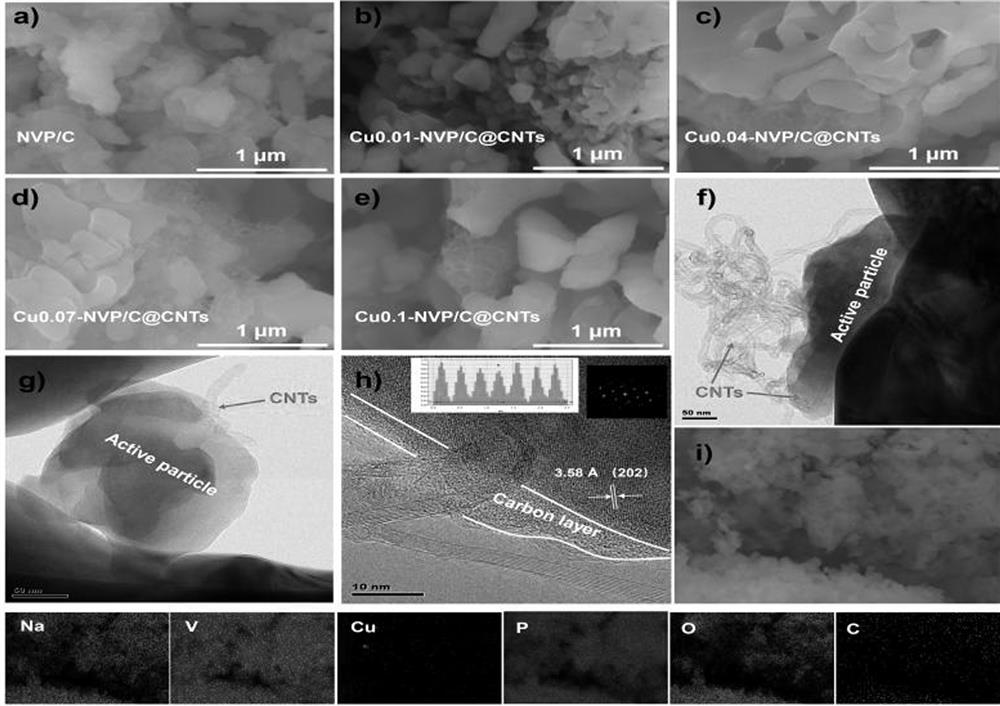
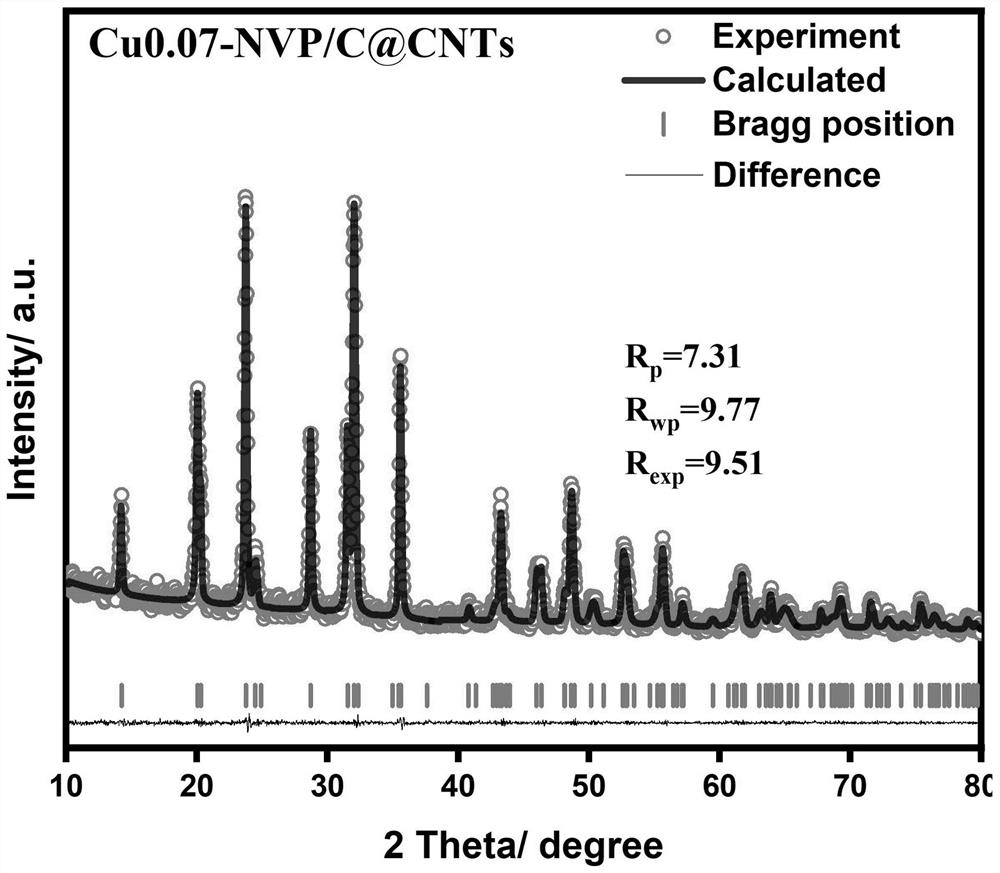
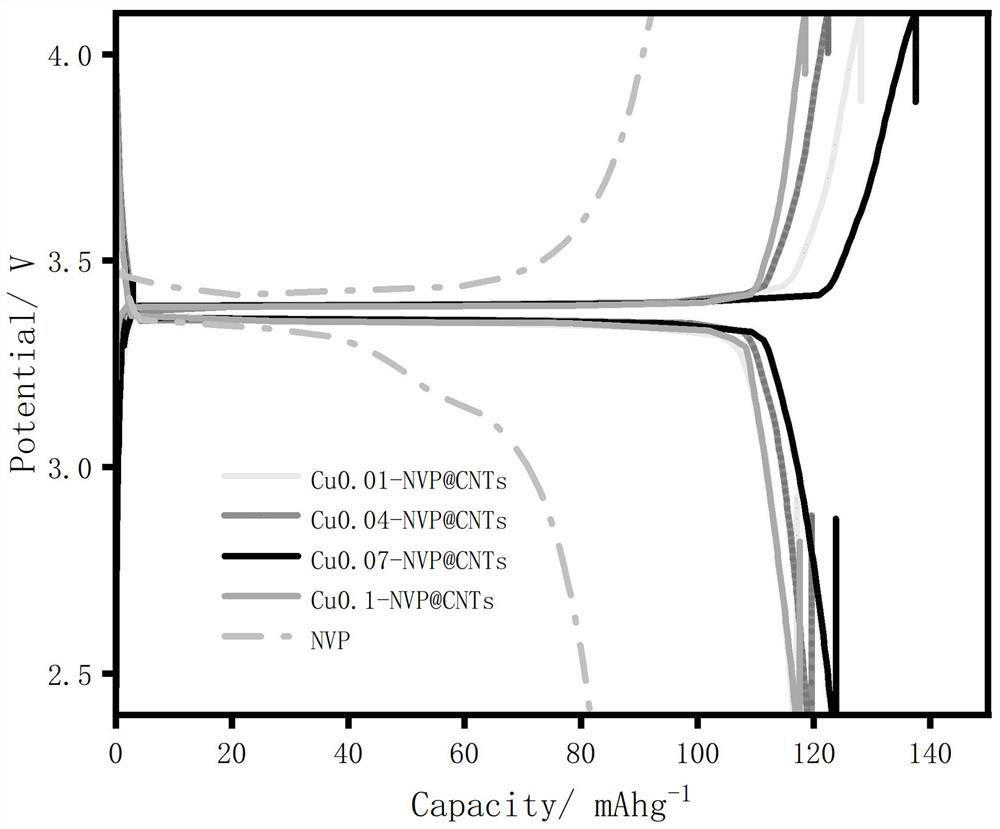
Sodium vanadium phosphate electrode material of vanadium-site copper-doped composite carbon nano tube and preparation method and application of sodium vanadium phosphate electrode material
A technology of sodium vanadium phosphate and electrode material, applied in the direction of positive electrode, battery electrode, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of weak structural stability, poor NVP ion and electronic conductivity characteristics, etc., to improve the rate performance and improve the electrochemical performance. , the effect of improving ionic conductivity and structural stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Na 3.01 V 1.99 Cu 0.01 (PO 4 ) 3 Preparation of / C@CNTs cathode material (Cu0.01-NVP / C@CNTs)
[0034] Take 1.5312 g ammonium metavanadate, 2.3673 g sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.00895 g sodium acetate trihydrate, 0.01589 g copper nitrate trihydrate, 4.9750 g oxalic acid, 0.15 g carbon nanotubes, oxalic acid and sodium acetate were dissolved in deionized water in sequence, Ammonium vanadate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate were respectively added to the above solution sequentially, heated to 80°C by a water bath and kept stirred for 12 hours to obtain a dark blue sol.
[0035] Add carbon nanotubes to the black blue sol, use a cell breaker to uniformly disperse them in the sol, and freeze-dry for 48 hours to obtain a powder sample. After the obtained product was ground into powder, the sample was placed in a ceramic boat for initial firing in a tube furnace. The initial firing condition was that the heating rate was 2 °C / min, and the temperature was kept a...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Na 3.04 V 1.96 Cu 0.04 (PO 4 ) 3 Preparation of @CNTs cathode material (Cu0.04-NVP / C@CNTs)
