Mesoporous biological glass fiber material and its prepn and application
A glass fiber and mesoporous technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials, achieves the effects of simple and easy operation, mild reaction conditions, and cheap and easy-to-obtain raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
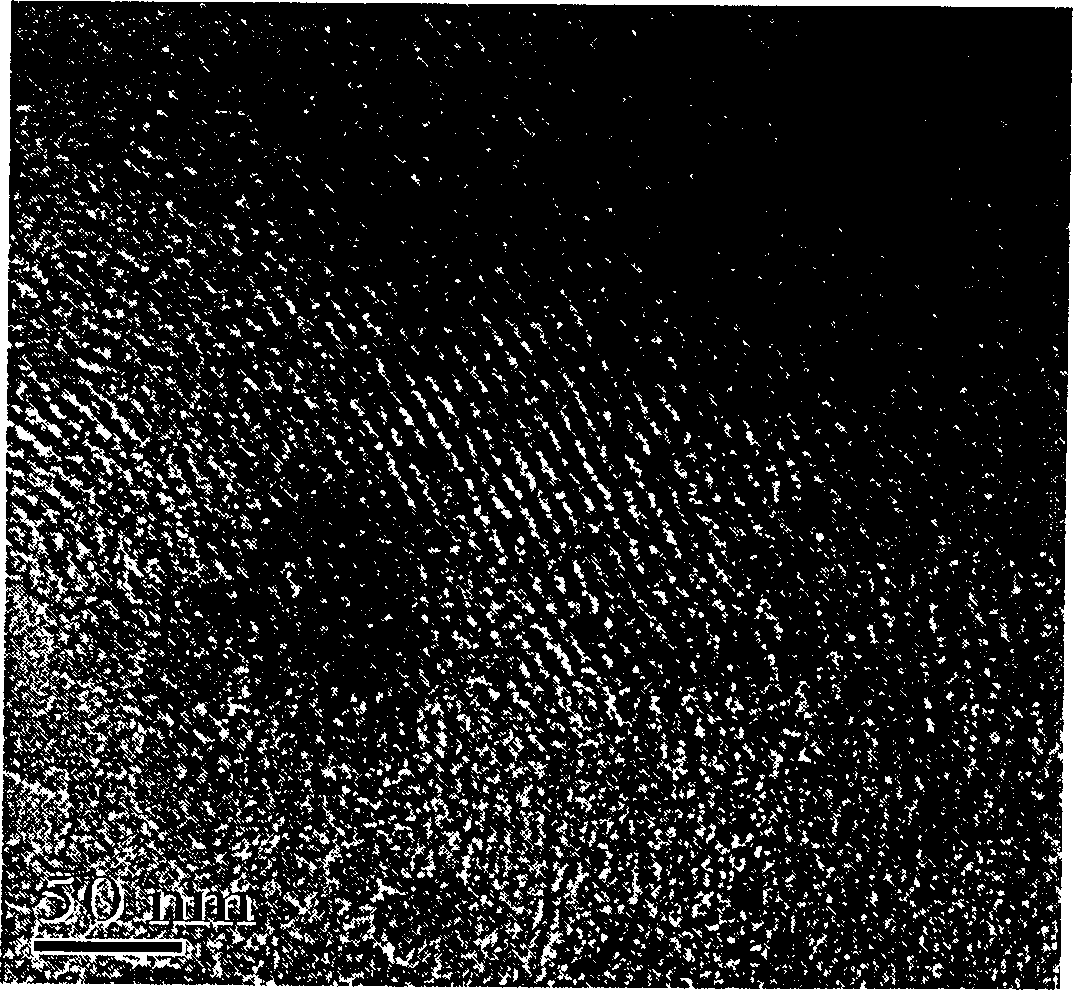
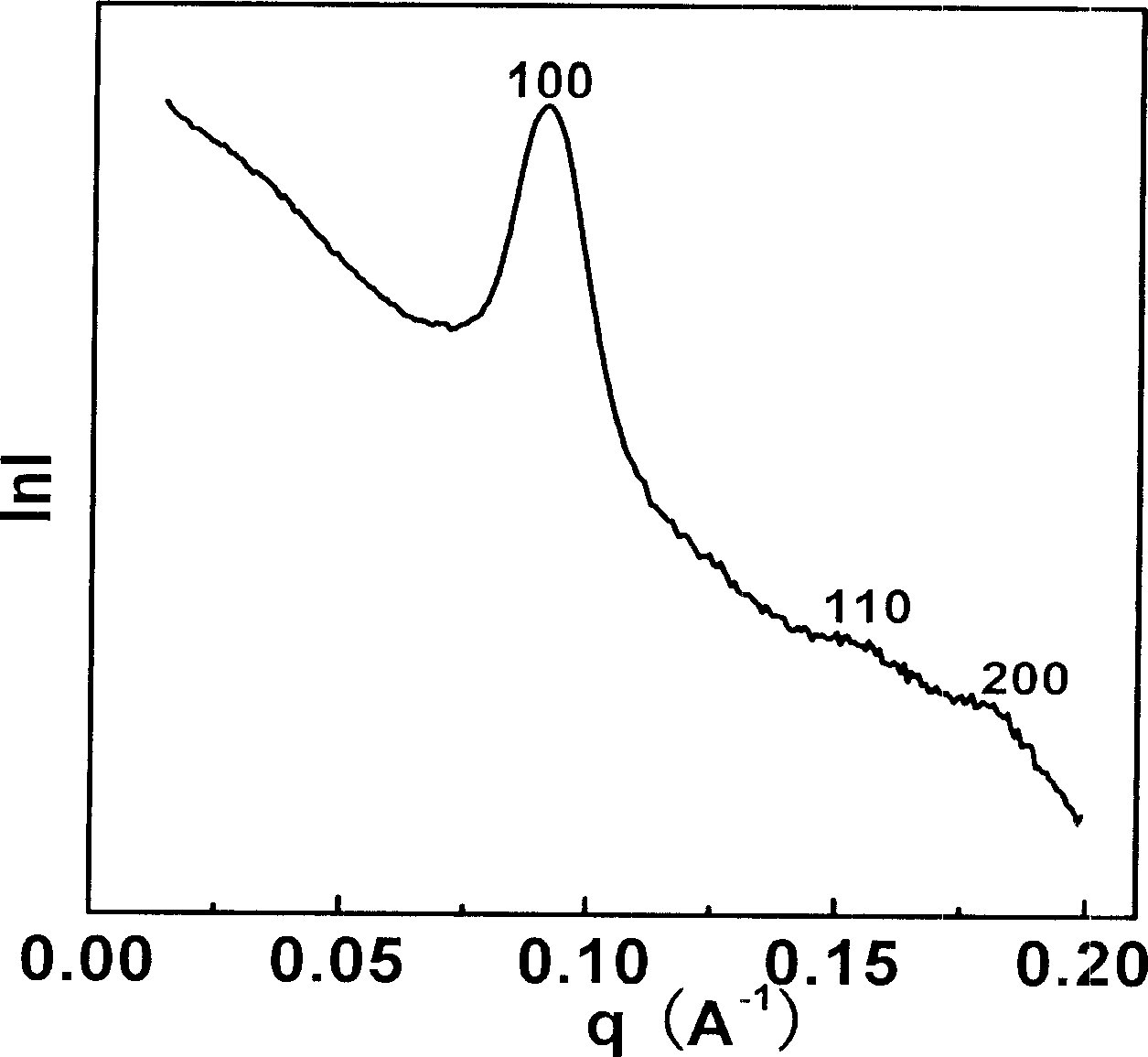
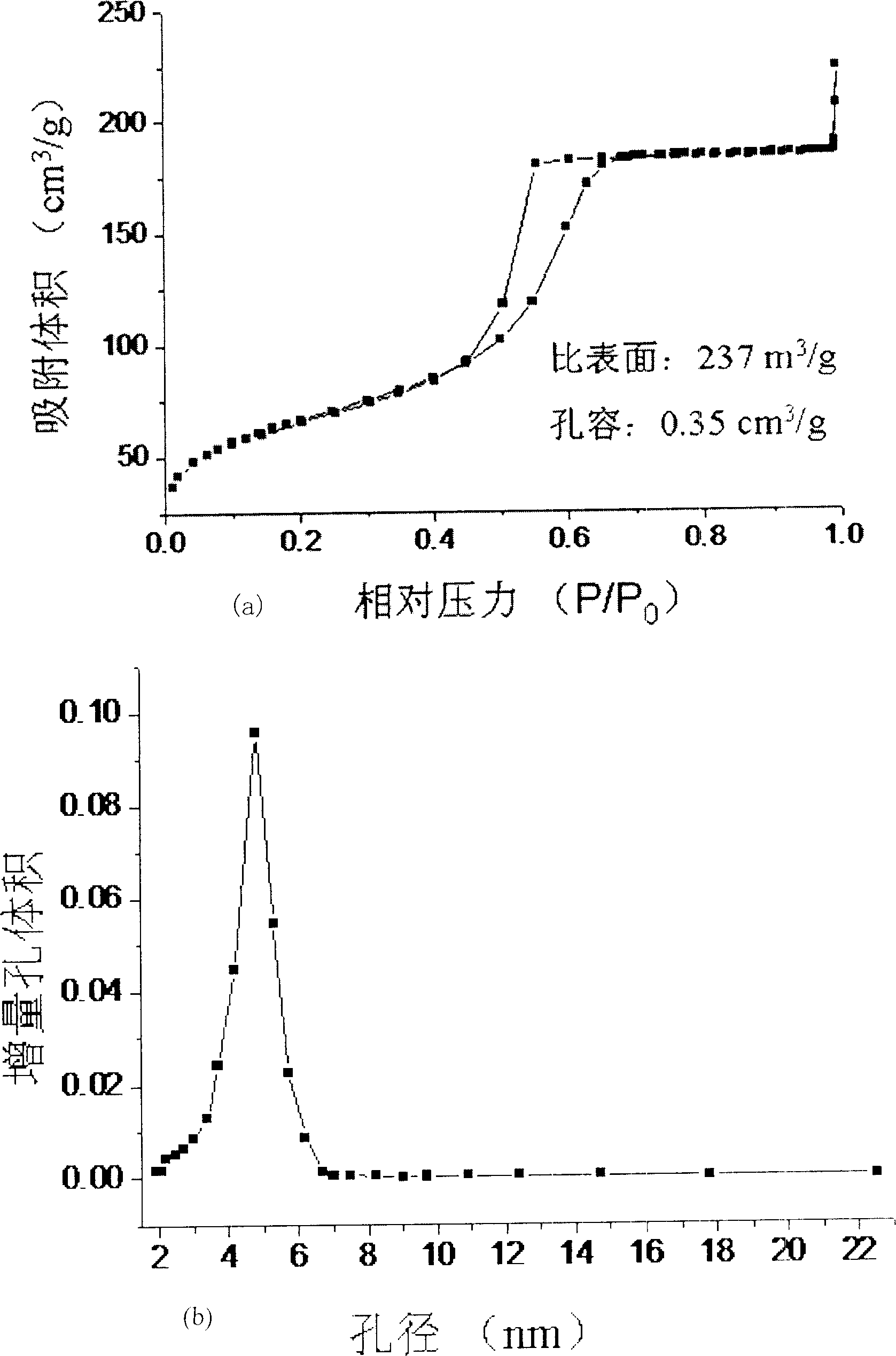
[0032] 4.0g nonionic surfactant EO 20 PO 70 EO 20 (P123), 1.4g calcium nitrate (Ca(NO 3 ) 4 4H 2(2), 6.7g tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), 0.72g triethyl phosphate (TEP) is dissolved in 60g ethanol, and adds 1.3g 4M hydrochloric acid solution, stirs 24h at room temperature, obtains stable sol; Open and volatilize at room temperature until the viscosity of the solution reaches the level where fibers can be sprayed; pour the sol into the spray gun, spray the fibers onto the silicon wafer, and age for about 72 hours to make the hydrolysis-polycondensation reaction fully proceed and form a gel. The glue is placed in a desiccator. The