Electrochemical sensor for detecting hepatitis B exosome miRNA as well as preparation and application of electrochemical sensor
An electrochemical and exosome technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of leakage, time-consuming and laborious, low hybridization efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Preparation of electrochemical sensors and detection of exosomal miRNA
[0074] 1. Materials
[0075] 6-Mercapto-1-hexanol (MCH) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). HPLC-purified oligonucleotides were synthesized by Shanghai Sangong. Hemin G-four-strand DNAzyme (solution) was purchased from Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (Shanghai).
[0076] 2. Testing instruments
[0077] Shanghai Chenhua CHI660D electrochemical workstation, the detection system is a three-electrode system, including an Ag / AgCl electrode as a reference electrode, a platinum wire electrode as a counter electrode, and a gold electrode with a diameter of 3mm as a working electrode.
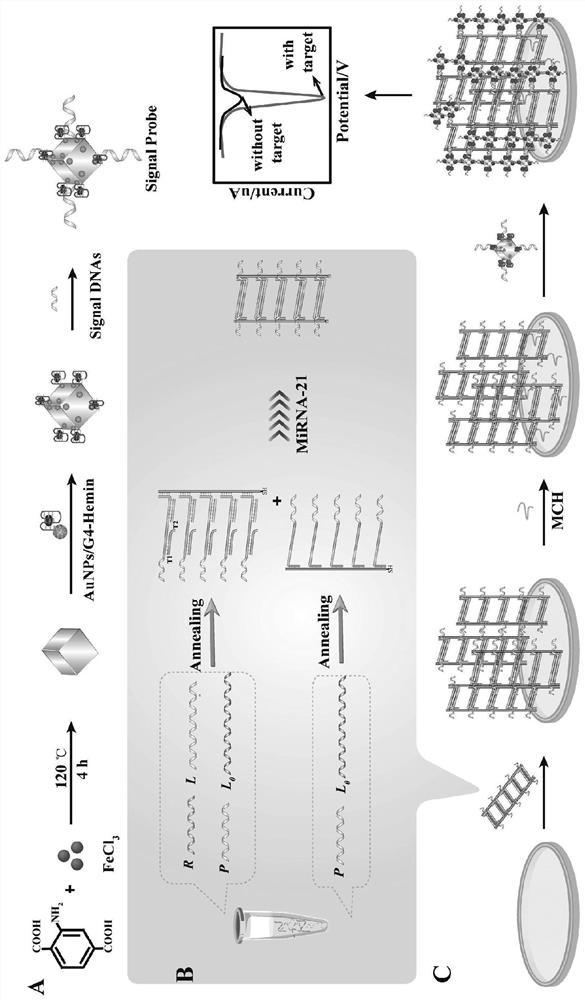
[0078] 3. Detection principle
[0079] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention builds an enzyme-free, label-free electrochemical sensor based on the cascade strand displacement reaction (L-TEDCR) and MOF / DNA cascade enzymes for detecting exosomal miRNA. The detection principle is: The chain di...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Validation of the feasibility of detecting exosomal miRNA electrochemical sensors
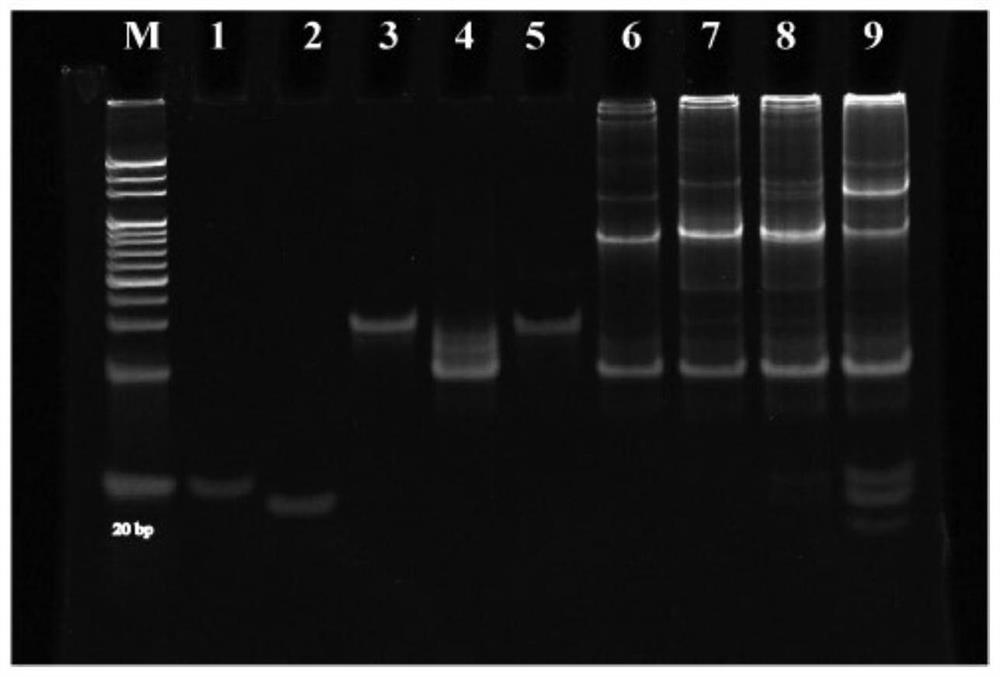
[0111] Determine whether Exo-miRNA triggers L-TEDCR by PAGE experiment, the results are as follows image 3 shown.
