Recycling method of waste lithium iron phosphate battery
A technology of lithium iron phosphate battery and recycling method, which is applied in battery recycling, recycling by waste collectors, recycling technology, etc. It can solve the problems of difficulty in removing impurities and purification of leachate, loss of lithium, and low purity of recycled products, and achieve low cost. High-value recovery and regeneration, lower production equipment requirements, and easy control of the reaction end point
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
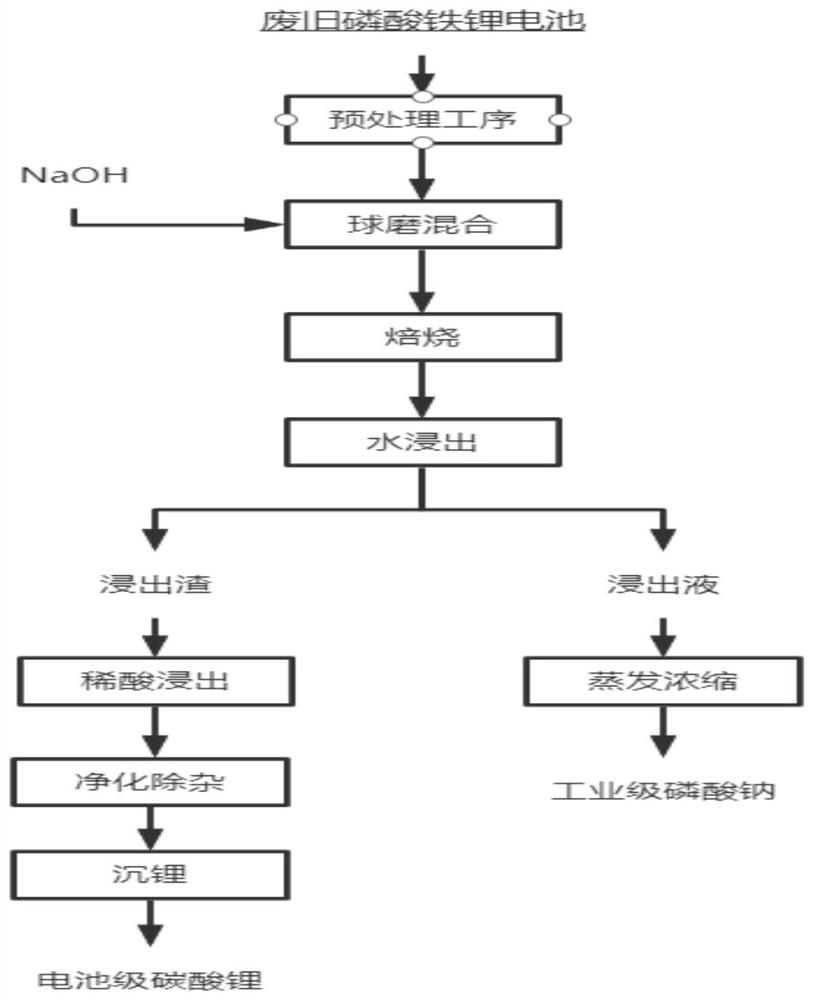
[0034] A method for recycling waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, comprising:
[0035] (1) Soak the waste lithium iron phosphate battery in 5% NaCl solution until the end-of-discharge voltage is 1V, disassemble the battery cell, and then carry out mechanical crushing, roasting, and screening to obtain electrodes with a particle size of less than 0.1mm The active material powder is washed with alkali, filtered and dried to obtain the material to be treated;
[0036] (2) The material obtained in step (1) is mixed with NaOH in a mass ratio of 1:2 to obtain a mixture to be roasted;
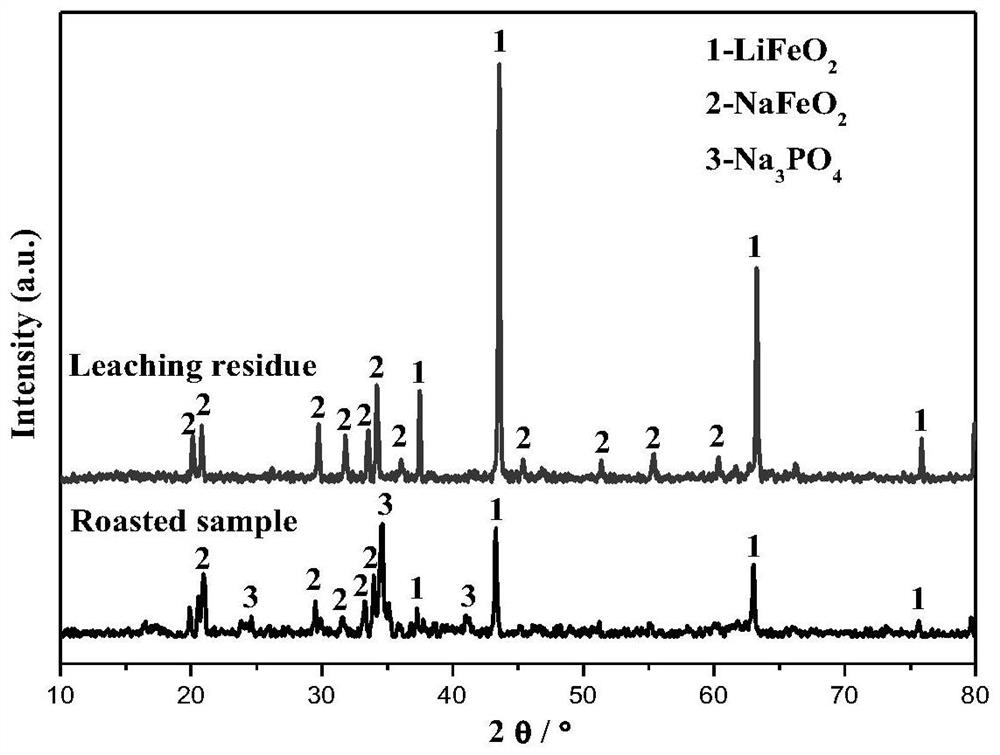
[0037] (3) The mixture obtained in step (2) is roasted at a low temperature in a muffle furnace, and the specific process parameters are as follows: the roasting temperature is 250° C., and the roasting time is 30 minutes;
[0038] (4) The roasted material is immersed in water, and the specific process is as follows: the water immersion temperature is 20°C, the water immersion time is 30min, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A method for recycling waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, comprising:
