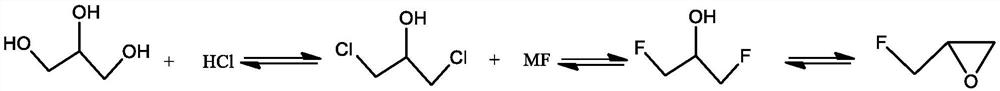Preparation method of epoxy fluoropropane
A technology of epoxyfluoropropane and propanol, which is applied in the field of preparation of epoxyfluoropropane, can solve the problems of unavailable, expensive starting materials, unsuitable for industrial production, etc., and achieve less by-products, high conversion rate and selectivity , The safe and controllable effect of the preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) Preparation of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol
[0030] Add 500 g of glycerin and 25 g of acetic acid into a 1 L reaction flask equipped with a gas distributor, condensing reflux tube, and water separator, stir, and slowly raise the temperature to 110°C. Introduce hydrogen chloride gas at a rate of 0.1kg / h, start condensation, and separate water. Pass through hydrogen chloride gas for 4h, stop the reaction, and slowly cool down to room temperature. Aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution was added, and the layers were separated. Add 4 g of anhydrous calcium chloride to the organic layer, dry and filter to obtain 625 g of the product 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol with a yield of 89.1%.
[0031] (2) Preparation of 1,3-difluoro-2-propanol
[0032] Add 625g of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol obtained above into a 2L reaction flask, add 500ml of propionamide and 420g of potassium fluoride, stir and heat up. Raise the temperature to 180°C, keep the temperature for 2 hours, stop the reaction, a...
Embodiment 2
[0036] (1) Preparation of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol
[0037] Add 500 g of glycerin and 25 g of acetic acid into a 1 L reaction flask equipped with a gas distributor, condensing reflux tube, and water separator, stir, and slowly raise the temperature to 110°C. Introduce hydrogen chloride gas at a rate of 0.1kg / h, start condensation, and separate water. Pass through hydrogen chloride gas for 4h, stop the reaction, and slowly cool down to room temperature. Aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution was added, and the layers were separated. Add 4 g of anhydrous calcium chloride to the organic layer, dry and filter to obtain 625 g of the product 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol with a yield of 89.1%.
[0038] (2) Preparation of 1,3-difluoro-2-propanol
[0039] Add 625g of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol obtained above into a 2L reaction flask, add 500ml of propionamide and 520g of potassium fluoride, stir and heat up. Raise the temperature to 180°C, keep the temperature for 2 hours, stop the reaction, a...
Embodiment 3
[0043] (1) Preparation of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol
[0044] Add 500 g of glycerin and 40 g of adipic acid into a 1 L reaction flask equipped with a gas distributor, condensing reflux tube, and water separator, stir, and slowly raise the temperature to 120°C. Introduce hydrogen chloride gas at a rate of 0.1kg / h, start condensation, and separate water. Pass through hydrogen chloride gas for 4h, stop the reaction, and slowly cool down to room temperature. Aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution was added, and the layers were separated. 4 g of anhydrous calcium chloride was added to the organic layer, dried and filtered to obtain 642 g of the product 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol with a yield of 91.5%.
[0045] (2) Preparation of 1,3-difluoro-2-propanol
[0046] Add 642g of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol obtained above into a 2L reaction flask, add 500ml of propionamide and 310g of sodium fluoride, stir and heat up. Raise the temperature to 180°C, keep the temperature for 2 hours, stop the reac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com