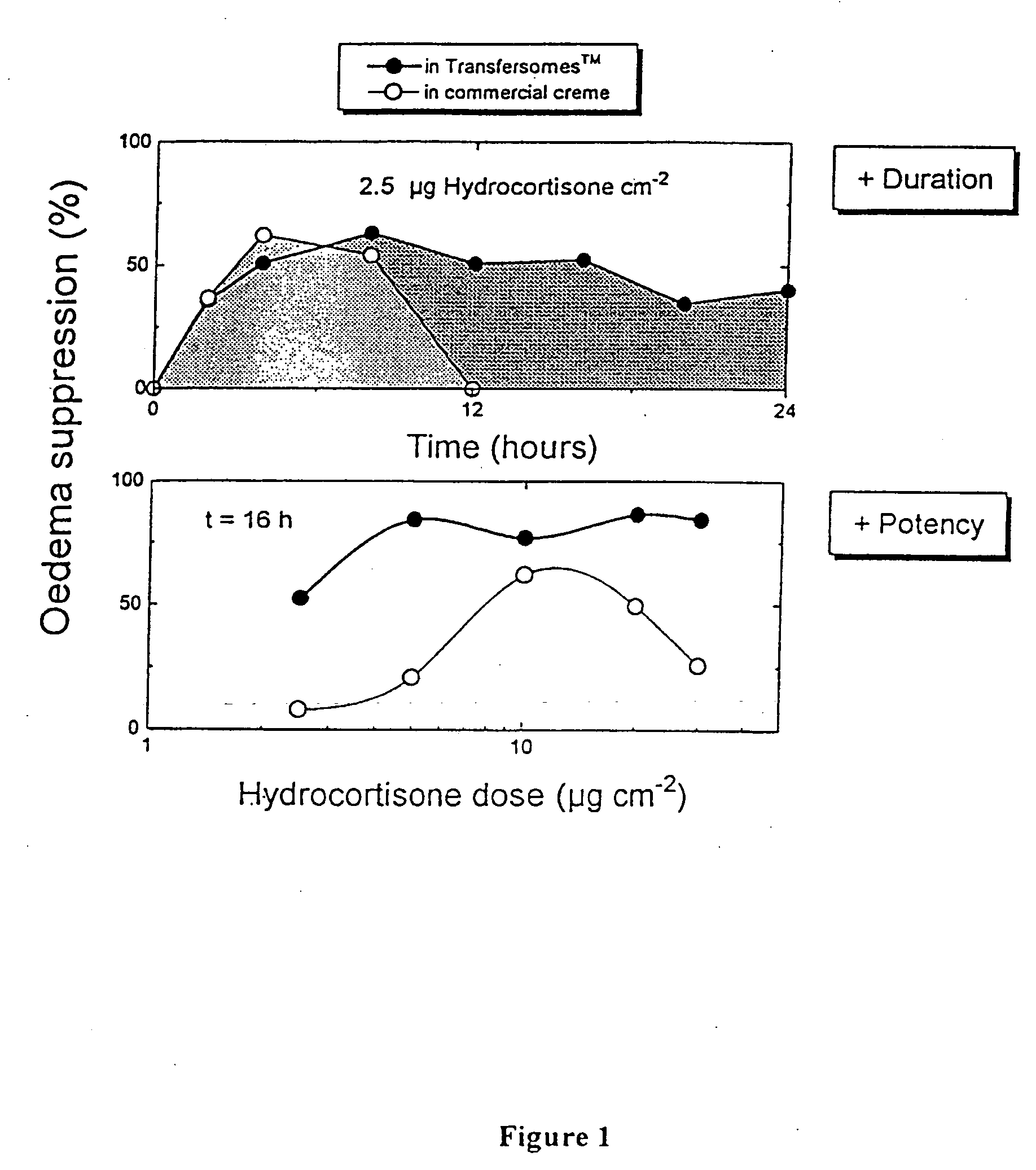
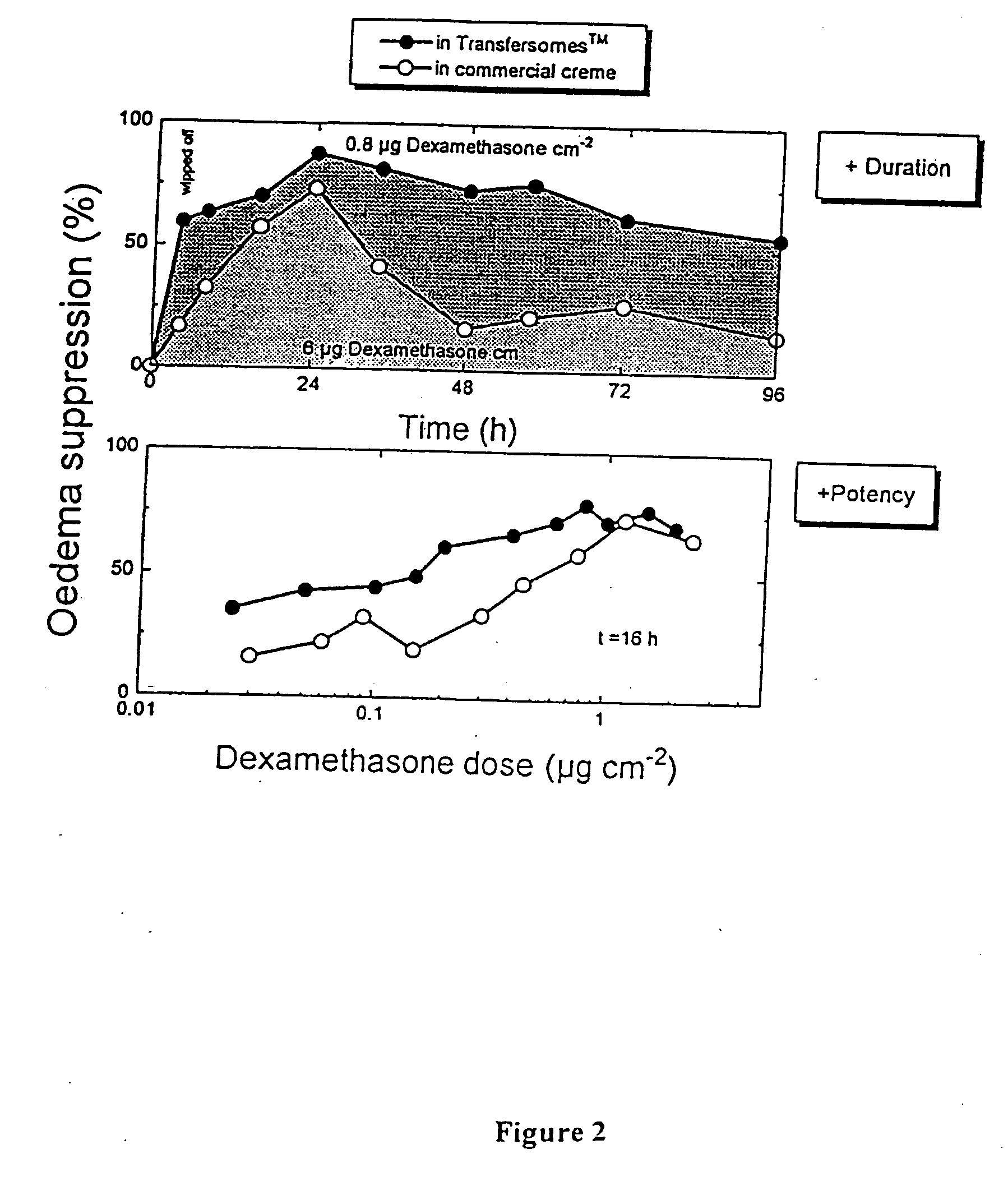
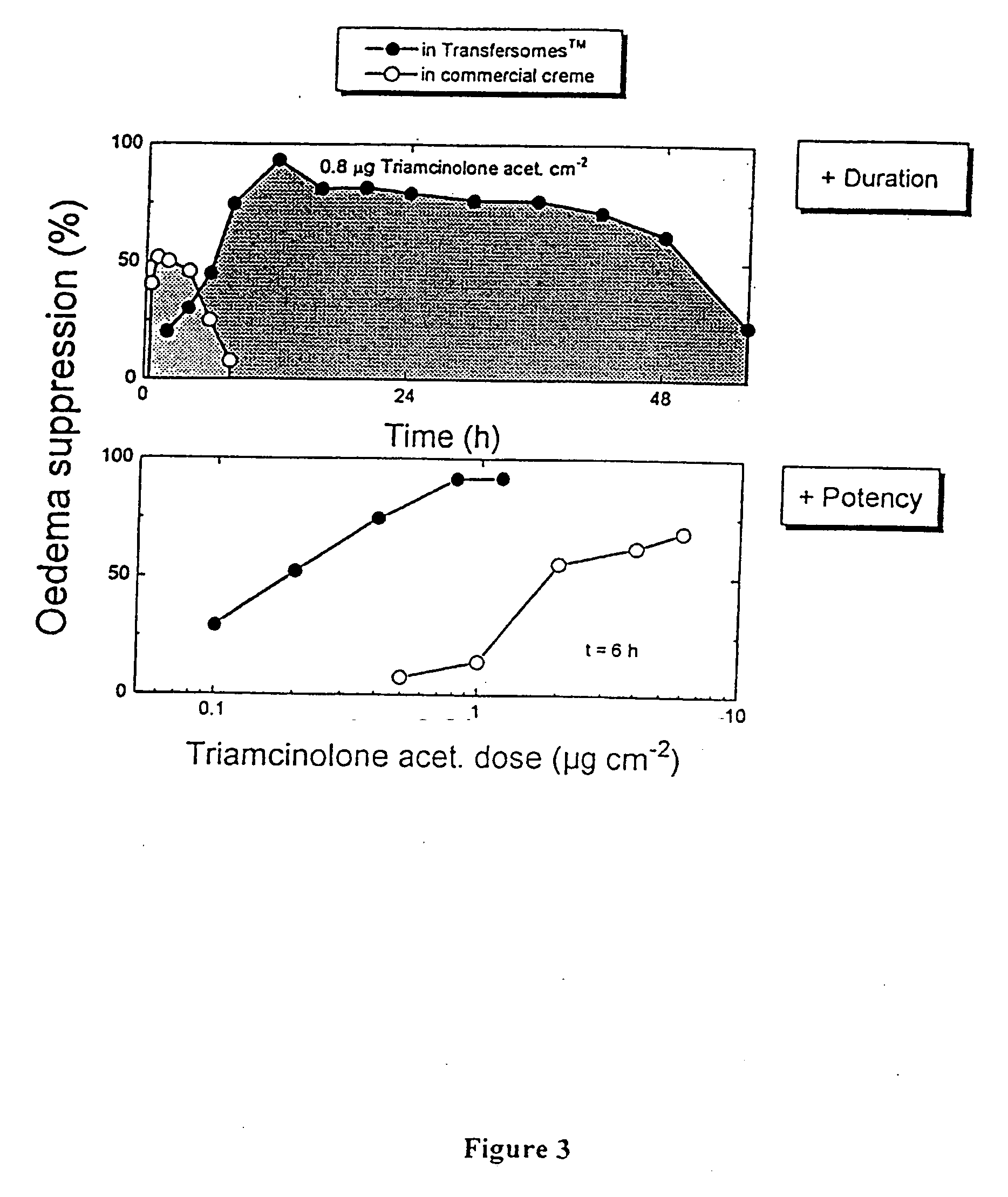
Formulation for topical non-invasive application in vivo
a technology of formulation and in vivo application, applied in the field of formulations, can solve the problems of lack of chemical, rapid development of desired biological action, lack of practical value of drugs, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing the practicability of formulation, prolonging storage and use of formulation, and increasing the viscosity of formulations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-4
[0080]
Composition:73.2 mg, 64.5 mg, 54.8 mg,Soy bean phosphatidylcholine (SPC)37.7mg26.8 mg, 35.5 mg, 45.2 mg,Polysorbate (Tween 80)62.3mg1mg / gTriamcinolone acetonide899mgPhosphate buffer (10 mM, pH 6.5)
Preparation:
[0081] Various SPC and triamcinolone acetonide amounts (as specified) are dissolved in 50 mL chloroform and 50 mL methanol. The solvent, which is kept warm (approx. 