Compositions of Hsp60 Peptides and Viral Antigens for Vaccination and Diagnosis
a technology applied in the field of compositions of hsp60 peptides and viral antigens for vaccination and diagnosis, can solve the problems of rarely avoiding pathogenic response, vaccines generated from complex materials, and inherently having a relatively high probability of inducing competing responses, so as to and increase the immunogenicity of antigens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Natural History of MCMV Dissemination in Spleen and Salivary Gland
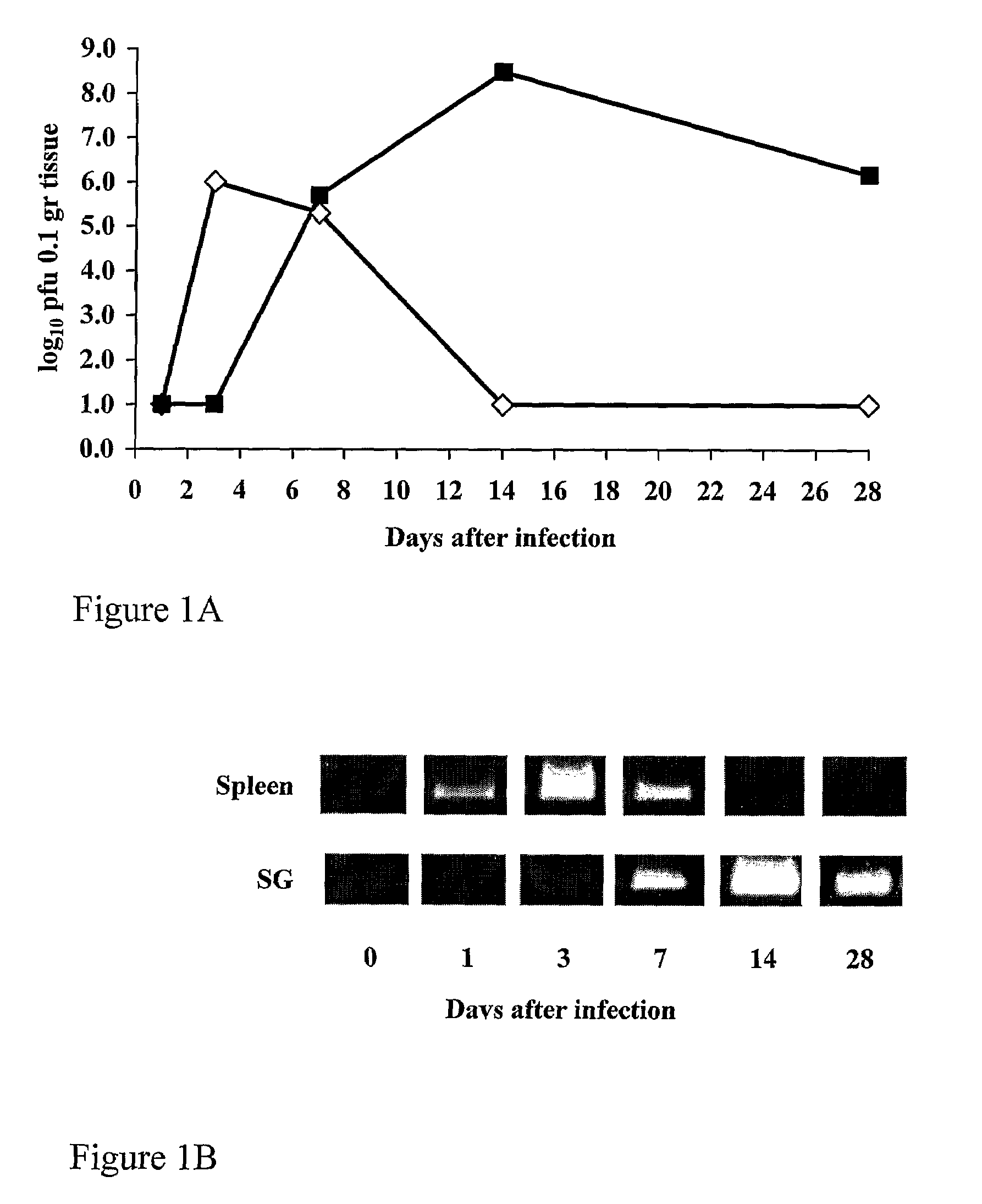
[0190]MCMV infection is characterized by different kinetics and viral loads in different organs (Mercer and Spector, 1986). BALB / c mice, 6-8 weeks old, were injected i.p. with 5×104 pfu of MCMV. Mice were sacrificed on days 1, 3, 7, 14 and 28 after infection, and spleens and salivary glands were assayed for infectious virus and MCMV DNA. FIG. 1, shows a typical pattern of MCMV replication in spleen (empty diamonds) and salivary gland (full squares). Virus replication peaked in the spleen on day 3 after infection, and slowly declined thereafter (FIG. 1A). By day 14, no infectious virus could be recovered from this organ. To detect MCMV DNA in infected organs, we used a sensitive PCR using a gB gene primer pair that amplifies a 356 bp segment (Palmon et al., 1996). Viral DNA was detected in the spleen as early as day 1 after infection, peaked on day 3 and by day 14 no DNA could be detected (FIG. 1B).
