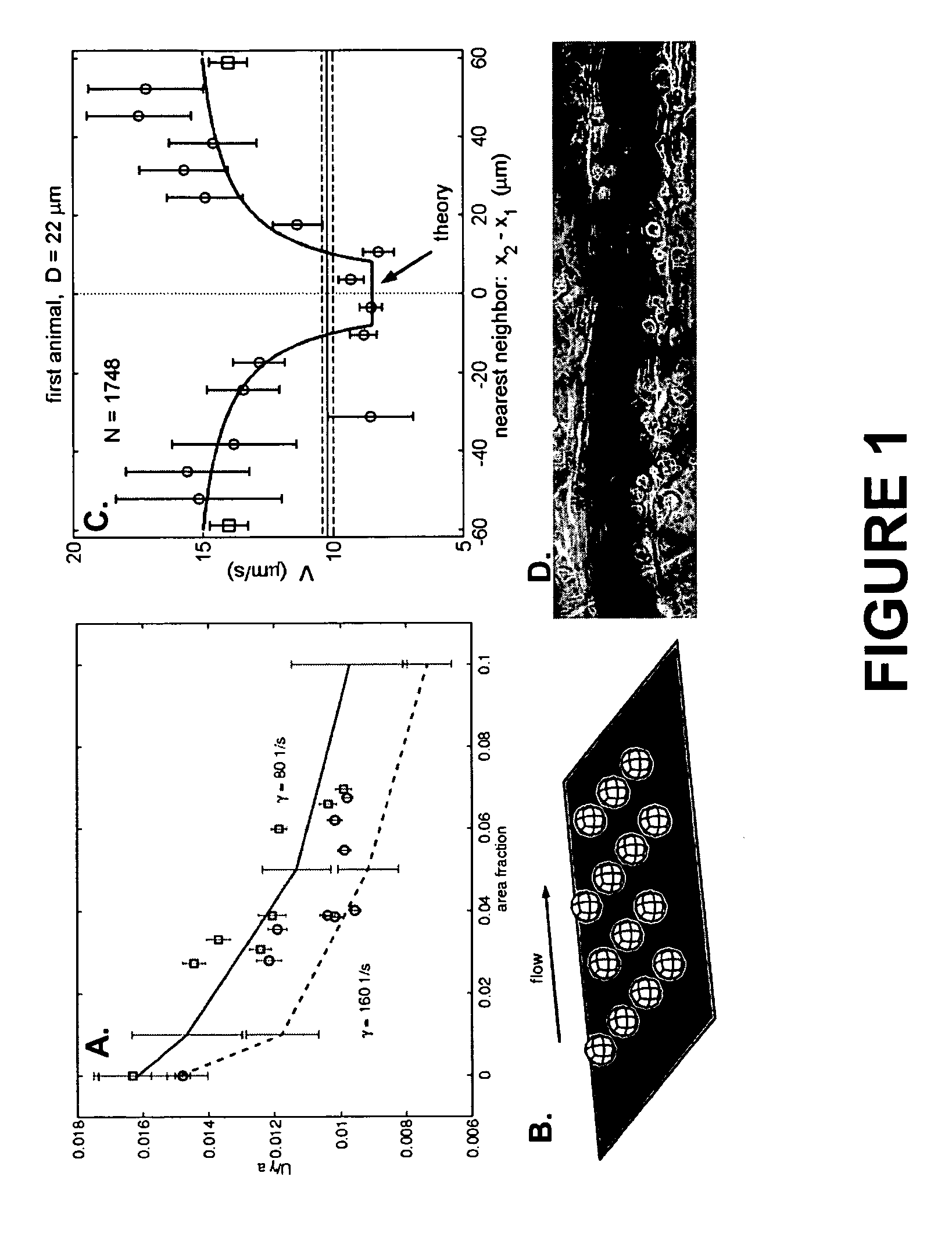
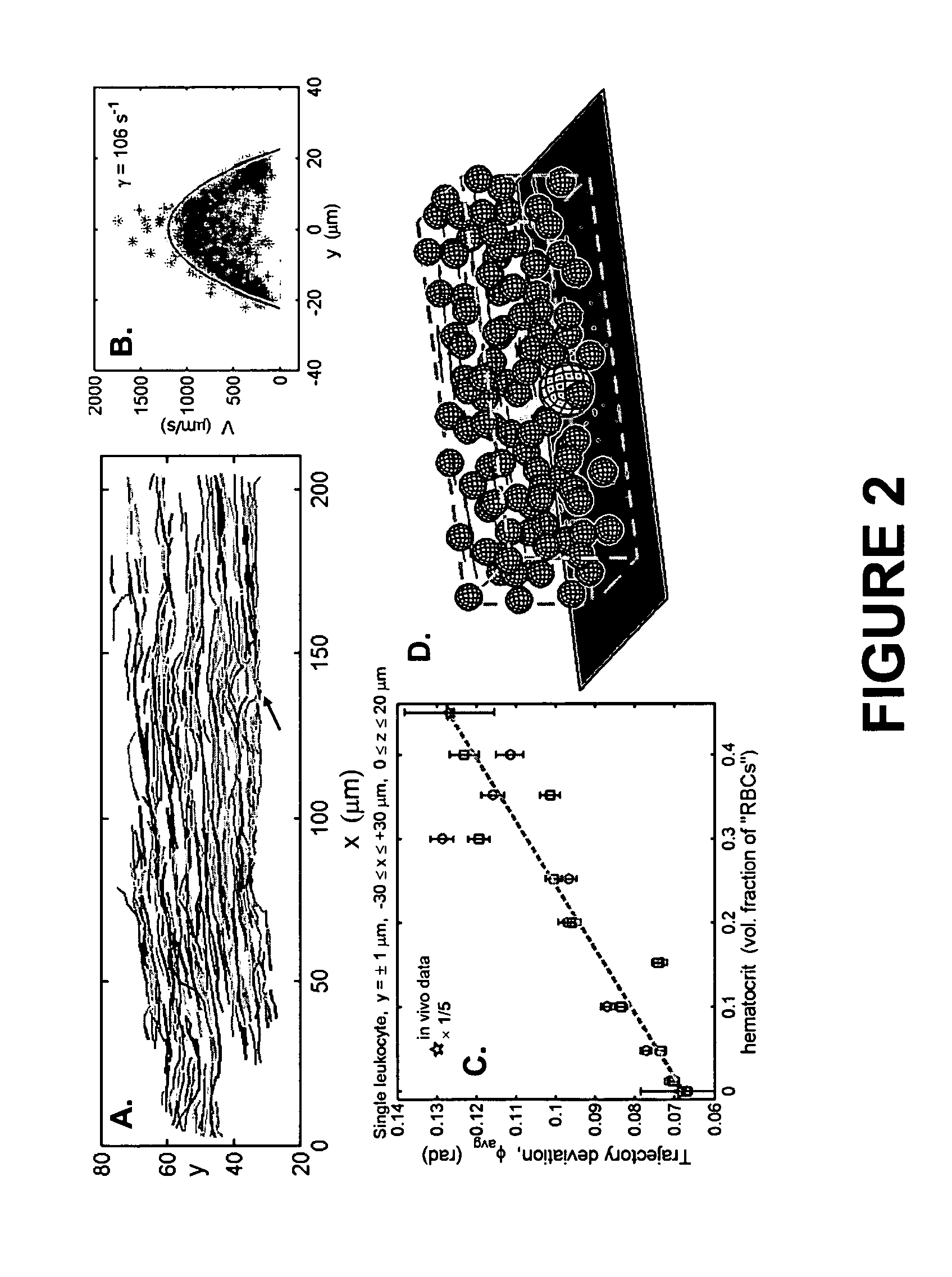
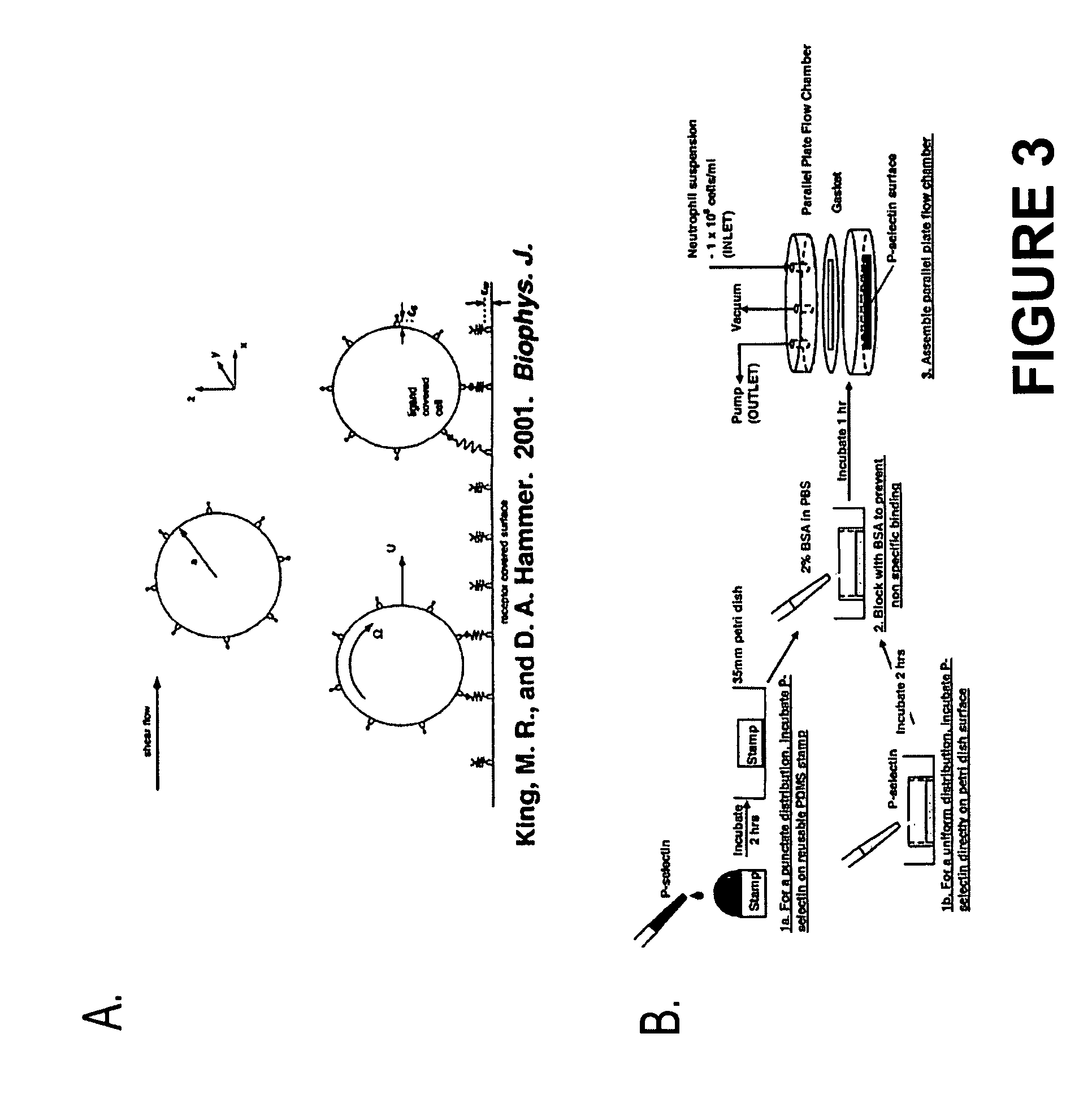
Continuous flow chamber device for separation, concentration, and/or purification of cells
a flow chamber and cell technology, applied in the field of cell separation methods and apparatuses, can solve the problems of reducing the overall yield of cells, increasing the cost of the process, and reducing the yield of cells, so as to achieve fewer steps, reduce the cost of the process, and improve the effect of cell separation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0063] In order to establish protocol without sacrificing precious HSPCs, we utilized a model system where CD34+ KG1a cells represented the HSPCs and CD34− HL60 cells represented the CD34− ABM cells. The KG1a / HL60 model was used to determine an optimum P-selectin concentration for subsequent HSPC experiments. We initially found that KG1a and HL60 cells rolled at very similar velocities at all P-selectin concentrations tested so, based on the data from Eniola et al. (2003), we co-immobilized anti-CD34 antibody together with the P-selectin and found that, at 0.5 μg / ml P-selectin and 40 μg / ml anti-CD34, there was a significant