Protein meal replacement powder and preparation method thereof
A technology for meal replacement powder and protein powder, applied in dairy products, milk preparations, applications, etc., can solve problems such as poor water solubility, difficult absorption, and protein powder denaturation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
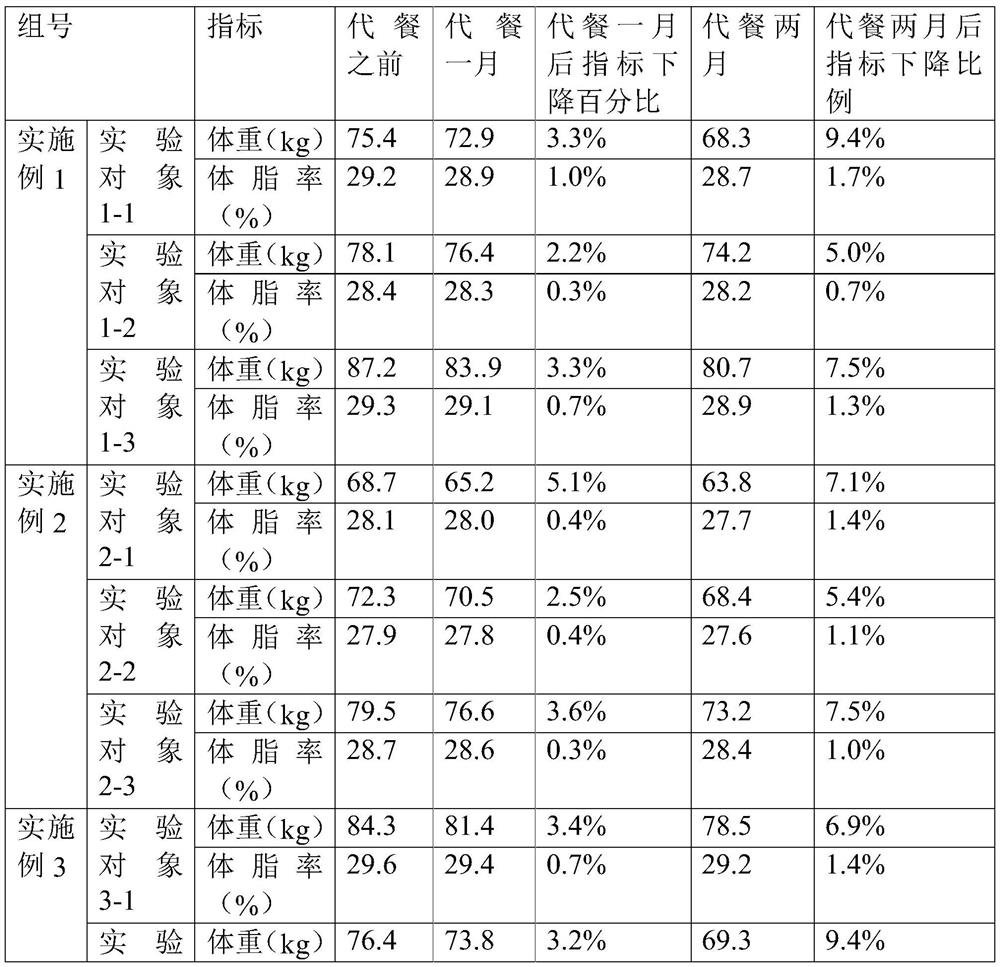
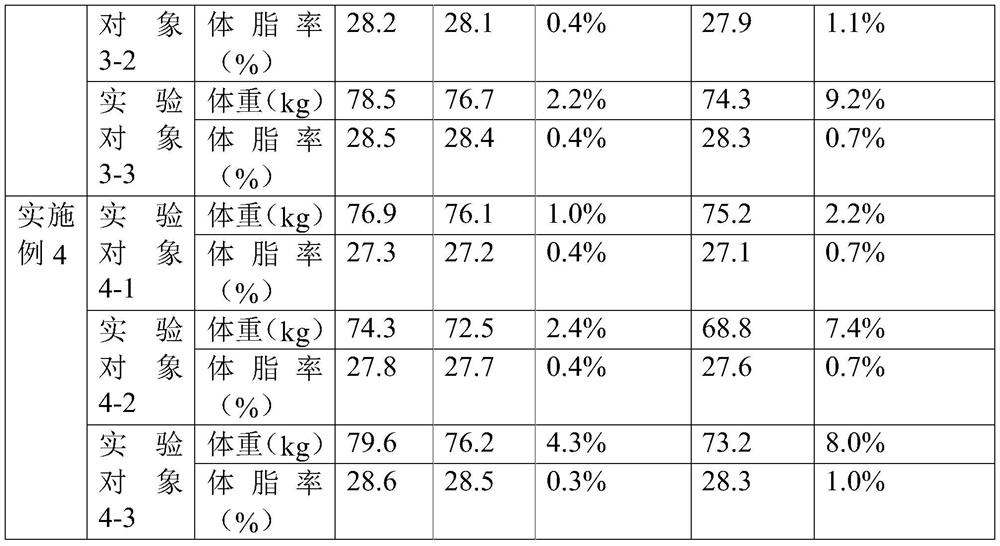
[0051] The invention provides a protein meal replacement powder, which is composed of the following raw materials in parts by mass: 43.0% of soybean protein powder, 28.9% of instant skim milk powder, 15% of resistant dextrin, 3% of psyllium husk, and inulin 3%, strawberry flavor essence 2%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 1.6%, stachyose 1%, L-carnitine 1%, soybean lecithin 1%, L-ascorbic acid 0.2%, ferrous gluconate (11%) 0.1%, Tea polyphenols 0.08%, gluconic acid (13%) 0.06%, dl-α-tocopheryl acetate 0.03%, niacin 0.022%, pantothenic acid 0.004%, pyridoxine hydrochloride 0.002%, vitamin B10.001%, vitamin B2 0.001 %.
[0052] The preparation method is:
[0053] S1. After premixing the soybean protein powder, resistant dextrin, and psyllium husk powder, add water to the premixed powder, add 0.9L of water per 1kg of the premixed powder, and stir evenly. The mixture is sheared and emulsified; the rotational speed of the dispersing emulsifier is controlled at 8000rmp; the particl...
Embodiment 2
[0058] A protein meal replacement powder, which is composed of the following raw materials in parts by mass: 44.2 parts of soybean protein powder, 28.3 parts of instant skim milk powder, 15.8 parts of resistant dextrin, 2.8 parts of psyllium husk, 2.3 parts of inulin, 2.3 parts of strawberry flavor essence, 1.4 parts