Method for fermentatively producing s-adenosylmethionine
A technology for adenosylmethionine and methionine, which is applied in the field of fermentative production of S-adenosylmethionine, and can solve problems that have not yet been observed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
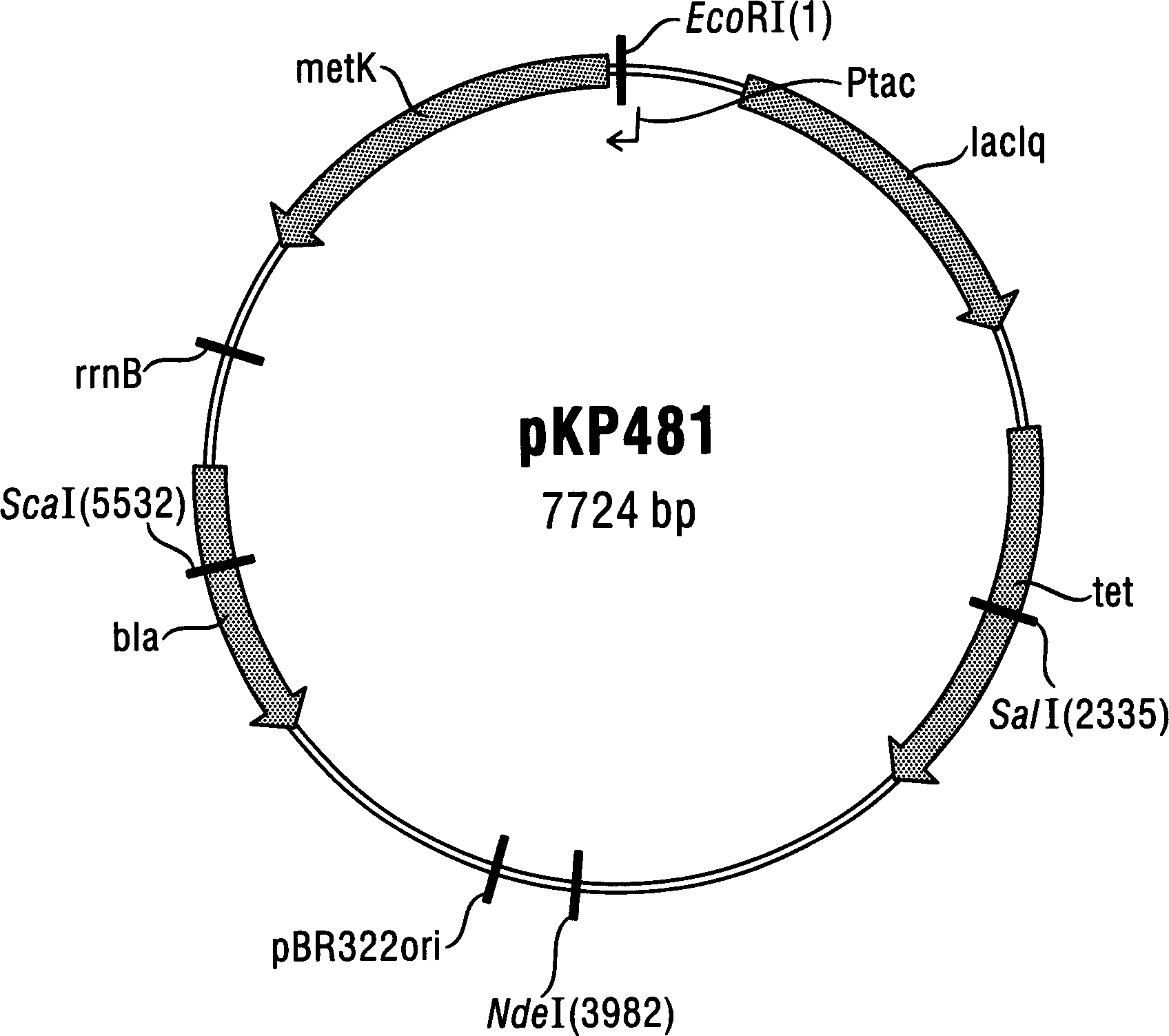
[0049] Experimental example 1: Construction of pKP481 plasmid
[0050] A. Amplification of the metK gene
[0051] The metK gene of Escherichia coli can be used as a template by using the chromosome of the Escherichia coli initial strain W3110 wild strain (ATCC 27325) as a template, and the metK gene can be amplified by polymerase chain reaction with TaqDNA polymerase. The primers used were oligonucleotides metK2 with sequence 5'-GGTTAATTAATGTCTGTTGTGGTTGGTGT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 3), and metK4 (sequence 5'-GGAATTCTCTTTAGGAGGTATTAAATATG-3') (SEQ ID NO: 4). A DNA fragment of about 1.2 kb can be obtained by polymerase chain reaction, and purified through the DNA adsorption column in the QIAprep SpinMiniprep kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), and the operation steps are according to the instructions for use.
[0052] B. Cloning metK gene into pJF118ut vector
[0053] An EcoRI restriction endonuclease cleavage site was introduced into the PCR fragment by primer metK4. Therefore, the purifi...
experiment example 2
[0058] Experimental Example 2: Preparation of S-adenosylmethionine-producing bacteria
[0059] The pKP481 plasmid described in Experimental Example 1 was transformed into Escherichia coli W3110 (ATCC 27325) by the method of calcium chloride, and then re-isolated from the LB solid agar medium containing 20 mg / L tetracycline after screening. A transformant was subjected to restriction endonuclease action and inspection to obtain a strain suitable for S-adenosylmethionine production, which was named W3110 / pKP481.
experiment example 3
[0060] Experimental example 3: Fermentative production of S-adenosylmethionine
[0061] A. Production of S-adenosylmethionine
[0062] The W3110 / pKP481 strain was used for fermentative production of S-adenosylmethionine, and the W3110 starter strain (ATCC 27325) without plasmid was cultured under the same conditions for comparison.
[0063] The following medium was used: one liter contained 0.0147 g calcium chloride dihydrate, 0.3 g magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 0.15 mg sodium molybdate dihydrate, 2.5 mg boric acid, 0.7 mg cobalt chloride hexahydrate, 0.25 mg pentahydrate Copper sulfate water, 1.6 mg manganese chloride tetrahydrate, 0.3 mg zinc sulfate heptahydrate, 3 g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 12 g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 5 g ammonium sulfate, 0.6 g sodium chloride, 0.002 g sulfurous acid heptahydrate Iron, 1 gram of sodium citrate dihydrate, 15 grams of glucose, 1 gram of tryptone, and 0.5 gram of yeast extract. To culture W3110 / pKP481, 20 micrograms / ml of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com