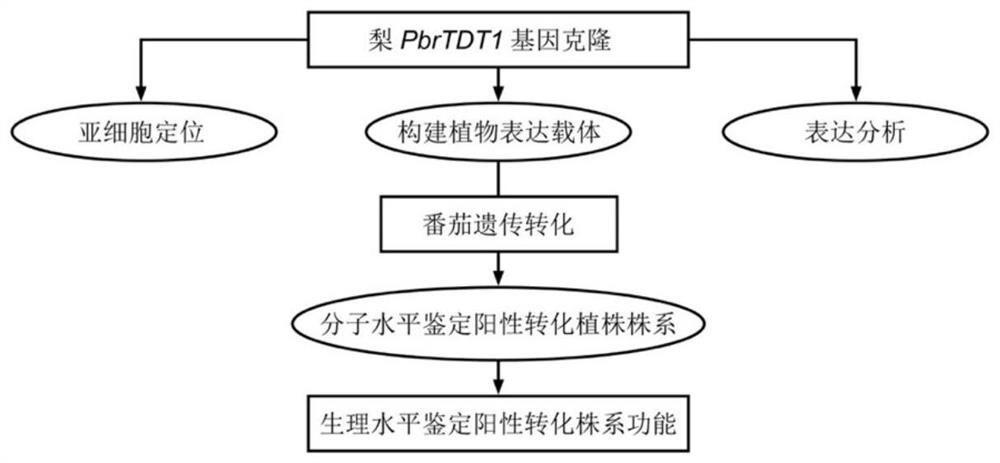
Malic acid transporter gene PbrTDT1 from pyrus bretschneideri and application of malic acid transporter gene PbrTDT1
A transporter, malic acid technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problem of unclear role of TDT transporter, and achieve the effect of improving screening efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Cloning of embodiment 1PbrTDT1 gene
[0036] The pulp of 'Dangshan Suli' which was 90 days after the full flowering stage was used as the test material, RNA was extracted and reverse transcribed, and the obtained first-strand cDNA was used to amplify the full length of the PbrTDT1 gene. Amplified gene PbrTDT1 primer pair is: forward primer PbrTDT1-F1: 5'-ATGGATCATCATCCAGTTTCCGACG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 3); reverse primer PbrTDT1-R1: 5'-TCACTGAACTGCAGGTTCATTTGTCC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 4 ). The 50μl reaction system includes 100ng template DNA, 1.0μM the aforementioned primers, 10mM dNTPs, 5×Q5 reaction buffer (Q5 Reaction Buffer), 1U Q5 high-fidelity polymerase (Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase) (the above buffer and Q5 High-fidelity polymerases were purchased from NewEngland Biolabs). The PCR reaction program was: 95°C, pre-denaturation for 30 seconds; 95°C, denaturation for 30 seconds, 60°C, annealing for 45 seconds, 72°C, extension for 1 minute, 35 cycles; after the cycle was comple...
Embodiment 2
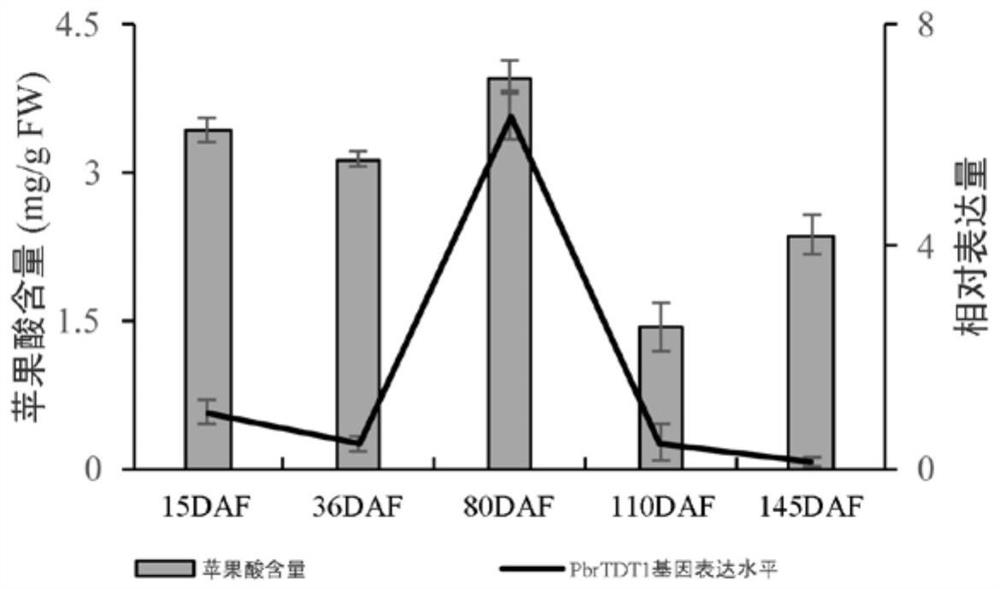
[0037] Example 2 Analysis of the expression pattern of the PbrTDT1 gene
[0038] 1. Changes of malic acid content during pear fruit development
[0039] To analyze whether the PbrTDT1 gene is related to the metabolism of malic acid in pear pulp. The present invention measures the malic acid content in five periods during the dynamic development of pear fruit. The specific measurement steps are as follows: Accurately weigh 2.0 g of the pulp tissue sample in a pre-cooled mortar, add 8 mL of 80% ethanol, fully grind it into a homogenate, transfer it to a 10 mL centrifuge tube, bathe in 37°C for 30 minutes, and ultrasonically for 15 minutes. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes, transfer the supernatant to a 25mL volumetric flask, repeat the operation 3 times, combine the supernatant and make to volume. Take 2mL of the extract, evaporate to dryness with a rotary evaporator (model: RE-3000, Shanghai Rongya Biochemical Instrument Factory), dissolve it in 1mL of sterile distille...
