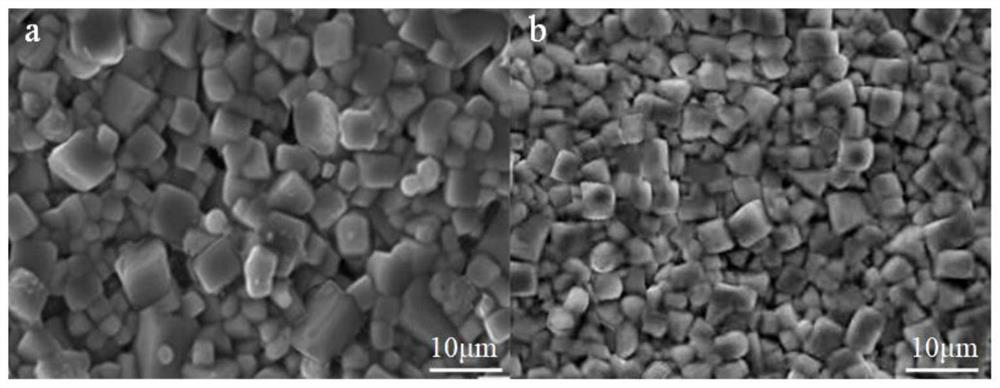
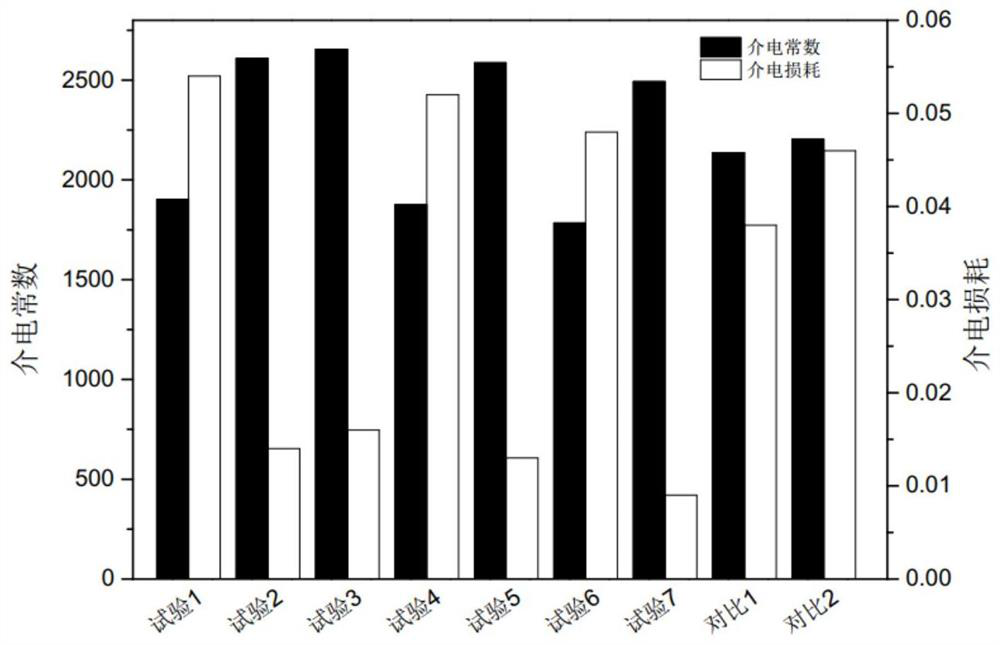
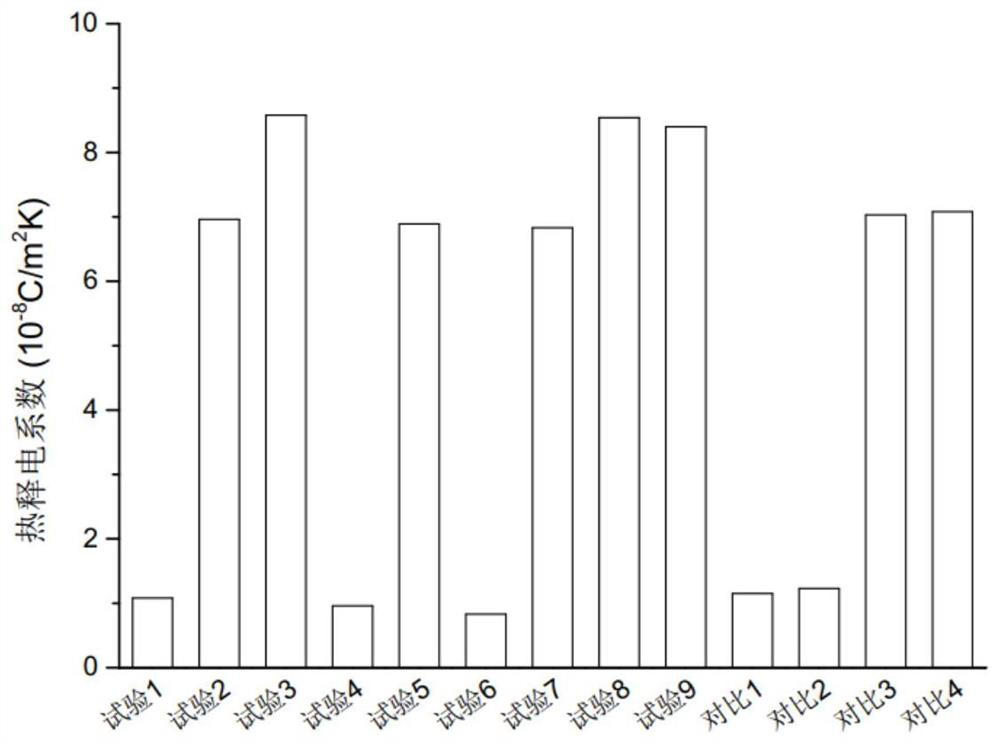
Ceramic powder and application thereof
A technology of ceramic powder and general formula, applied in the field of ceramic powder, can solve the problem that it is difficult to meet the requirements of high-end electronic equipment, and achieve the effects of improving sintering and organizational structure, reducing dielectric loss and increasing dielectric constant.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0047] One embodiment of the present invention also provides a preparation method of ceramic powder, comprising: using a solid phase method to synthesize barium strontium titanate ceramic powder, ball milling barium carbonate, strontium carbonate, and titanium dioxide, and sintering to obtain barium strontium titanate ceramic powder . In the preparation method of this embodiment, the barium strontium titanate ceramic powder is synthesized by a solid-state method, and the prepared ceramic powder has a higher constant and a lower dielectric loss.
[0048] In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for preparing ceramic powder doped with lutetium oxide and scandium oxide includes:
