Chemical small molecule composition and method for directly reprogramming in-vitro and in-vivo chemically induced fibroblasts into hepatocytes
A fibroblast, chemically induced technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, animal cells, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete differentiation, high cost and low differentiation efficiency of stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0126] The preparation method of the small molecule composition of the present invention is determined according to the dosage form to be prepared and the route of administration. Those skilled in the art, after referring to the combination and proportioning provided by the present invention, adopt the conventional preparation method of the pharmaceutical composition The chemical small molecule composition of the present invention can be prepared.
[0127] It should be understood that although in the specific embodiment, the inventor listed several composition forms, those skilled in the art can also deduce from this that any other small molecule combination form of the present invention also has outstanding effects.
[0128] The present inventors have confirmed for the first time that the small molecule composition of the present invention can induce fibroblasts to transform into hepatocytes in situ in vivo, and reduce or reduce the fibroblasts or fibroblasts in tissues / organs...
Embodiment 1
[0156] Example 1. Small molecule composition for direct reprogramming (transdifferentiation) of fibroblasts induced by small molecules into hepatocytes, and preparation of transdifferentiation medium and reagents thereof
[0157] Design the following composition or transdifferentiation medium, which can be prepared according to molar concentration or weight concentration:
[0158] 1. Formula of small molecule composition for fibroblast transdifferentiation liver cell
[0159] (1) Fibroblast transdifferentiation liver cell composition 1
[0160] GSK3β inhibitor CHIR-99021: final concentration 3 μM;
[0161] G9aHMT inhibitor BIX01294: final concentration 3 μM;
[0162] (2) Fibroblast transdifferentiation liver cell composition 2
[0163] GSK3β inhibitor LY2090314: final concentration 0.3 μM;
[0164] G9aHMT inhibitor UNC0642: final concentration 2 μM;
[0165] (3) Fibroblast transdifferentiation liver cell composition 3
[0166] GSK3β inhibitor LiCl: final concentration 10...
Embodiment 2
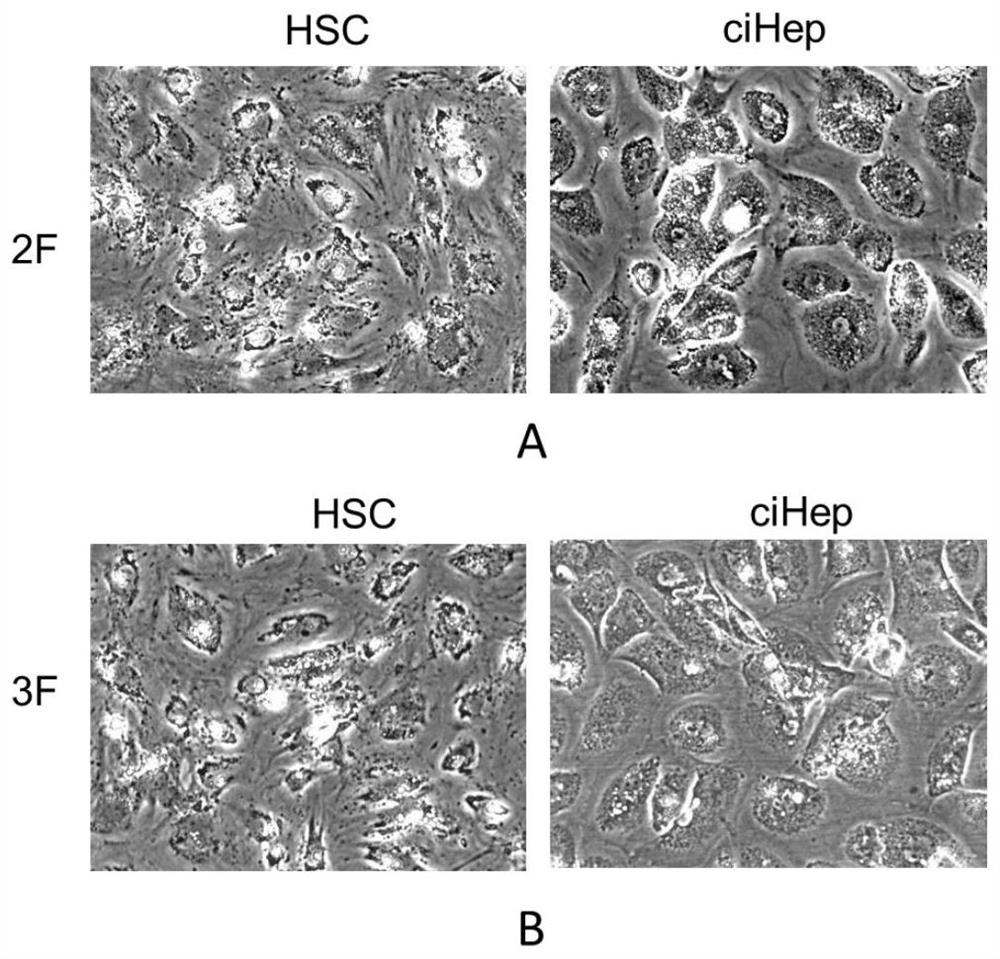
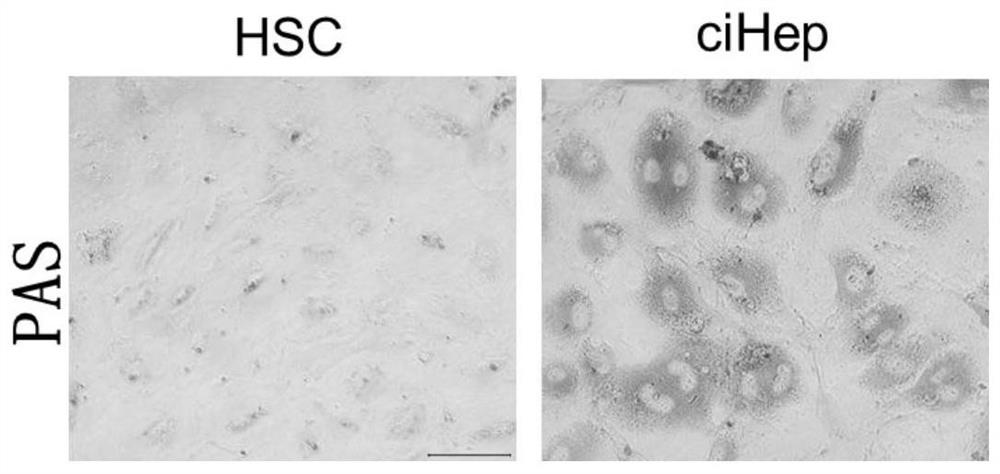
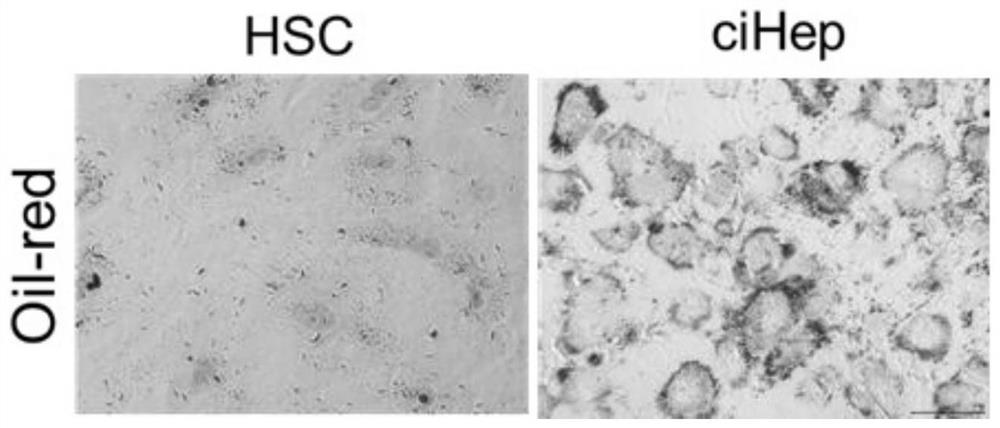
[0212] Example 2, Fibroblast Transdifferentiation Hepatocyte Medium 1, 11 Chemically induced hepatic fibroblast (hepatic stellate cell HSC) transdifferentiation into hepatocyte comparative experiment
[0213] 1. Fibroblast transdifferentiation hepatocyte culture
[0214] Mouse hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), that is, hepatic fibroblasts, were suspended in DMEM, a cell base medium containing 10% calf serum, plated, and cultured at 37°C. Set up control group and treatment group;
[0215] After hepatic stellate cells adhered to the wall, the original medium was discarded, and the treatment groups were replaced with Fibroblast Transdifferentiated Hepatocyte Culture Substrates 1 and 11 were cultured at 37°C, and the medium was changed every 3 days; passage was performed once every 3-7 days.
[0216]2. Subculture of Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSC) Transdifferentiated Hepatocytes
[0217] Subculture steps: Discard the original culture medium, wash once with PBS, add cell digestion so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com