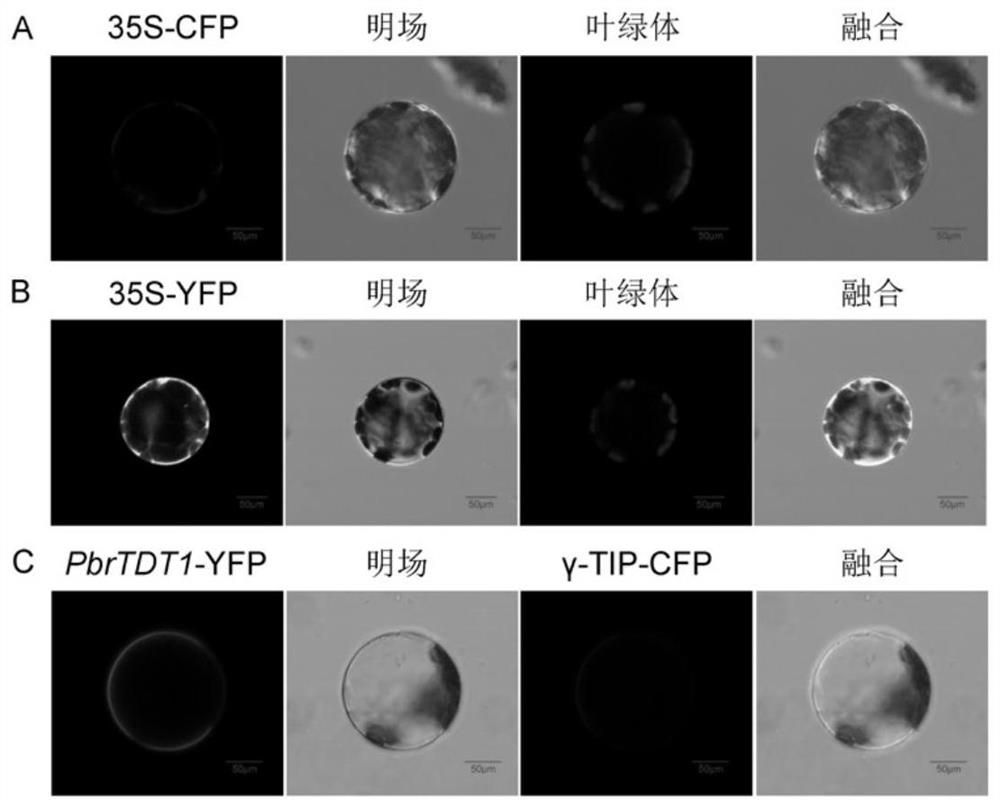
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Subcellular Localization of PbrTDT1 Gene
[0046] The present invention uses Arabidopsis protoplasts to study the subcellular localization of PbrTDT1. The entire open reading frame of the PbrTDT1 gene was amplified by PCR, and two restriction sites, XbaI and BamHI, were respectively added to the two ends of the amplification primers. The nucleotide sequence of the primer is: forward primer PbrTDT1-F3:5'-GCTCTAGAATGGATCATCATCCAGTTCCGACG-3'(SEQ ID NO:9); reverse primer PbrTDT1-R3:5'-CGGGATCCCTGAACTGCAGGTTCATTTGTCC-3'(SEQ IDNO:10) . The underline is the enzyme cutting site, TCTAGA is the XbaI restriction site, GGATCC It is the restriction site of BamHI restriction enzyme. Firstly, the amplified product was loaded on the pEASY-Blunt Zero vector to obtain a pEASY-Blunt Zero-PbrTDT1 recombinant vector. At the same time, the pEASY-Blunt Zero-PbrTDT1 and 35S-YFP vectors were digested with XbaI and BamHI, and the products were recovered and ligated to obtain the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com