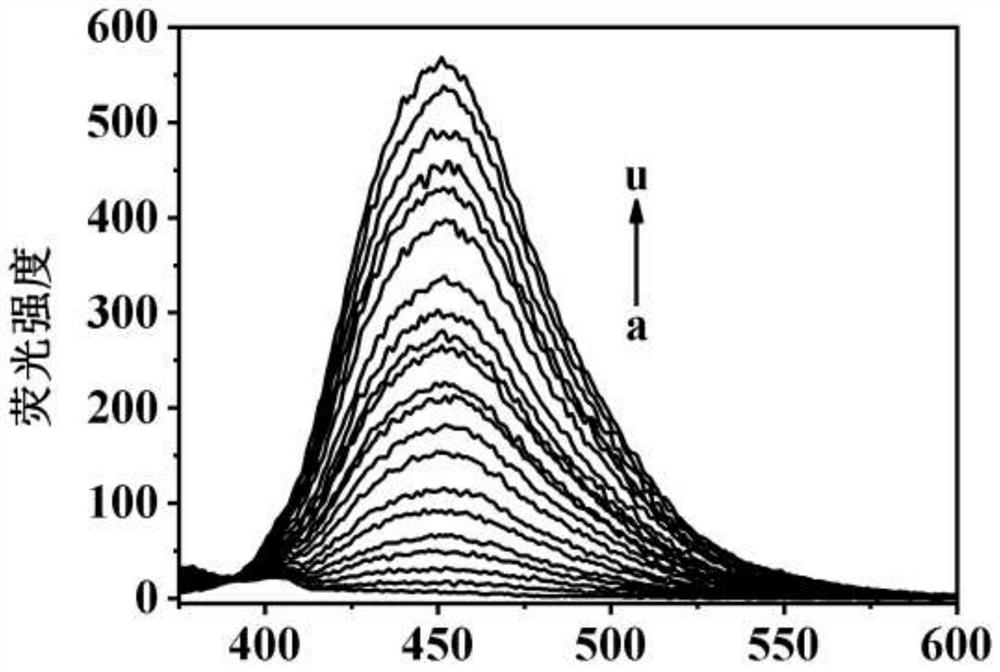
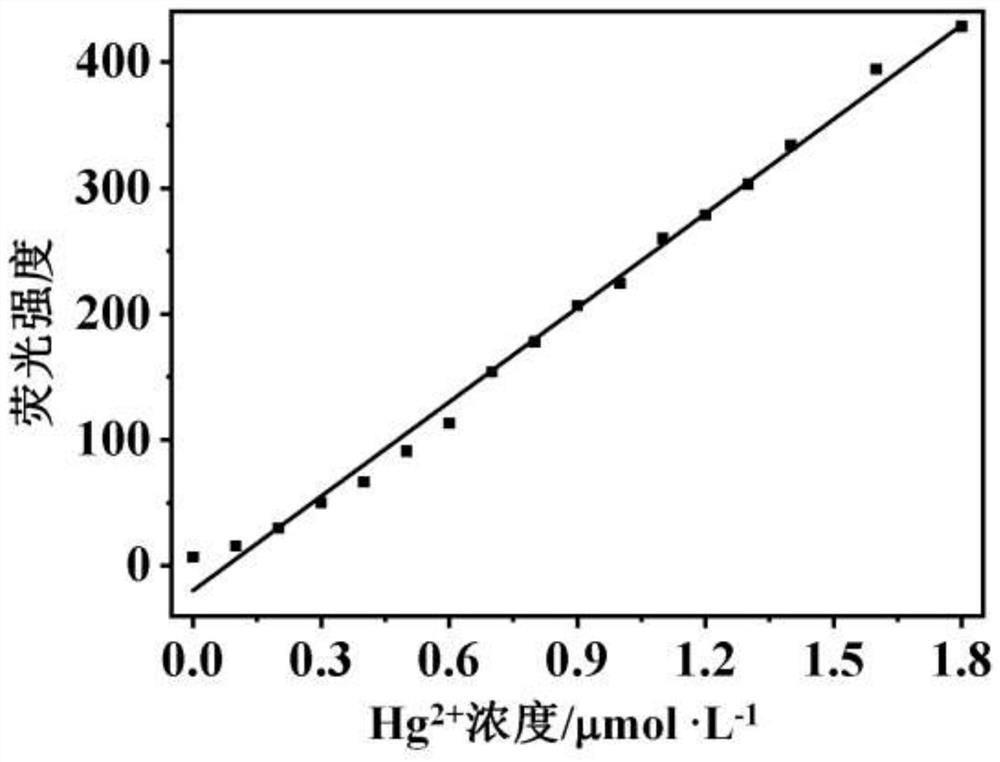
A fluorescent probe for highly selective detection of mercury ions and its synthesis method and application
A synthesis method and technology of fluorescent molecular probes, which are applied in the application field of fluorescent probes for highly selective detection of mercury ions and detection of mercury ions, achieving high sensitivity, strong recognition ability, and stable optical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Synthesis of the dipeptide-mimetic compound 1
[0032] In a 250mL round-bottom flask, add L-valine benzyl ester hydrochloride (1.3g, 6mmol), 40mL tetrahydrofuran, triethylamine (2.6mL), stir at room temperature for 0.5h, and then add 6-amino-2- Naphthoic acid (1.3 g, 6 mmol), 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt, 0.9 g), 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI, 1.5 g). The reaction was stirred for 24 hours. After the reaction, the organic phase was obtained by washing, drying, and extraction. The crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain 1.9 g of compound 1 as a pink solid with a yield of 83%. The reaction formula is as follows:
[0033]
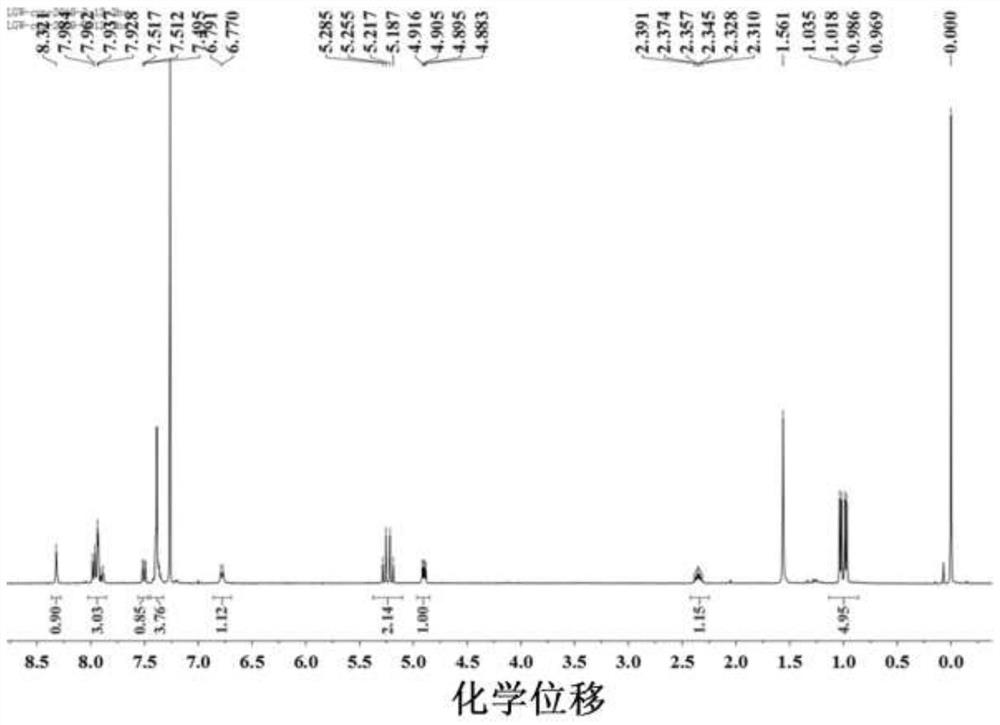
[0034] m.p.=131.1–131.6℃, =+51.13(c 0.20, in CHCl 3 ); 1H NMR(400MHz, CDCl3)δ8.18-8.17(d,J=1.2Hz,1H),7.75-7.74(t,2H),7.62-7.61(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),7.39-7.26( q,4H),7.00-6.98(d,2H),5.27-5.17(dd,J=27.1,12.2Hz,2H),4.91-4.88(dd,J=8.7,4.7Hz,2H),4.01(s, 2H), 2.36-2.28 (qd, J=11.7, 6.8Hz, 2...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Synthesis of pseudo-dipeptide carboxamide compound 2
