Recycling and resourceful treatment method of alkaline wastewater in tantalum-niobium hydrometallurgy
A hydrometallurgical and resource-recycling technology, applied in the fields of metallurgical wastewater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, neutralized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor practicability, resin poisoning, insufficient distillation separation, etc., and reduce washing water. , The effect of simple equipment and stable process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
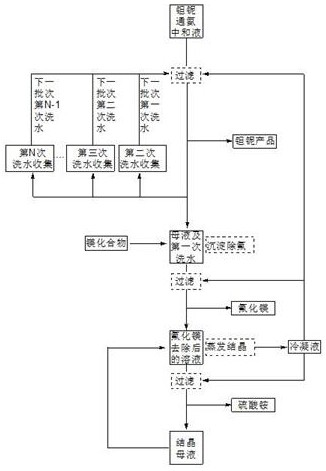
[0025] Measure 500 mL of niobium return solution to neutralize with NH3, filter the obtained precipitate and wash with 50 mL of deionized water each time, combine the filtered neutralization mother liquor and the waste water from the first washing, and directly enter the next magnesium Compound precipitation defluorination process, the remaining waste water from the second, third, and sixth washings are collected separately in different containers marked A, B, C, D, and E; the neutralized mother liquor obtained by the above filtration and The wastewater from the first washing was tested to contain F-7500mg / L, NH3-N13000mg / L, magnesium sulfate was added to it at room temperature to form magnesium fluoride precipitate, the temperature was raised to 75°C until the reaction was complete, aged for 2 hours, filtered and dried Dry to obtain magnesium fluoride by-product, the filtrate is tested to contain F- 5 mg / L, NH3-N 12400 mg / L, carry out distillation and crystallization, and cent...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Measure 500 mL of niobium return aqueous solution and neutralize it with NH3, filter the obtained precipitate and wash it with the waste water in container A, combine the waste water generated this time with the neutralization mother liquor, and directly enter the next magnesium compound precipitation defluorination process, continue Use the waste water in container B for the second wash, the waste water in C container for the third wash, until the waste water in D container for the fifth wash, and finally use the recovered distilled water for the sixth wash, the above washing waste water is still separated Collected in different containers of A, B, C, D, and E above, and circulated sequentially as washing water for subsequent batches of products. The neutralized mother liquor obtained by the above filtration and the first washing waste water are detected to contain F-7520mg / L, NH3-N 13180mg / L, magnesium sulfate is added thereto at normal temperature to generate magnesiu...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Measure 500 mL of niobium-return aqueous solution and neutralize it with NH3, wash with waste water circulation and treat the waste water as described in Example 2. The neutralized mother liquor and the first washing wastewater obtained by the above filtration contain F-7525 mg / L and NH3-N 13195 mg / L after testing. Magnesium sulfate is added thereto at normal temperature to generate magnesium fluoride precipitation, and the temperature is raised to 75 ° C to react complete, aging for 2 hours, filtering, washing, and drying to obtain magnesium fluoride, and filtering the mother liquor and washing waste water to enter the process of concentrating and recovering ammonium sulfate. The solution obtained by the above filtration after removing magnesium fluoride was tested to contain F-6 mg / L, NH3-N 12540 mg / L, distilled and crystallized, and centrifuged to obtain ammonium sulfate by-product.
[0032] Only a small amount of fresh deionized water is needed, the magnesium fluori...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com