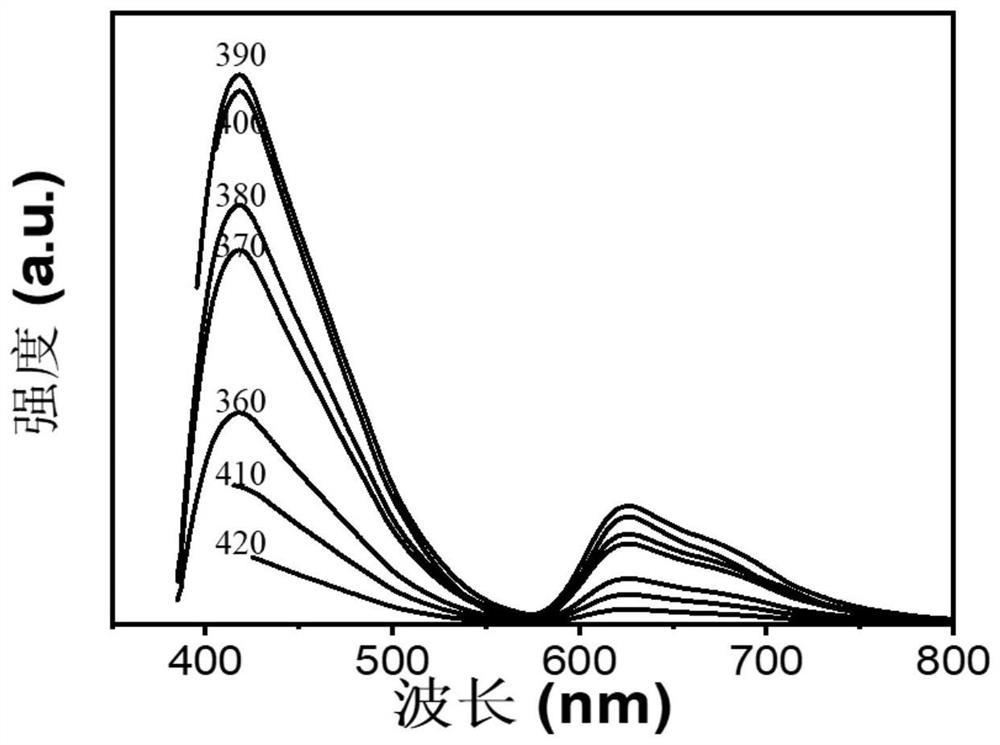
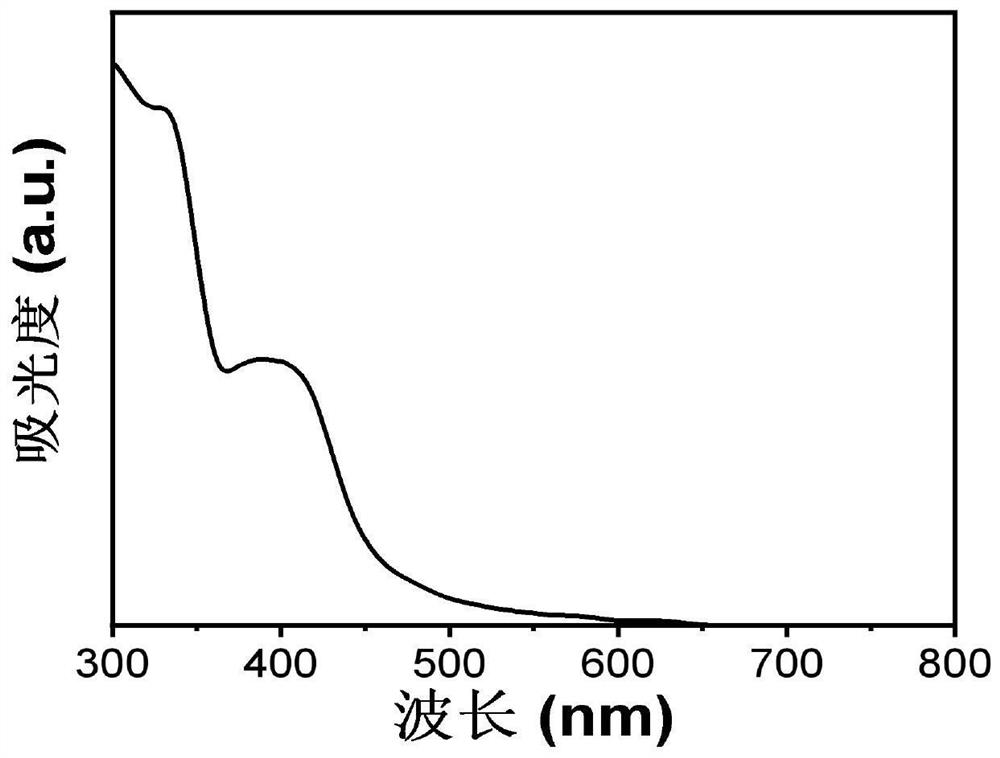
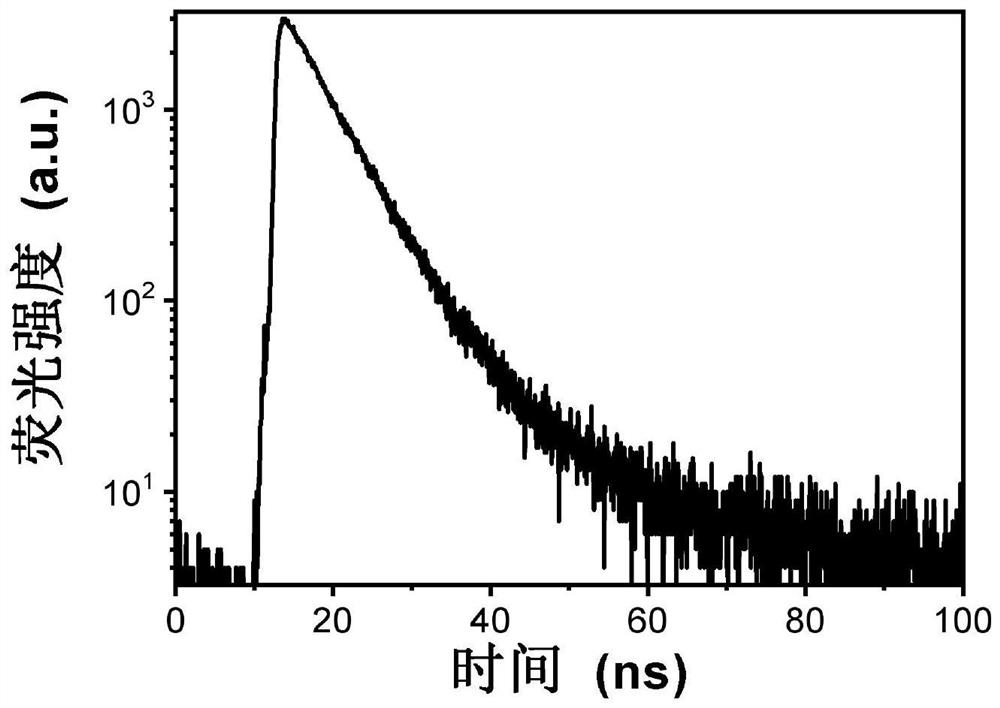
Solution-processable solid blue fluorescent-red phosphorescent carbon quantum organic frameworks with high quantum yield and their preparation and applications
A blue fluorescent and solution processing technology, applied in the field of fluorescent-phosphorescent carbon nanomaterials, can solve the problems of low quantum yield, low phosphorescent quantum yield, and limiting the application of phosphorescent CQDs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1. Preparation of a solid blue fluorescent-red phosphorescent carbon quantum organic framework with high quantum yield and solution processability
[0048] Weigh trimesic acid, guanidine phosphate, and 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride solids with a mass ratio of 20:10:1 as the carbon source precursor, and dissolve them in 15ml of N,N-dicarbonate with ultrasonic stirring. in methylformamide. 1 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid was added to the reaction system as a reaction catalyst. The above solution was transferred to a 25mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave, and the lid was tightened. Solvothermal reaction was performed at 200°C for 4 hours, and then the reactor was naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain a light blue carbon quantum dot organic framework N,N-dimethylformamide solution, which was then mixed with 20 mL of 0.01 mole per Neutralize to neutral with 1 liter of sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, then filter, take the filtrate...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2. Preparation of electroluminescent diode based on red phosphorescent carbon quantum dot organic framework structure
[0054] The high quantum yield solution-processable solid blue fluorescent-red phosphorescent carbon quantum organic framework prepared in Example 1 is used as an active light-emitting layer in a monochromatic electroluminescent diode. Such as Figure 19 As shown, the light-emitting diode device structure includes a transparent glass substrate (glass), an anode layer (ITO), a hole injection layer poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene: polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT) from bottom to top. :PSS), active light emitting layer (red phosphorescent carbon quantum organic framework with high quantum yield), electron transport layer 1,3,5-tris(1-phenyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)benzene (TPBI ), the cathode layer (LiF / Al). The structure of the electroluminescent diode device is described as: ITO / PEDOT:PSS / CDOFs / TPBi / LiF / Al.
[0055] The preparation method of the mono...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| luminance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com