Radiation preparation method of silicon carbide quantum dots and product thereof
A silicon carbide and quantum dot technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve problems such as danger, high energy consumption, pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing raw material costs, energy consumption, and environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
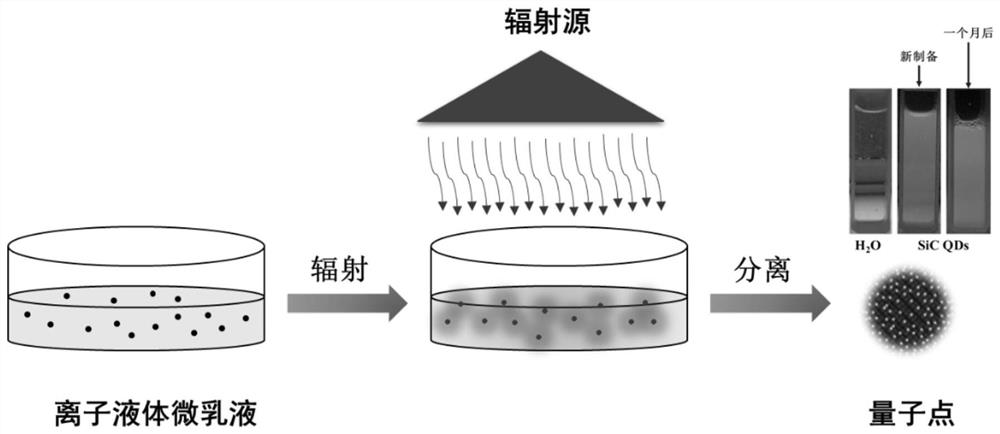
[0024]Generally speaking, the radiation preparation method of silicon carbide quantum dots of the present invention may include the following steps:
[0025] S1: Mix the silane coupling agent and the ionic liquid uniformly at a mass ratio of 0.01-5:1 to obtain a mixed solution for use.
[0026] S2: Take the above mixed solution to prepare an ionic liquid-in-water microemulsion, so that the microemulsion components include the following components by weight: 70-80 parts by weight of water, 20-30 parts by weight of surfactant , and 0-10 parts by weight of the ionic liquid. The obtained microemulsion was magnetically stirred at room temperature until uniform and transparent. Then, it can be divided into 10×15cm PE bags for later use.
[0027] S3: Under normal temperature and pressure, electron beams or gamma rays are used to irradiate the microemulsion prepared in S2 with 10 kGy-200 kGy to prepare silicon carbide quantum dots in situ.
[0028] S4: Finally, use a mixture of ace...
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) The total mass of the prepared microemulsion system is 100 g, and the mass ratio of the immobilized coupling agent to 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate is about 0.2. Add 0.3764g of silane coupling agent to 1.8189g of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, then add 18.1899g of Triton-100 (ie, TX-100), 80.02g of H 2 O mixed and stirred for 1h. Pack each 20g into a PE bag.
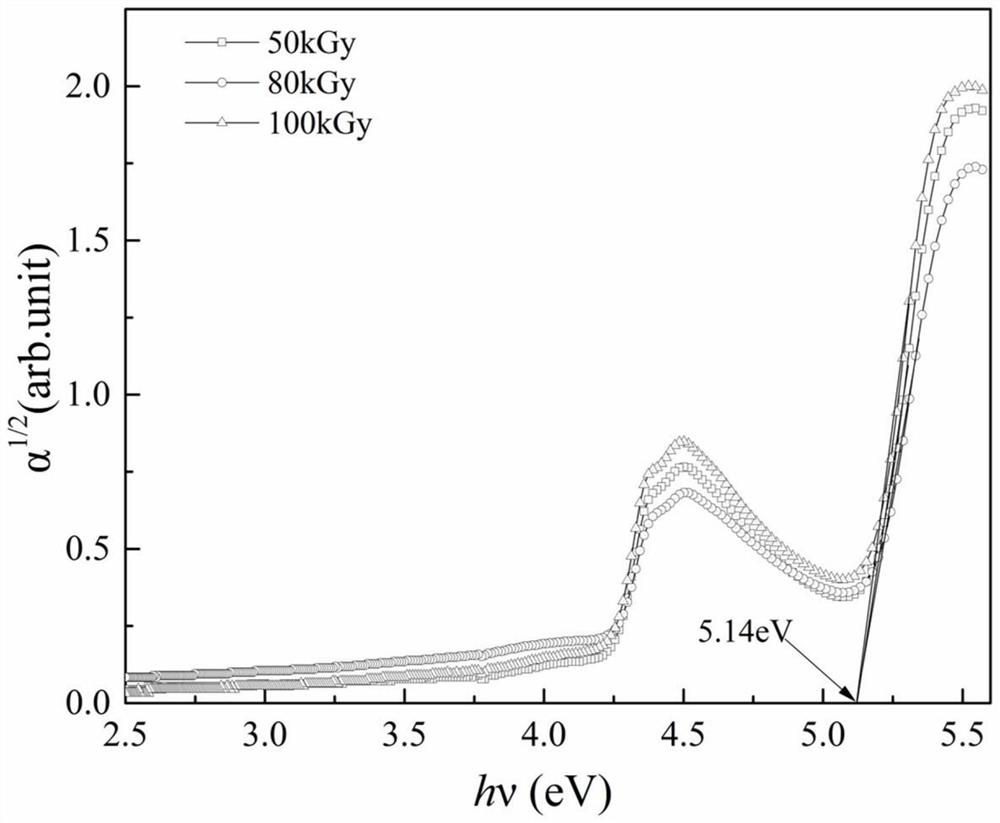
[0032] (2) Using an electron accelerator above 0.4 MeV or cobalt-60 as a radiation source to irradiate with a dose of 10kGy-200kGy to prepare silicon carbide quantum dots in situ. Take 3 samples obtained in step (1), and treat them with irradiation doses of 50kGy, 80kGy, and 100kGy respectively.
