Kit for detecting helicobacter pylori drug-resistant gene polymorphism by multiple fluorescent PCR melting curve method
A technology for Helicobacter pylori and drug resistance genes, which is applied in the field of biological detection, can solve the problems of reduced sensitivity, high detection cost, long operation time, etc., and achieves the effects of high amplification efficiency and sensitivity, short detection time and convenient operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
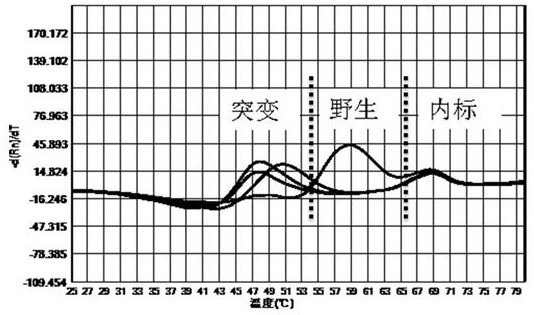
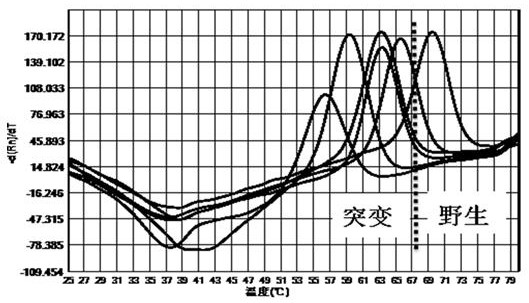
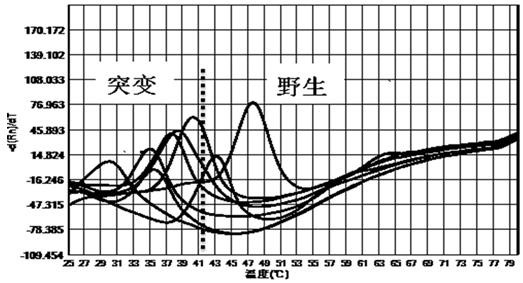
[0057] The kit of the present invention is used for the mutation detection of 260-261, 271-272 drug-resistant sites of Helicobacter pylori gyr A gene, 2142, 2143 drug-resistant sites of 23S rRNA gene, and 926-928 drug-resistant sites of 16S rRNA gene .
[0058] 1. Design of primers and probes
[0059] According to the sequences of the Helicobacter pylori gyr A gene, 23S rRNA base and 16S rRNA gene downloaded from NCBI, the primer probes were designed around the drug resistance sites to be detected according to the comparison results, and the primer design principles were followed. At 15-25bp, the primer Tm was kept at 53°C±2°C, and the probe design followed the probe design principles. The designed primers and probes were compared by BLAST to ensure the specificity of the primers and probes. The primer probe sequences are as follows:
[0060] The primer probe sequence for the resistance mutation site of Helicobacter pylori gyr A gene is as follows:
[0061] Upstream primer...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Embodiment 2: Primer probe screening and detection ability comparison
[0108] The primer probe is the key raw material of the kit, and the optimization of the primer probe is more important. According to the sequences of the Helicobacter pylori gyr A gene, 23S rRNA base and 16S rRNA gene downloaded from NCBI, after comparison, the comparison results surround the Design primer probes for detecting drug-resistant sites, follow the design principles of primers, keep the length at 15-30bp, keep the Tm of primers at 53°C±2°C, and follow the design principles of probes. The designed primers and probes were compared by BLAST to ensure the specificity of the primers and probes.
[0109] The drug-resistant site sequence is a known sequence, and different kits design and optimize primers and probes around the same sequence, resulting in large differences in specificity and sensitivity between kits. The following describes the difference between the optimized primer probe of thi...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Embodiment 3: clinical applicability verification
[0126] (1) According to the preparation method shown in Example 1, the relevant components of the kit were prepared and stored at -20°C for later use.
[0127] (2) About 300 cases of gastric mucosal tissue samples were collected from clinical units, and about 300 cases of clinical samples were extracted with the tissue extraction kit that has been filed by the company, and the purity and concentration of the extracted products were measured with Nanodrop2000, and the ratio of OD260 / OD280 of the samples All were between 1.6-2.1, and the nucleic acid concentration was >20ng / μL.
[0128] (3) According to the steps shown in Example 1, the steps of mixing the PCR reaction solution, adding samples, and operating on the machine were carried out. The detector needs to use an amplification instrument capable of multiple melting curve detection. The amplification instrument used in this experiment is Hongshi's slan.
[0129] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com