difference between the rolling velocities of the two cells (FIG. 6A). This more closely represented previous findings that HSPCs tend to roll slower than CD34− cells on selecting, which was further confirmed by our own HSPC / CD34− ABM cells experiments using 0.5 μg / ml P-selectin (FIG. 6B). The presence of the antibody had little effect on the rolling velocity of t...
example 2
[0064] Cell retention as a function of time was also determined for both cell models at a shear stress of 3 dyn / cm2 for 10 minutes. Cells were initially loaded over the entire surface and allowed to settle for 40 s for KG1a / HL60 cells, and 2 minutes for ABM cells, based on the Stokes settling velocity of the cells of interest. We found that KG1a Cells had a higher accumulation than HL60 cells on the P-selectin / antibody surface and similarly, there was higher retention of HSPCs than Cd34− ABM cells on the P-selectin surface (FIG. 7).
[0065] We were able to use this data to predict and confirm with experiments that there would be significant enrichment of KG1a cells for KG1a / HL60 cell mixtures ranging from 10-50% KG1a cells. Predictions using physiologic ABM concentrations of 1-5% HSPC showed more modest improvements and were not confirmed experimentally (FIG. 8).
[0066] We extended the prediction to determine the length of time for optimum enrichment, i.e., the time for purity and re...
example 3
[0067] As mentioned before, we established conditions for determining the effectiveness of our system based on recommendations from Johnsen et al (1999)—Cell purity >80-90%, Cell retention >50% and optimum separation within 30 minutes. It was evident that our current system needed significant improvements to achieve these preliminary goals, so we investigated whether our cell loading system was optimized for this type of separation. Instead of loading the entire surface, only a small portion (<10%) of the surface would be used for the initial cell loading step so that the device could make use of the natural tendency of the cells to separate based on rolling velocity (FIG. 10).
[0068] We used an exponentially modified Gaussian (EMG) distribution to describe the velocity distribution of cells at 3 dyn / cm2 (FIG. 11). The peak to peak resolution for HL60 / KG1a cells and HSPC / CD34− ABM cells was about 0.4, corresponding to about 40% cross contamination. Coupled with the cell retention da...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com