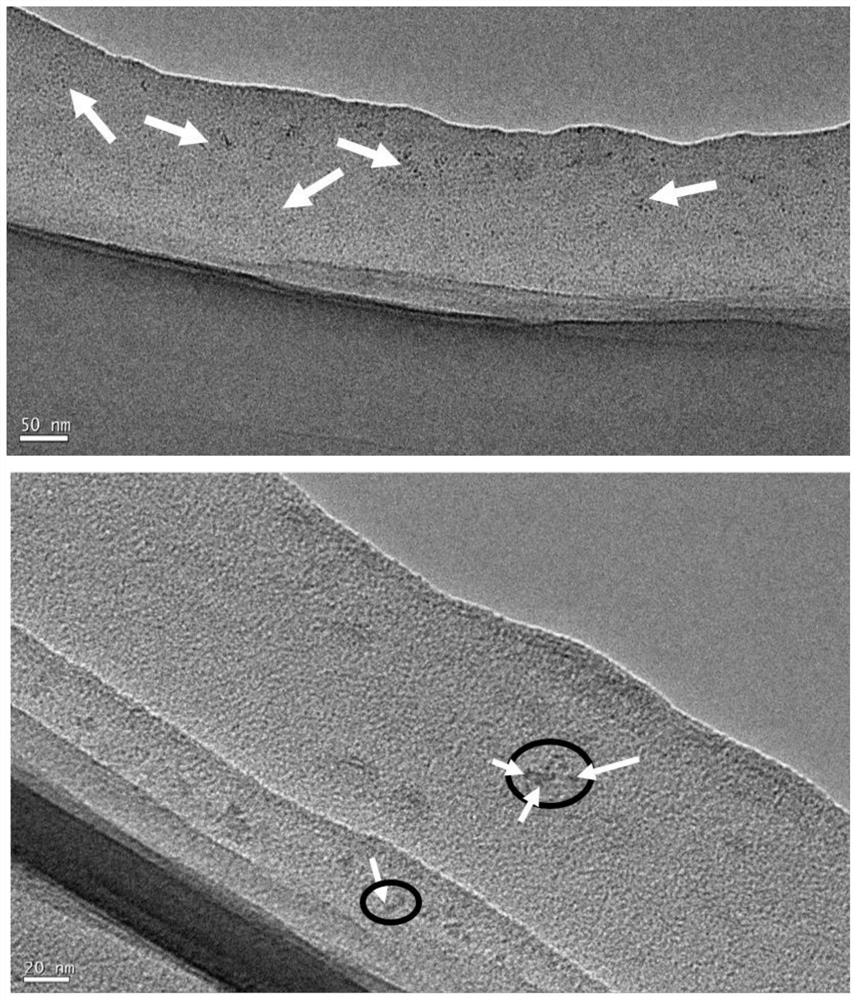
[0033] (3) After the irradiation is completed, purification and separation are carried out according to the treatment method of step S4 above. The obtained silicon carbide quantum dot is about 1nm, has a stable, blue fluorescent silicon carbide quantum dot ( figure 1 ).
[003...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) The total mass of the prepared microemulsion system is about 60 g, and the mass ratio of the immobilized coupling agent to the ionic liquid is about 0.5. Add 0.5396g silane coupling agent to 1.1002g 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, with 10.9068g TX-100, 48.0038g H 2 O mixed and stirred for 1h. Pack each 20g into a PE bag.
[0039] (2) Using an electron accelerator above 0.4 MeV or cobalt-60 as a radiation source to irradiate with a dose of 10kGy-200kGy to prepare silicon carbide quantum dots in situ. Specifically, an irradiation dose of 80kGy is used for treatment.
[0040] (3) After the irradiation is completed, purification and separation are carried out according to the treatment method of step S4 above. The obtained silicon carbide quantum dots are about 1nm in size, have stable and blue fluorescent emission silicon carbide quantum dots.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com