Tantalum-silver coating dental implant and preparation method thereof
A technology for dental implants and coatings, applied in the field of tantalum silver coated dental implants and its preparation, can solve the problem of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis that are easy to cause, and polymer materials that are easily degraded by organisms , high brittleness of carbon materials, etc., to achieve the effect of no tissue repellency, no cytotoxicity, and high metal flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
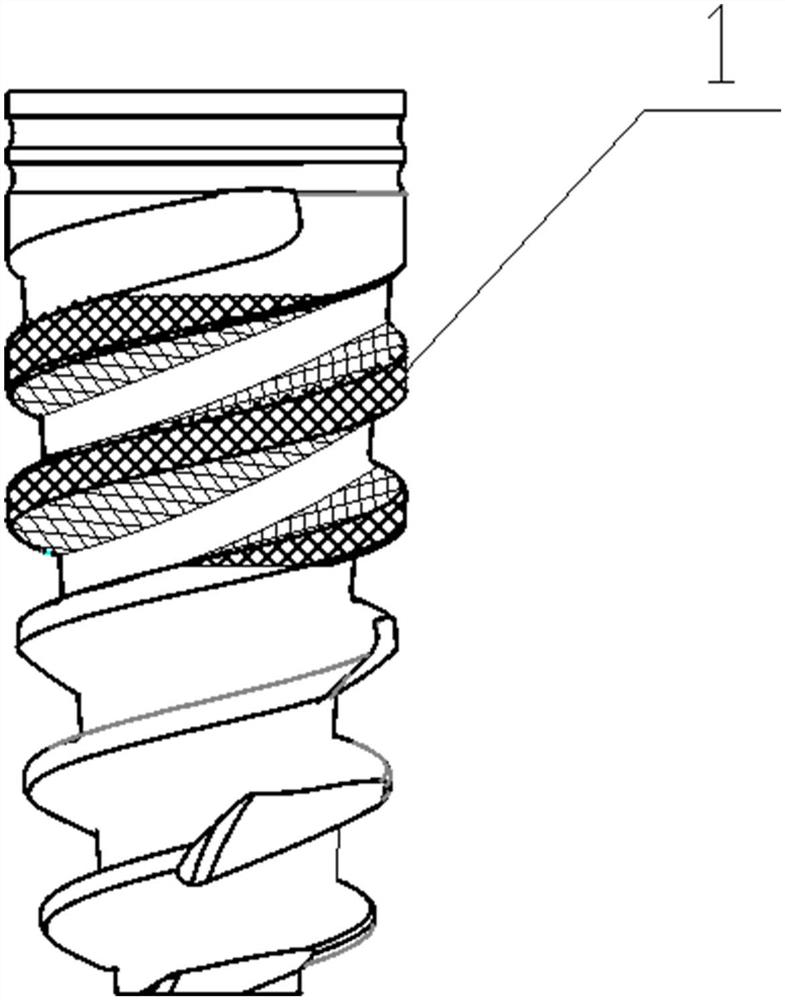
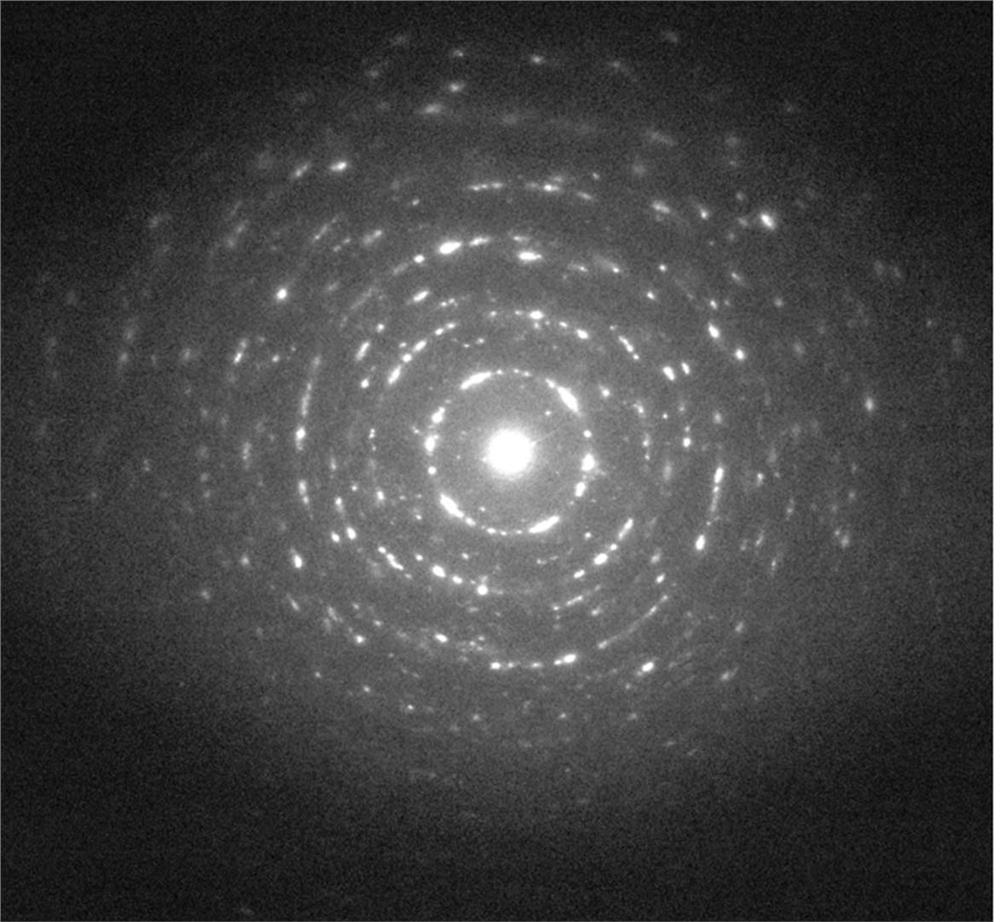
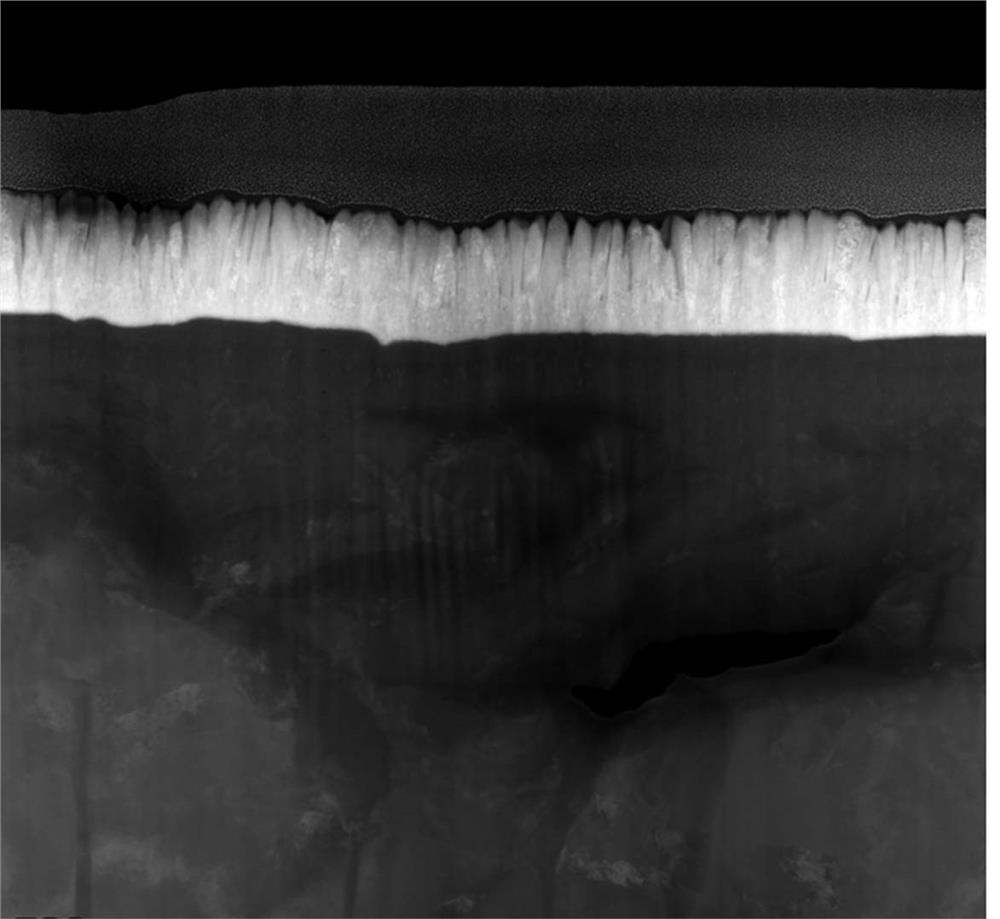
[0066] refer to Figure 1-4 as shown, figure 1 Schematic diagram of the structure of a dental implant, figure 2 The coating electron diffraction figure that provides for the embodiment of the present invention, image 3 Dental implant electron micrograph provided for the embodiment of the present invention, Figure 4 Moiré patterns of the coatings provided for the examples of the present invention. The polycrystalline structure and moiré fringes of the coating can be clearly seen in the figure, image 3 The coating area in the middle and the substrate area at the bottom can also be clearly distinguished in the middle.
[0067] The preparation method of the tantalum-silver coated dental implant provided in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0068] Metal powders of titanium, yttrium, niobium, zirconium and silver were mixed according to the ratio of 1.1%, 3%, 70.9%, 14.6% and 10.4% by mass to obtain composite powder, and the composite powder was processed by ...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Concrete operation steps are consistent with embodiment 1, only the metal powder mass percentages of titanium, yttrium, niobium, zirconium and silver are 0.5%, 5%, 60%, 25% and 3%;