[0036] To a 100 mL round-bottomed flask, formic acid (14.12 mL, 10.2 mmol) was added, and compound 1 (1.8 g, 4.79 mmol) was weighed under stirring at room temperature and reacted for about 48 h. When the TLC tracking reaction showed that the reaction of the raw materials was complete, 20 mL of water was added to quench the reaction, extracted with ethyl acetate, and the layers were separated. 1.6 g, 82% yield. The reaction formula is as follows:
[0037]
[0038] m.p.=147.5–148.1℃, =+49.91(c 0.20, in CHCl 3 ); 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ10.53(s,1H),8.77-8.75(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),8.43-8.37(q,J=14.3,12.7Hz,2H),8.01-7.99(d,J=8.9Hz ,1H),7.66(s,1H)7.41-7.32(m,4H),5.22-5.13(q,J=12.5Hz,2H),4.40-4.36(t,J=7.6Hz,1H).4.04-4.02 (d,1H),1.02-0.95(q,4H). 13 C NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 )δ172.2,159.1,135.5,131.2,130.1,128.7,128.6,128.5,128.3,127.4,125.0,124.4,120.4,119.4,116.6,114.4,67.3,57.6,31.8,19.1,17.9.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Synthesis of fluorescent probe molecule 1
[0040] Weigh compound 2 (0.85 g, 2.1 mmol), triethylamine (0.75 mL, 5.5 mmol, 2.0 eq.), 25 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, add them to a dry flask, evacuate and fill with nitrogen, and place in an ice bath Stir for half an hour to cool. The solid phosgene (BTC, 443 mg, 1.5 mmol) was dissolved in 10 mL of dry dichloromethane, and added dropwise to the reaction system with a syringe. After warming to room temperature, stirring was continued for 3 h, and saturated sodium bicarbonate solution was added to quench the reaction. , extracted and separated, washed with brine, and the organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The excess solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the obtained crude product was separated by flash column chromatography to obtain fluorescent probe molecule 1, a yellow solid of 0.61 g with a yield of 81%. The reaction formula is as follows:
[0041]
[0042] m.p.=128.1–128....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com