Photocatalyst for efficiently degrading antibiotics and preparation method and application of photocatalyst
A technology for photocatalysts and antibiotics, applied in catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
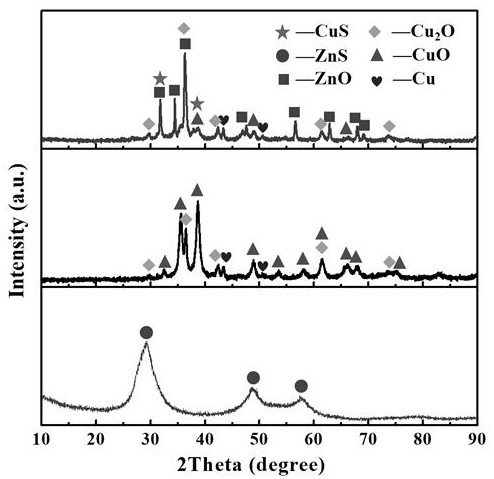
[0032] (1) Preparation of nanocomposite CuO@Cu 2 O@Cu: Weigh 0.9983g copper acetate, 1.0000g sodium hydroxide, 0.4403g ascorbic acid, 1.0812g formamidine sulfinic acid and dissolve them in deionized water to obtain copper acetate solution, sodium hydroxide solution, ascorbic acid solution and formamidine sulfinic acid Sulfonic acid solution, then successively add sodium hydroxide solution and ascorbic acid solution into copper acetate solution to form precursor solution, take out the reaction mixture after 10 minutes of microwave irradiation at a power of 130W, then add formamidine sulfinic acid solution, and After mixing evenly, microwave reaction at 130W for 10 minutes again. After the reaction, cool to room temperature, let stand overnight, filter the precipitate, wash with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times, and dry for more than 6 hours to obtain black nano Composite CuO@Cu 2 O@Cu;
[0033] (2) Preparation of five-component composite photocatalyst CuO@Cu ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Preparation of nanocomposite CuO@Cu 2 O@Cu: Weigh 0.9983g copper acetate, 0.8000g sodium hydroxide, 0.4403g ascorbic acid, 0.5406g formamidine sulfinic acid and dissolve them in deionized water to obtain copper acetate solution, sodium hydroxide solution, ascorbic acid solution and formamidine sulfinic acid Sulfonic acid solution, then successively add sodium hydroxide solution and ascorbic acid solution into copper acetate solution to form precursor solution, take out the reaction mixture after 8 minutes of microwave irradiation under the power of 130W, then add formamidine sulfinic acid solution, and After mixing evenly, microwave reaction at 130W for 8 minutes again. After the reaction, cool to room temperature, let stand overnight, filter the precipitate, wash 3 times with deionized water and absolute ethanol, and dry for more than 6 hours to obtain black nano-particles. Composite CuO@Cu 2 O@Cu;
[0039] (2) Preparation of five-component composite photocatalys...
Embodiment 3
[0043] (1) Preparation of nanocomposite CuO@Cu 2 O@Cu: Weigh 1.2484g copper sulfate, 0.4000g sodium hydroxide, 0.8806g ascorbic acid, 0.5406g formamidine sulfinic acid and dissolve them in deionized water to obtain copper acetate solution, sodium hydroxide solution, ascorbic acid solution and formamidine sulfinic acid Sulfonic acid solution, then successively add sodium hydroxide solution and ascorbic acid solution into copper acetate solution to form precursor solution, take out the reaction mixture after 10 minutes of microwave irradiation at a power of 130W, then add formamidine sulfinic acid solution, and After mixing evenly, microwave reaction at 130W for 10 minutes again. After the reaction, cool to room temperature, let stand overnight, filter the precipitate, wash with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times, and dry for more than 6 hours to obtain black nano Composite CuO@Cu 2 O@Cu;
[0044] (2) Preparation of five-component composite photocatalyst CuO@Cu ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com