[0089] The mass percentages of tantalum, silver, magnesium and strontium are 94%, 5%, 0.2% and 2%;
[0090] The parameters in the process of laser melting technology include: laser power 130w, scanning speed 80mm / s, scanning line spacing 0.03mm, slice layer thickness 15μm, substrate temperature 50℃;
[0091] The porosity of the bionic trabecular bone structure is 15%;
[0092] The aperture size of the bionic trabecular bone structure is 0.1mm;
[0093] The average wire diameter of the bionic trabecular bone structure is 180 μm;
[0094] The pore structure on the bionic bone trabecular structure is a face-centered cube.
Embodiment 3
[0096] Concrete operation steps are consistent with embodiment 1, just the metal powder mass percent of titanium, yttrium, niobium, zirconium and silver is 5%, 1%, 80%, 5% and 17%;
[0097] The mass percentages of tantalum, silver, magnesium and strontium are 98%, 0.5%, 2% and 0.2%;
[0098] The parameters in the process of laser melting technology include: laser power 350w, scanning speed 400mm / s, scanning line spacing 0.15mm, slice layer thickness 60μm, substrate temperature 250℃;
[0099] The porosity of the bionic trabecular bone structure is 85%;
[0100] The aperture size of the bionic trabecular bone structure is 1 mm;
[0101] The average wire diameter of the bionic trabecular bone structure is 780 μm;
[0102] The pore structure on the bionic bone trabecular structure is a rotating face-centered cube.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com