40 degrees Celsius), is evaporated under a stream of nitrogen and the residue is dried in vacuum at room temperature. Tween 80 in the specified quantity and phosphate buffer is added to the lipid film and the resulting crude suspension is sonicated to prepare smaller mixed lipid vesicles. The resulting suspension should be opalescent and slightly yellow, which requires up to a few minutes of sonication, and is stable for at least 1 day. The test sample is used within 24 h after the preparation.
Biological and / or Characterisation Experiments:
[0082] with this and all following suspensions were done as descri...
examples 5a-5b
[0083]
Composition:37.74mgSoy bean phosphatidylcholine (SPC)62.26mgTween 800.4mgTriamcinolone Acetonide0, 26.25mgBenzyl alcohol4.47gPhosphate buffer 50 mM pH 6.50.3mgProbucol0.3mgDesferal
Preparation:
[0084] SPC, probucol and triamcinolone acetonide are dissolved in a chloroform / methanol mixture. Dry lipid mixture is prepared as described for example 1. Desferal, Tween 80, and 894.23 mg buffer is added to the dry lipid. The resulting suspension is stirred over night. After adding, if so chosen, 26.25 mg benzyl alcohol in 3.58 g buffer to the suspension, the mixture is extruded through a 200 nm polycarbonate membrane and then through a 50 nm membrane using sufficient excess pressure to give an acceptable flow rate. The resulting particle diameter is below 150 nm
example 6
[0085]
Composition:37.74mgSPC62.26mgTween 8035mgEthanol0.4mgTriamcinolone acetonide26.25mgBenzyl alcohol4.47gPhosphate buffer (50 mM pH 6.5)0.3mgProbucol0.3mgDesferal
Preparation:
[0086] SPC, probucol and triamcinolone Acetonide are dissolved in ethanol. Desferal, Tween 80, 5.25 mg benzyl alcohol and 894.23 mg buffer is added. The resulting suspension is stirred over night. The following day a solution of 21 mg benzyl alcohol in 3.58 g buffer is added to the suspension. The suspension is extruded, first, through a 200 nm pore polycarbonate membrane and then through a 50 nm membrane. This results in particle radius around 60 nm.
[0087] Analysis of formulation stability by means of HPLS suggests that the presence of probucol and desferal is advantageous to the chemical stability of suspension.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com