gel block obtained after drying is calcined at 700° C. for 5 hours in a muffle furnace to obtain a two-dimensional hexagonal phase (p6mm structure) mesoporous bioglass fiber material.
Embodiment 2
[0034] 4.0g nonionic surfactant EO 20 PO 70 EO 20 (P123), 0.95g calcium nitrate (Ca(NO 3 ) 4 4H 2 O), 6.7g tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), 0.72g triethyl phosphate (TEP), 0.40g magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O) Dissolve in 60g of ethanol, add 1.3g of 2M hydrochloric acid solution, stir at room temperature for 20 hours to obtain a stable sol; volatilize the sol at room temperature until the viscosity of the sol reaches the level where fibers can be sprayed, and pour the sol into the spray gun , Spray the fiber onto a silicon wafer that can withstand high temperature, and age it for about 80 hours to make the hydrolysis-polycondensation reaction fully proceed to form a gel, and place the gel in a desiccator. The gel block obtained after drying is calcined at 600° C. for 4 hours in a muffle furnace to obtain a two-dimensional hexagonal phase (p6mm structure) mesoporous bioglass fiber material.
Embodiment 3
[0036] 4.0g nonionic surfactant EO 20 PO 70 EO 20 (P123), 0.95g calcium nitrate (Ca(NO 3 ) 4 4H 2 O), 6.7g tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), 0.72g triethyl phosphate (TEP), 0.681g n-butyl titanate were dissolved in 60g ethanol, and 1.3g 3M hydrochloric acid solution was added, stirred at room temperature for 28h, A stable sol was obtained. Volatilize the sol at room temperature until the viscosity of the solution reaches the level where fibers can be sprayed. Pour the sol into a spray gun to spray fibers. Spray the fibers onto silicon wafers that can withstand high temperatures. Aging for about 60 hours, hydrolysis-polycondensation The reaction fully proceeds to form a gel, which is placed in a desiccator and fully dried. The gel block obtained after drying was calcined at 550°C for 6 hours in a muffle furnace to obtain a two-dimensional hexagonal phase (p6mm structure) mesoporous bioglass fiber material, but without the addition of TiO 2 The order of the time structure ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com