Water-solubility molecule associatad three-construction units hydrophobic associated polymer and synthesizing process thereof
A hydrophobic association and intermolecular technology, applied in the field of intermolecular association ternary hydrophobic association polymers and their synthesis, can solve the problems of large dynamic adsorption capacity, large filtration factor, poor resistance to high salt, etc., and achieve Simple synthetic process conditions, good solubility and stability, good temperature and salt resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1 The synthesis of allyl-nonylphenyl ether / acrylamide / sodium acrylate terpolymer
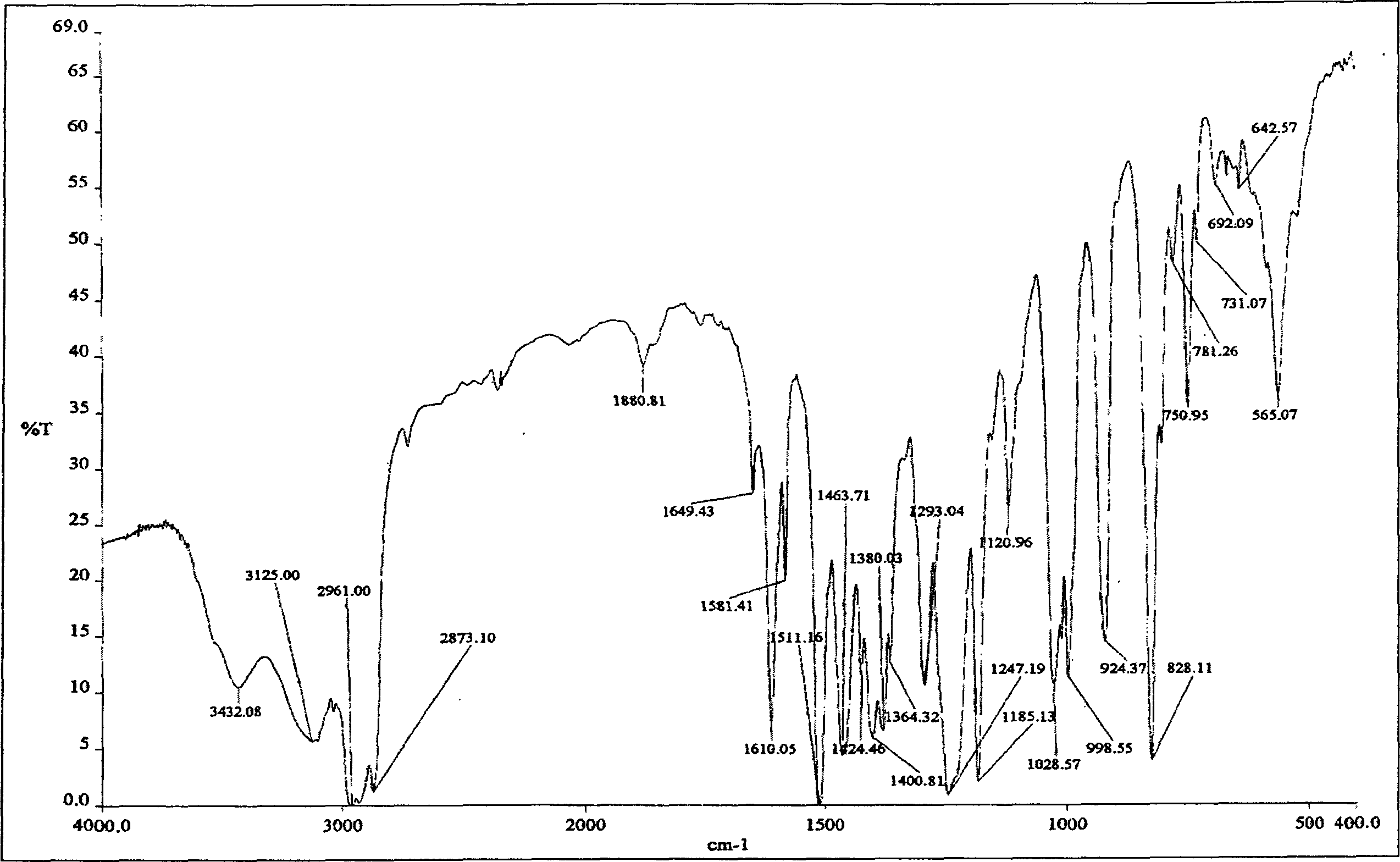
[0042] First synthesize the intermolecular associative hydrophobic monomer (allyl-(p-nonyl)phenyl ether): in a 250mL three-port round bottom equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, a reflux condenser, a dropping funnel, and a nitrogen inlet tube Add 22.1 g (0.10 mol) of nonylphenol to the alkane bottle, keep the external bath temperature at 50°C, add a certain concentration of NaOH solution 10 mL (0.12 mol) and acetone 10 mL dropwise, and blow nitrogen. Stir until the solution is transparent, slowly drop into 20mL dissolved phase transfer catalyst (1.2×10 -2 mol) in aqueous solution. The temperature was raised to 45°C, and 50 mL of organic solution dissolved with allyl chloride (0.10 mol) was added dropwise. After dropping, the temperature was raised to 60°C, and reacted for 1 hour; the temperature was raised to 65°C, and refluxed for 4 hours. Lower the temperature, replace t...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 Synthesis of allyl-(4-isopropyl-3-methyl)phenyl ether / acrylamide / sodium acrylate terpolymer
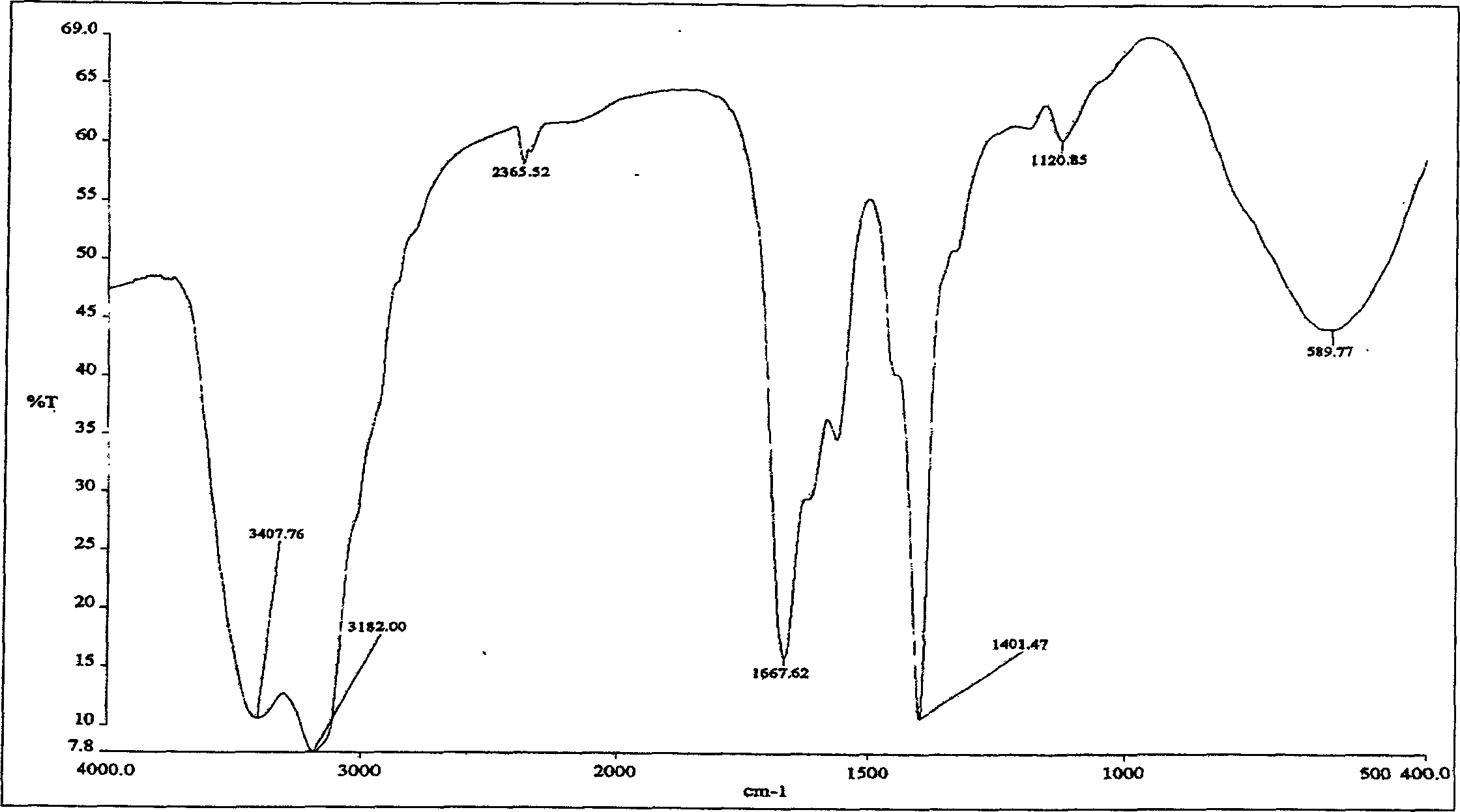