[0112] image 3 The PAGE electrophoresis characterization results of the cascade strand displacement reaction (L-TEDCR) of the present invention are shown. Among them, lane M is the DNA gradient marker, and lanes 1-5 are P strand, R strand, L strand, L strand 0 chain, auxiliary chain Fs, lane 6 is Ts complex, lane 7 is Ts+auxiliary chain Fs, swimming lane 8 is Ts+auxiliary chain Fs, and lane 9 is Ts+auxiliary chain Fs+target substance.
[0113] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that in the absence of Exo-miRNA, almost no P chain was produced (lanes 7, 8), which indicated that the constructed L-TEDCR strategy had negligible background leakage. In the presence of different concentrations of Exo-miRNA, the auxiliary chain Fs chain decreased, and at the same time a new ba...
Embodiment 3
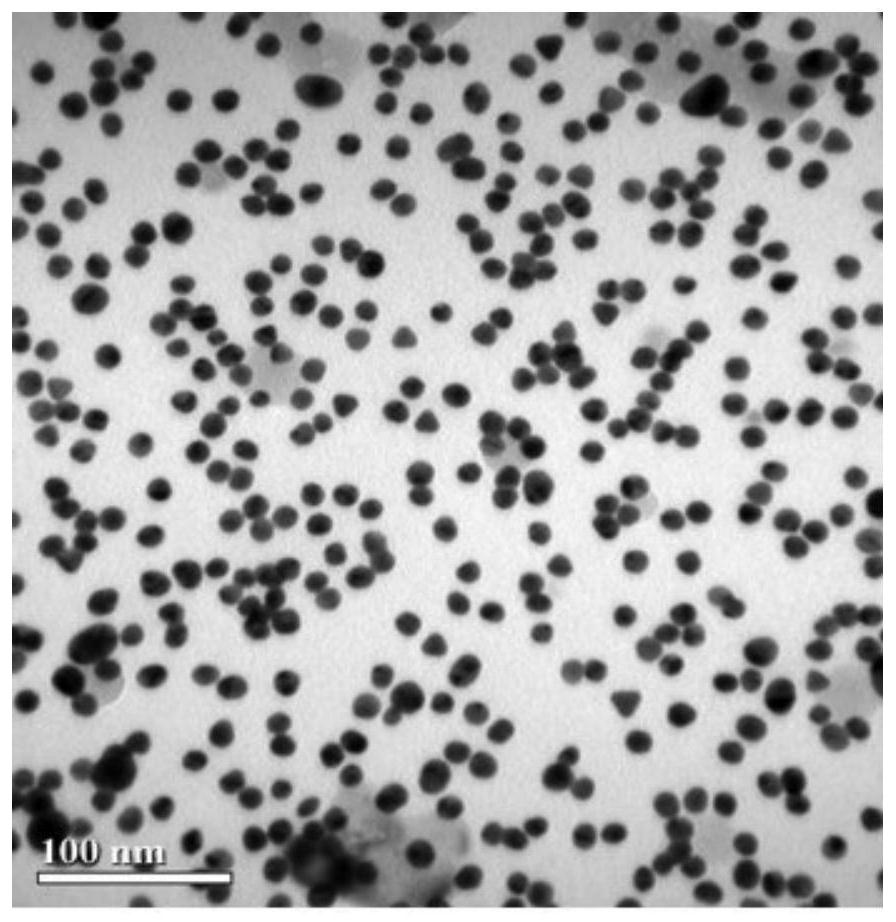
[0115] Take the MOF nanosheets prepared in Example 1, and verify the synthesis of MOF by TEM.
[0116] Figure 4 shows the TEM images of the MOF nanosheets, given by Figure 4 It can be seen that the MOF synthesized in the present invention exhibits an obvious sheet structure, and its lateral size is about 2 μm, indicating that the MOF nanosheet has a large specific surface area, which is conducive to loading more biomolecules. It shows that the MOF we built was successfully synthesized.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com