Preparation method and application of extracellular matrix scaffold with controllable pore structure
A technology of acellular matrix and pore structure, applied in medical science, tissue regeneration, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of long material preparation cycle and uncontrollable material composition, and achieve the effect of shortening the preparation cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
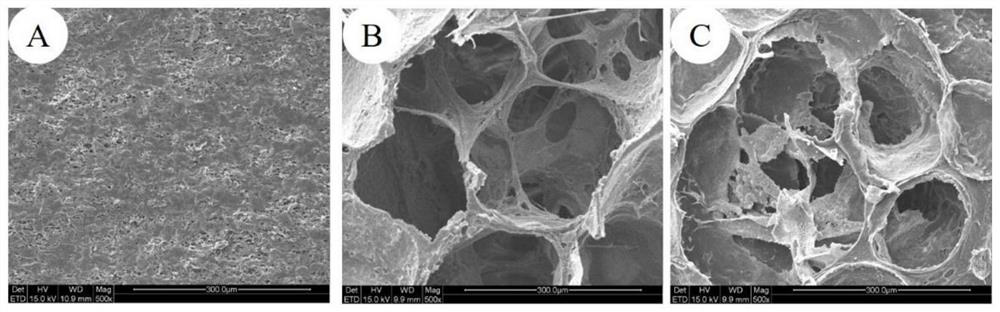
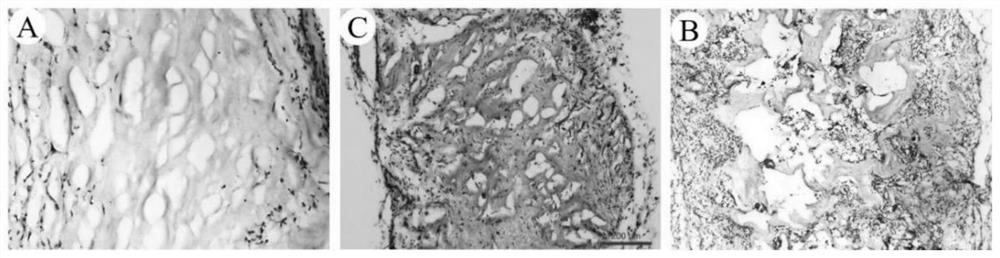
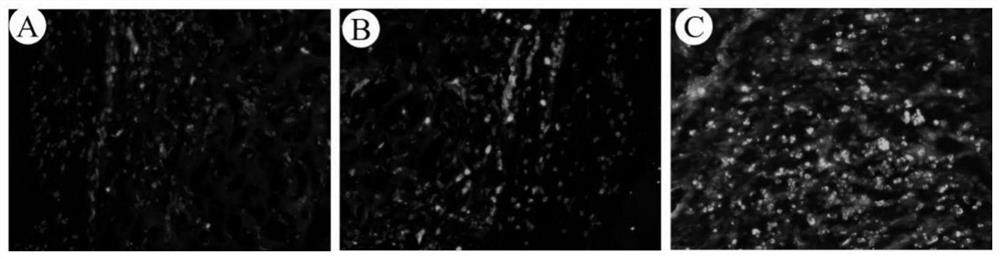
[0036] Preparation of Porcine Liver Acellular Matrix Scaffold with Controllable Pore Structure Using PCL Microsphere Aggregates as Template
[0037]Preparation of polycaprolactone (PCL) microsphere template: PCL microspheres were prepared by emulsification solvent evaporation method. Weigh 10.0 g of PCL with a molecular weight of 80,000, add it into 200 mL of dichloromethane, stir and dissolve at room temperature until clear, and prepare a PCL solution with a concentration of 50 g / L. The obtained PCL solution was added to 1800mL of 2% polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) solution by mass fraction, stirred at 1000rpm, volatilized at room temperature to remove dichloromethane, left to settle to collect the microspheres at the bottom, and washed 5 times with distilled water Residual PVA was removed, and the collected microsphere particles were freeze-dried to obtain PCL microspheres, which were then filtered through different meshes to obtain PCL microspheres with different diameters (diamete...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Preparation of porcine intestinal mucosa acellular matrix scaffold with controllable pore structure using PLA microsphere aggregates as template
[0044] Preparation of PLA microspheres: Weigh 8.0 g of PLA with a molecular weight of 200,000, add it into 200 mL of chloroform, stir and dissolve at room temperature until clear, and prepare a PLA solution with a concentration of 40 g / L. Add the above PLA solution to 1800mL of 3% polyvinyl alcohol (PVC) solution with a mass fraction of 3%, stir at 800rpm, volatilize and remove chloroform at room temperature, collect the microspheres by static precipitation, wash with distilled water 5 times to remove residual PVA , the collected microspheres were freeze-dried to obtain PLA microspheres. Then, it was filtered with different meshes to obtain PLA microspheres with different diameters (diameter range: 40-500 μm). Place 0.4 g of PLA microspheres with different diameters in circular holes with a diameter of 1.0 cm and a height of...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Preparation of bovine Achilles tendon tissue acellular matrix scaffold with controllable pore structure using PLGA microsphere aggregates as template
[0051] Preparation of PLGA microspheres: Weigh 10.0 g of PLGA with a molecular weight of 20,000, add it into 100 mL of chloroform, stir and dissolve at room temperature until clear, and prepare a PLGA solution with a concentration of 100 g / L. The above PLGA solution was added to 1900mL of 1% PVA solution with a mass fraction of 1900mL, stirred at 1200rpm, volatilized at room temperature to remove chloroform, left to settle to collect microspheres, washed with distilled water 5 times to remove residual PVA, and collected microspheres The pellets were freeze-dried. Then, the PLGA microspheres with different diameters (diameter range: 40-500 μm) were obtained by filtering with different meshes. 1.0 g of PLGA microspheres with different diameters were placed in circular holes with a diameter of 2.0 cm and a height of 0.8 cm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com