Method for preparing graphene by electrochemically stripping graphite
A technology for exfoliating graphite and graphene, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of insufficient utilization of raw materials, loss of raw material mineralization, insufficient exfoliation of graphite raw materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
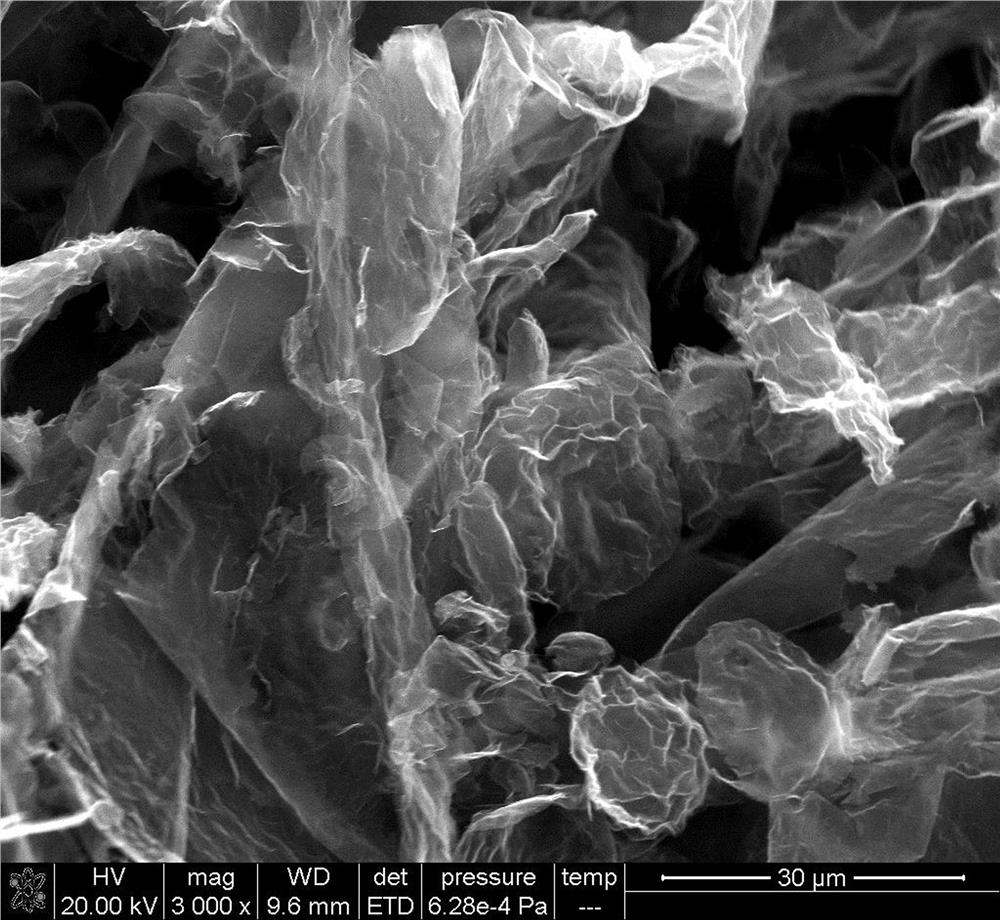
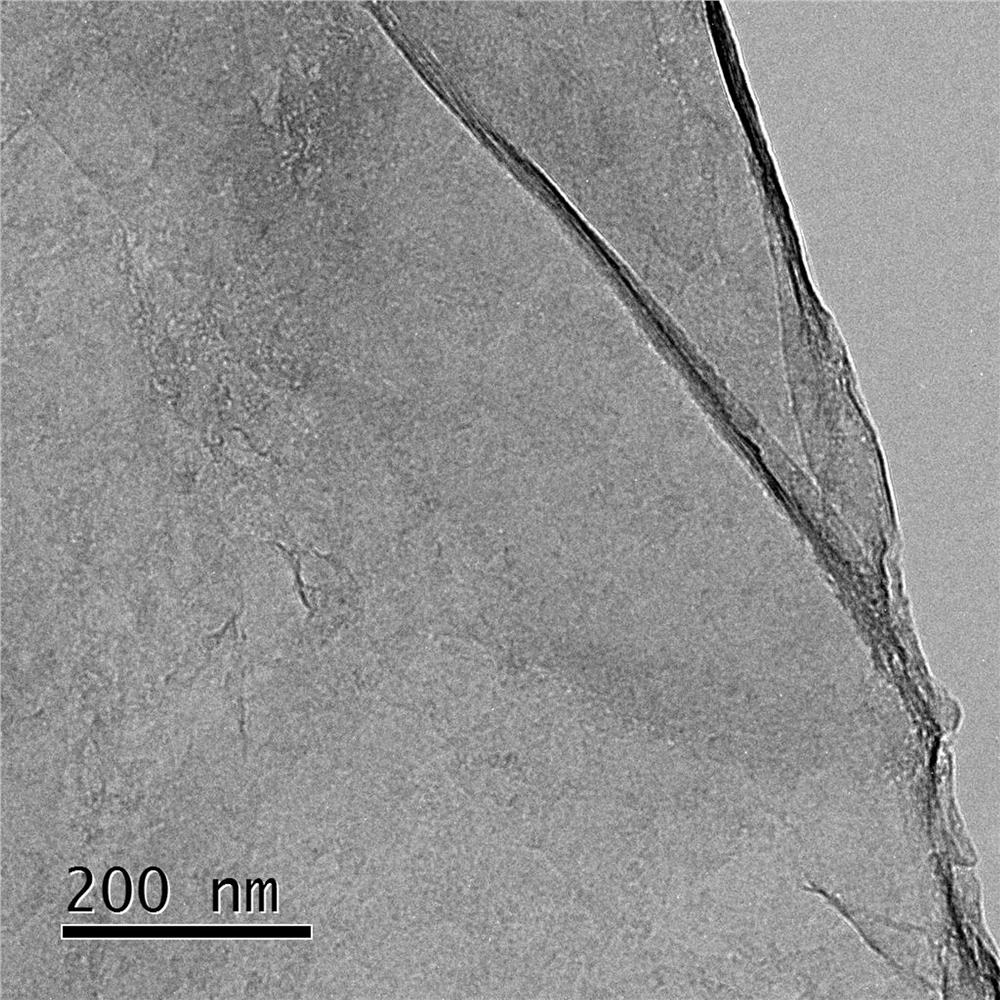
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A method for electrochemically exfoliating graphite to prepare graphene, comprising the steps of:
[0032] 1) A graphite sheet with a weight of 5 g and a thickness of 1 mm was used as the anode, and a thermally cracked high-purity graphite of 4 cm*10 cm*1 mm was used as the cathode. The concentration of acetic acid in the mixed electrolyte was 0.2 M and sulfuric acid was 16 M. The electrolytic reaction was carried out to realize the electrochemical stripping of the anode material, and the molar concentration ratio of acetic acid to sodium sulfate was 1:32; in the electrolytic reaction, the distance between the anode and the cathode was 2 cm, and the voltage was constant at 7 V without stirring, resulting in Bubbles can form natural convection. During the peeling process, the electrolyte is kept at a constant temperature of 25°C through a circulating refrigeration system, and the graphite sheet is electrochemically peeled for 10 minutes to obtain a graphene precursor;
...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method for electrochemically exfoliating graphite to prepare graphene, comprising the steps of:
[0037] 1) Highly oriented pyrolytic graphite with a weight of 5 g and a thickness of 1mm was used as the anode, a 4cm*10cm*1mm artificial graphite plate was used as the cathode, and a mixed solution of 0.05M malonic acid and 0.2M ammonium sulfate (500 ml) was used as the electrolysis Liquid, that is, the molar concentration ratio of malonic acid and ammonium sulfate is 1:4, and the electrolytic reaction is carried out to realize the electrochemical stripping of the anode material; in the electrolytic reaction, the distance between the anode and the cathode is 3cm, and the voltage is constant at 8V, without stirring , is still natural convection formed by electrolysis. During the stripping process, the temperature of the electrolyte is kept constant at 30°C through a circulating refrigeration system, and the highly oriented pyrolytic graphite is electrochemically stripped f...
Embodiment 3
[0041] A method for electrochemically exfoliating graphite to prepare graphene, comprising the steps of:
[0042] 1) Use flake graphite with a weight of 5 g and a thickness of 1mm as the anode, a high-purity graphite plate of 4cm*10cm*1mm as the cathode, and a mixed solution of 0.1M formic acid and 1M nitric acid (500 ml) as the electrolyte, namely formic acid The molar concentration ratio with nitric acid is 1:10, and the electrolytic reaction is carried out to realize the electrochemical stripping of the anode material. In the electrolysis reaction, the distance between the anode and the cathode is 1cm, the voltage is constant at 5V, no stirring, natural convection in the electrolytic cell, and the temperature of the electrolyte is kept constant at 20°C through a circulating refrigeration system, and the flake graphite is electrochemically stripped for 2h to obtain Graphene precursor;
[0043] 2) Filter the electrolyte reacted in step 1) with a filter bucket to quickly reco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com