of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 0.8 parts of stachyose, 0.7 parts of L-carnitine, 1.2 parts of soybean lecithin, 0.1 part of L-ascorbic acid, 0.1 part of ferrous gluconate (11%), tea polyphenols 0.05 parts, 0.05 parts of gluconic acid (13%), 0.02 parts of dl-α-tocopheryl acetate, 0.018 parts of niacin, 0.003 parts of pantothenic acid, 0.002 parts of pyridoxine hydrochloride, 0.001 parts of vitamin B1, and 0.002 parts of vitamin B2.
[0059] The preparation method is:
[0060] S1. After premixing the soybean protein powder, resistant dextrin, and psyllium husk powder, add water to the premixed powder, add 0.9L of water per 1kg of the premixed powder, and stir ev...
Embodiment 3
[0065] A protein meal replacement powder, which is composed of the following raw materials in parts by mass: 41.3 parts of soybean protein powder, 27.6 parts of instant skim milk powder, 14.5 parts of resistant dextrin, 2.4 parts of psyllium husk, 3.4 parts of inulin, 1.5 parts of strawberry flavor essence, 1.8 parts of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 1.3 parts of stachyose, 1.2 parts of L-carnitine, 1.4 parts of soybean lecithin, 0.1 part of L-ascorbic acid, 0.2 parts of ferrous gluconate (11%), tea polyphenols 0.10 parts, 0.04 parts of gluconic acid (13%), 0.03 parts of dl-α-tocopheryl acetate, 0.022 parts of niacin, 0.004 parts of pantothenic acid, 0.001 parts of pyridoxine hydrochloride, 0.001 parts of vitamin B1, and 0.002 parts of vitamin B2.
[0066] The preparation method is:
[0067] S1. After premixing the soybean protein powder, resistant dextrin, and psyllium husk powder, add water to the premixed powder, add 0.8 L of water per 1 kg of the premixed powder, and stir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com