[0045] Synthesize the intermolecular associative hydrophobic monomer (allyl-(4-isopropyl-3-methyl)phenyl ether) at first: in the room equipped with stirrer, thermometer, reflux condenser, dropping funnel and nitrogen ventilation Add 15.1 g (0.10 mol) of p-isopropyl-m-cresol into a 250 mL three-necked circular bottom alkane bottle, keep the temperature of the external bath at 40°C, add 10 mL (0.12 mol) of a certain concentration of NaOH solution and 10 mL of acetone dropwise, and pass nitrogen. Stir until the solution is transparent, slowly drop into 20mL dissolved phase transfer catalyst (1.0×10 -2 mol) in aqueous solution. Raise the temperature to 45°C, add dropwise 50mL organic solution dissolved with 0.10mol of allyl chloride, after the drop is complete, raise the temperature to 50°C, and react for 1 hour; raise the temperature to 60°C, and reflux for 2 hours. L...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Rheology of intermolecular associative terpolymers
[0048] See Figure 5 , the apparent viscosity (Apparent Viscosity, abbreviated as AV)-concentration relationship of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM) aqueous solution is approximately a straight line, and the apparent viscosity increases with the increase of polymer concentration, but the increase is not large, and basically maintains a linear increase . The apparent viscosity of the allyl-nonylphenyl ether / acrylamide / sodium acrylate aqueous solution prepared in Example 1 continued to increase with the increase of the polymer concentration, especially when the concentration exceeded a certain value (>2000mg / L ), the apparent viscosity increases sharply. It shows that the polymer has better viscosity-increasing property in aqueous solution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com