[0046] (1) Soak the waste lithium iron phosphate battery in 5% NaCl solution until the end-of-discharge voltage is 1V, disassemble the battery cell, and then carry out mechanical crushing, roasting, and screening to obtain electrodes with a particle size of less than 0.1mm The active material powder is washed with alkali, filtered and dried to obtain the material to be treated;
[0047] (2) the material that step (1) obtains and NaHCO 3 Carry out ball milling and mixing by mass ratio 1:7, obtain the mixture to be roasted;
[0048] (3) The mixture obtained in step (2) is roasted at a low temperature in a muffle furnace, and the specific process parameters are as follows: the roasting temperature is 150° C., and the roasting time is 80 minutes;
[0049] (4) The roasted material is immersed in water, and the specific process is as follows: the water immersion temperature is 10°C, the water immer...
Embodiment 3
[0056] A method for recycling waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, comprising:
[0057] (1) Soak the waste lithium iron phosphate battery in 5% NaCl solution until the end-of-discharge voltage is 1V, disassemble the battery cell, and then carry out mechanical crushing, roasting, and screening to obtain electrodes with a particle size of less than 0.1mm The active material powder is washed with alkali, filtered and dried to obtain the material to be treated;
[0058] (2) the material that step (1) obtains and Na 2 SO 4 Carry out ball milling and mixing at a mass ratio of 1:10 to obtain the mixture to be roasted;
[0059] (3) The mixture obtained in step (2) is roasted in a muffle furnace, and the specific process parameters are as follows: the roasting temperature is 500° C., and the roasting time is 200 min;
[0060] (4) The roasted material is immersed in water, and the specific process is as follows: the water immersion temperature is 30°C, the water immersion time is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com