[0049] --Weigh barium carbonate, strontium carbonate and titanium dioxide in proportion, ball mill for 24-48 hours, and sinter at 950-1100°C for 2-5 hours to obtain barium strontium titanate ceramic powder;
[0050] --The barium strontium titanate ceramic powder, lutetium oxide and scandium...
Embodiment 1
[0075] A kind of ceramic powder, its general chemical formula is Ba 0.15 Sr 0.25 TiO 3 , and its preparation method comprises: weighing barium carbonate, strontium carbonate and titanium dioxide in proportion, ball milling for 24 hours, and sintering at 1000° C. for 4 hours to obtain barium strontium titanate ceramic powder.
Embodiment 2
[0077] A kind of ceramic powder, it is Ba doped with 0.1mol% lutetium oxide and 0.016mol% scandium oxide 0.15 Sr 0.25 TiO 3 Ceramic powder, its preparation method, comprises:
[0078] --Weigh barium carbonate, strontium carbonate and titanium dioxide in proportion, ball mill for 24 hours, and sinter at 1000°C for 4 hours to obtain barium strontium titanate ceramic powder;
[0079] --Ball-mill the barium strontium titanate ceramic powder, lutetium oxide and scandium oxide for 24 hours for the second time, and sinter for 3 hours at 1440°C to obtain the ceramic powder.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| sintering temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com