[0040] 1.5046 g ammonium vanadate, 2.3619 g sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.03572 g sodium acetate trihydrate, 0.0634 g copper nitrate trihydrate, 4.9636 g oxalic acid, and 0.15 g carbon nanotubes were dissolved in deionized water. The specific preparation method is the same as the method described in Example 1.
[0041] The obtained sample is used as the positive electrode material to prepare a button battery and test its electrochemical performance. The process is as follows:
[0042] Using 1.4 mL of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) as a solvent, the Na prepared in this example with a mass ratio of 7:2:1 3.01 V 1.99 Cu 0.01 (PO 4 ) 3 @CNTs active material, acetylene black, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are mixed and added to it. The above mixture was ball milled for four hours to obtain a uniform slurry. Use a coating machine to evenly coat the above mixture on...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Na 3.07 V 1.93 Cu 0.07 (PO 4 ) 3 Preparation of @CNTs cathode material (Cu0.07-NVP / C@CNTs)
[0045] 1.4782 g ammonium vanadate, 2.3564 g sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.06236 g sodium acetate trihydrate, 0.1107 g copper nitrate trihydrate, 4.9520 g oxalic acid, and 0.15 g carbon nanotubes were dissolved in deionized water. The specific preparation method is the same as the preparation method described in Example 1.
[0046] The obtained sample is used as the positive electrode material to prepare a button battery and test its electrochemical performance. The process is as follows:
[0047] Using 1.4 mL of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) as a solvent, the Na prepared in this example with a mass ratio of 7:2:1 3.01 V 1.99 Cu 0.01 (PO 4 ) 3 @CNTs active material, acetylene black, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are mixed and added to it. The above mixture was ball milled for four hours to obtain a uniform slurry. Use a coating machine to evenly coat the abov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com