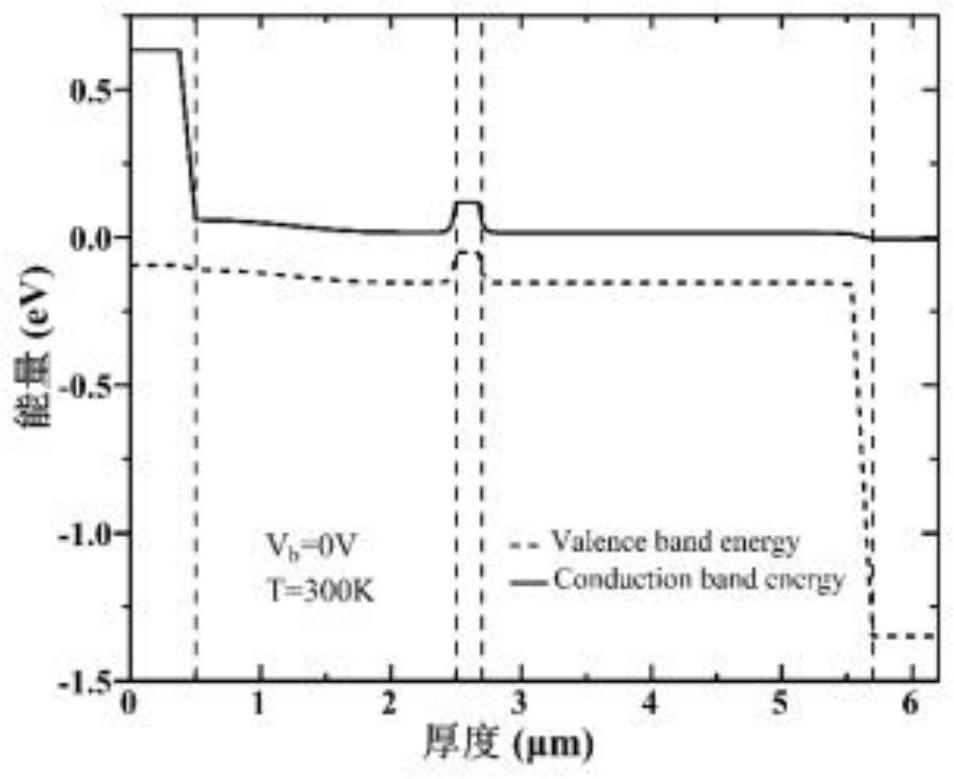
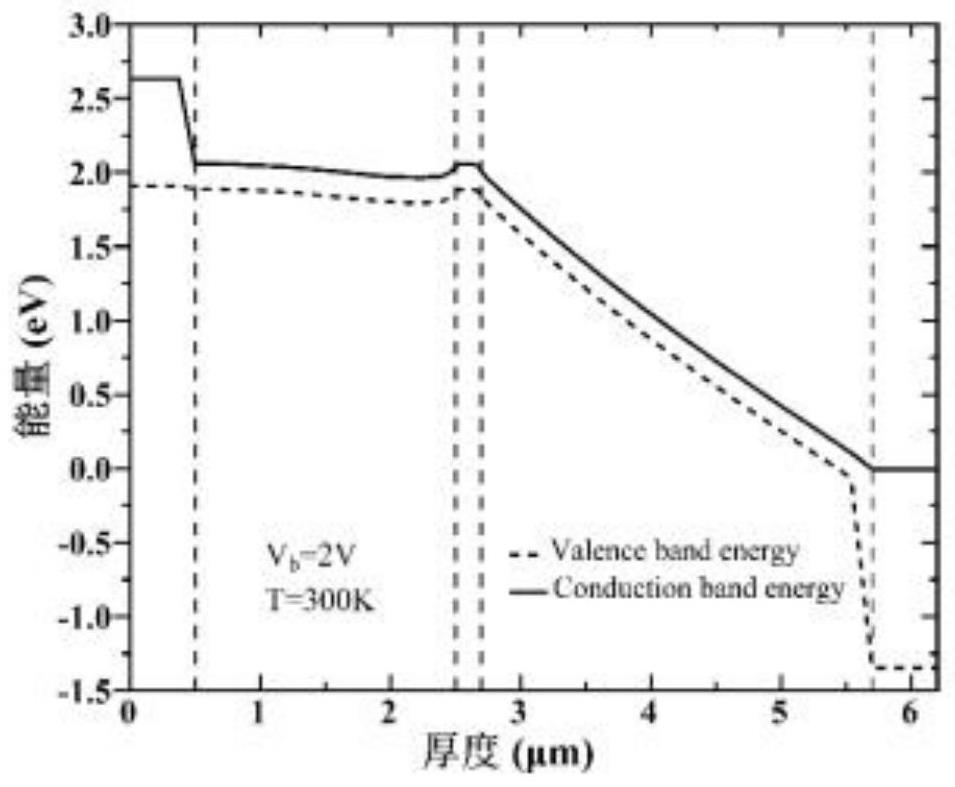
InSb-APD intermediate infrared detector with SACM structure and preparation method of InSb-APD intermediate infrared detector
An infrared detector, N-type technology, used in semiconductor devices, final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve the problems of device dark current increase, high dark current, and narrow band gap material band-to-band tunneling, etc. Achieve the effect of suppressing diffusion current and high gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
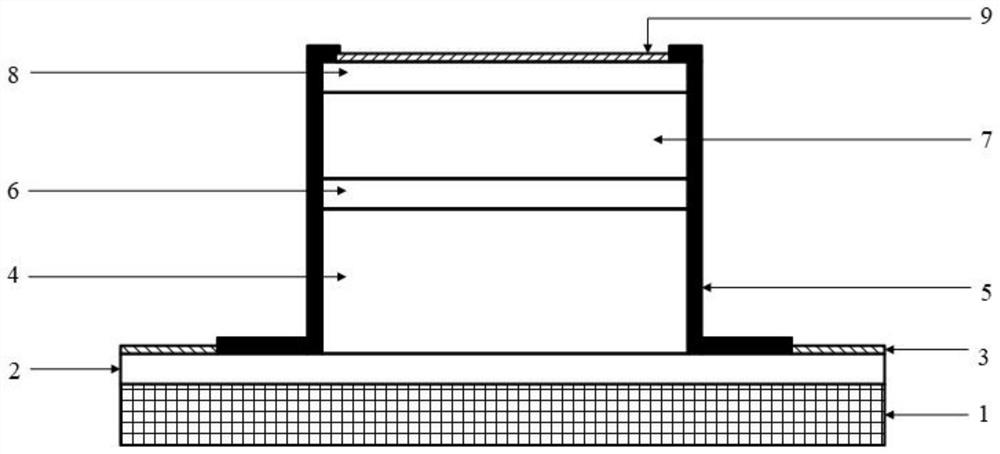
[0054] The preparation method of the SACM structure InSb-APD mid-infrared detector of the present invention, the specific steps are as follows:
[0055] The N-type InP single wafer was selected as the substrate as the N-type InP substrate 1. After cutting, the substrates were successively prepared on the surface-treated substrates such as ultrasonic cleaning with acetone, anhydrous ethanol and deionized water, and drying at 100 °C in an oven. Floor. The fabrication of the device includes the following steps:
[0056] Step 1, preparation of N-type InP buffer layer 2;
[0057] At room temperature, using InP target, donor dopant. On the N-type InP substrate 1, a magnetron sputtering method is used to deposit an N-type InP buffer layer 2 with a thickness of 0.5 μm at room temperature;
[0058] Step 2, preparation of intrinsic InSb multiplication layer;
[0059] At room temperature, using an InSb target material, a magnetron sputtering method is used to deposit a 3 μm thick uni...
Embodiment
[0076] An N-type InP single wafer was selected as the substrate. After cutting, each layer was prepared sequentially on the substrate after surface treatment such as ultrasonic cleaning with acetone, anhydrous ethanol and deionized water, and drying at 100 °C in an oven. The fabrication of the device includes the following steps:
[0077] Step 1, preparation of N-type InP buffer layer 1;
[0078] At room temperature, an InP target was used, and the dopant was Te. On the N-type InP substrate 1, a magnetron sputtering method is used to deposit an N-type InP buffer layer 2 with a thickness of 0.5 μm at room temperature;
[0079] Step 2, preparation of intrinsic InSb multiplication layer;
[0080] At room temperature, using an InSb target material, a magnetron sputtering method is used to deposit a 3 μm thick unintentionally doped InSb multiplication layer 4 on the basis of the N-type InP buffer layer 2 obtained in step 1;
[0081] Step 3, preparation of P-type InSb charge laye...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com