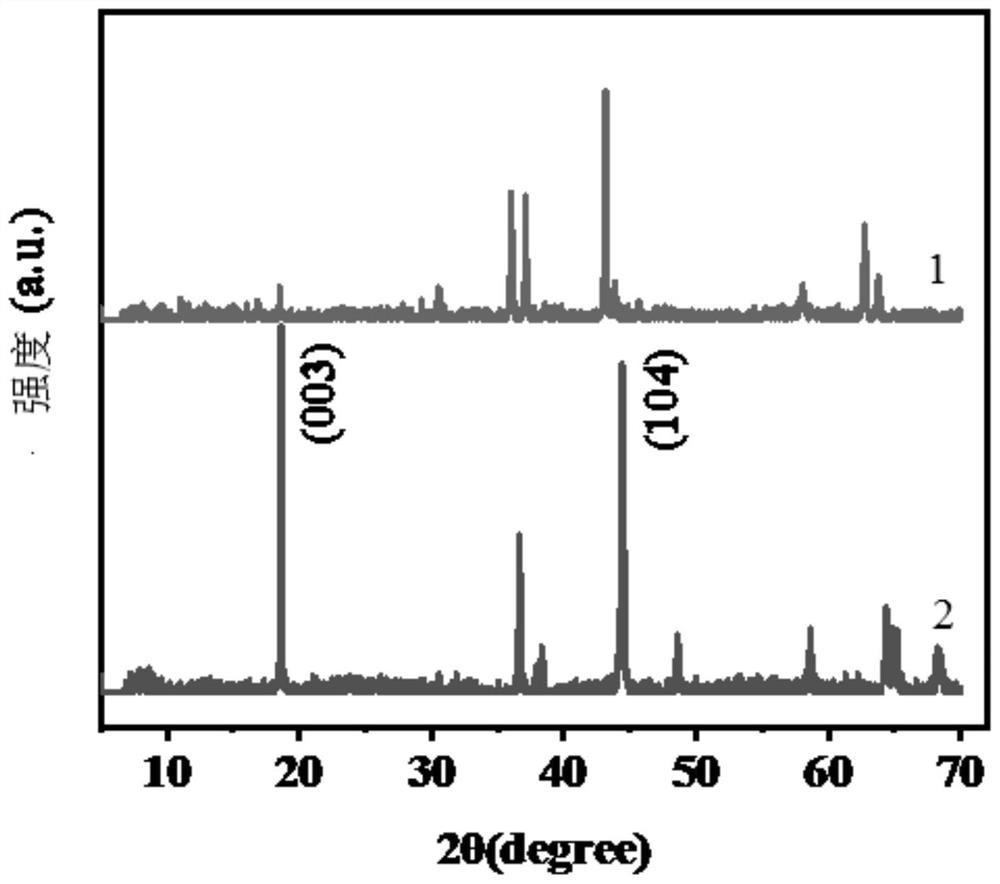
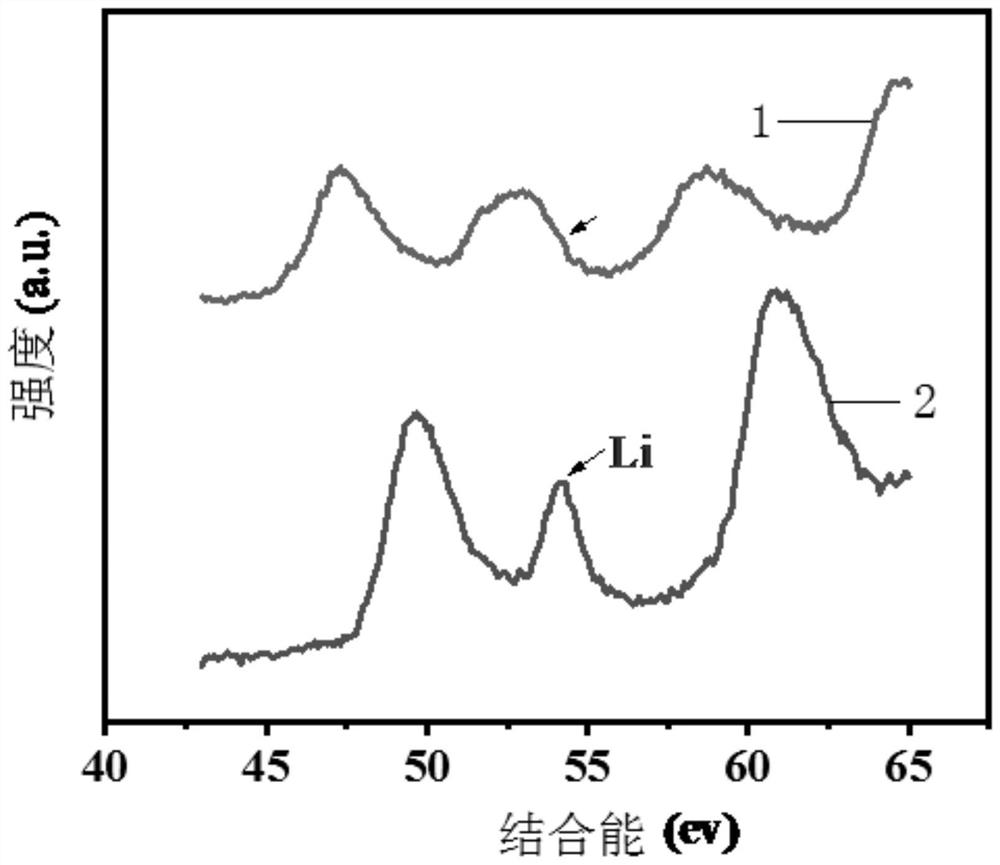
Method for selectively recovering lithium from waste lithium ion battery by utilizing ultralow-temperature roasting
A lithium-ion battery, ultra-low temperature technology, applied in battery recycling, waste collector recycling, secondary batteries, etc., can solve the problems of high consumption of acid, alkali and reducing agent, difficult treatment of waste water and waste liquid, high energy consumption cost, etc. Achieve the effect of low equipment anti-corrosion requirements, low energy consumption cost and low regeneration cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0023] Specific Embodiment 1: This embodiment is a method for selectively recovering lithium from waste lithium-ion batteries by ultra-low temperature roasting, specifically according to the following steps:
[0024] 1. Use a mechanical crusher to crush the positive electrode sheet of the waste lithium-ion battery to obtain the positive electrode powder of the lithium-ion battery; put the positive electrode powder of the lithium-ion battery into Al 2 o 3 Put it in a crucible, then place it in a tube furnace, raise the temperature from room temperature to 500°C to 650°C at a rate of 1°C / min to 10°C / min and keep it warm for 0.5h to 6h to remove the conductive agent and binder, and then cool naturally to room temperature; pass through a 200-400-mesh sieve to obtain waste lithium-containing cathode materials with a particle size of 0.035mm-0.075mm;
[0025] 2. Put the waste lithium-containing positive electrode material obtained in step 1 into an agate mortar together with the co...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the quality of lithium-ion battery positive electrode powder and Al 2 o 3 The volume ratio of the crucible is 1g:(10mL~15mL). Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0034] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that: the method for obtaining the positive electrode sheet of the waste lithium-ion battery described in step one is: soak the collected waste lithium-ion battery at room temperature Discharging treatment is carried out in an aqueous sodium chloride solution with a mass fraction of 5% to 10% for 12h to 72h, and then the waste lithium ion battery is disassembled to obtain a positive electrode sheet. Others are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com