[0191]In the salivar...
example 2
Immunization with p458-89pep Suppresses MCMV Persistence in the Salivary Gland
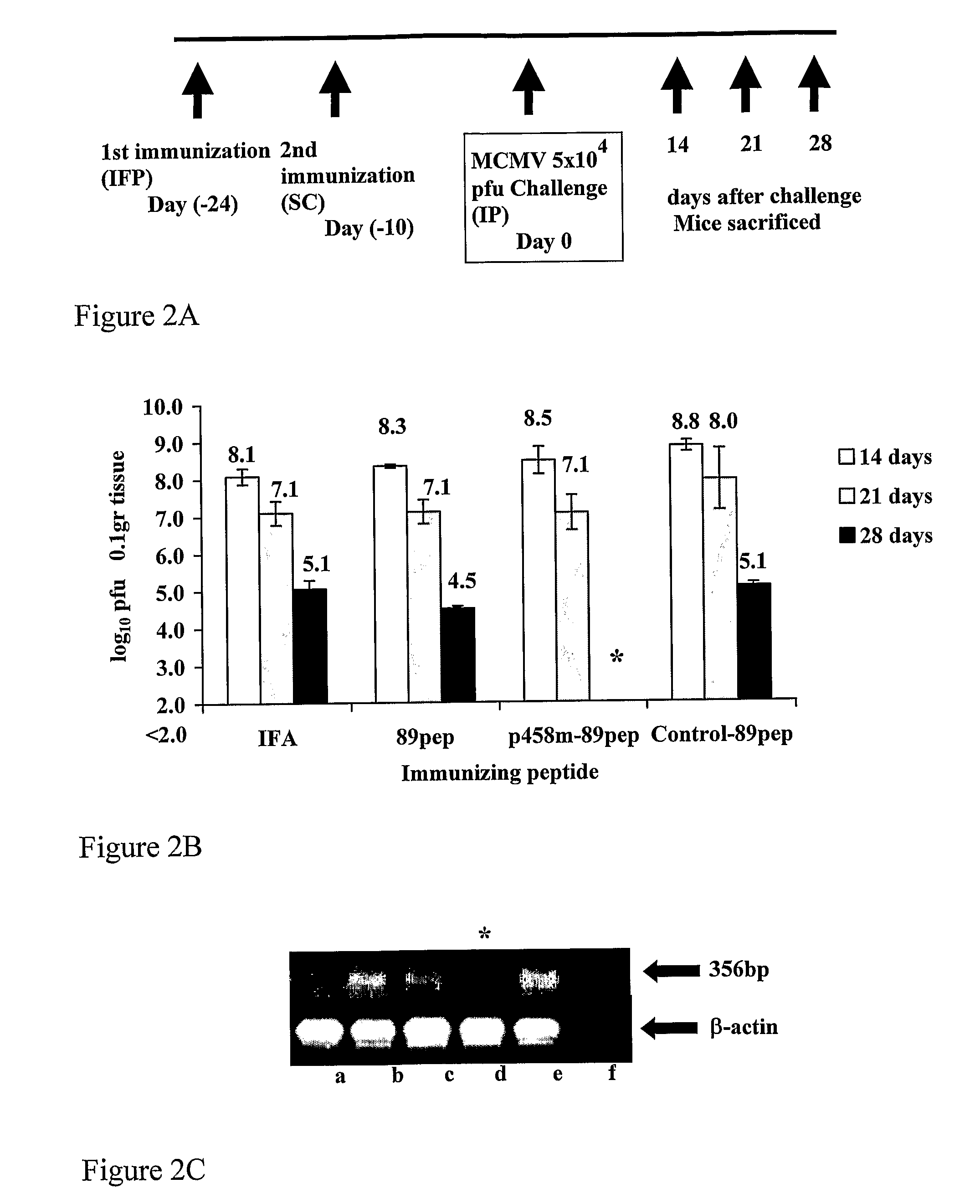
[0192]89pep is the H-2Ld-restricted YPHFMPTNL epitope of MCMV-pp 89 (Reddehase et al., 1989). We synthesized chimeric p458-89pep and compared its protective efficacy against MCMV to that induced by 89pep alone or by negative control-89pep. p458 is a MHC class II-restricted peptide derived from murine HSP60 (aa 458-474) and capable of inducing CD4+ T responses in BALB / c mice (Amir-Kroll et al., 2003). The mycobacterial HSP60 431-447 aa peptide (with a val deletion at position 442) did not elicit an immune response to itself or to p458, and thus served as a negative control peptide for immunization; control-89pep.
[0193]To investigate whether immunization with the different peptides would decrease MCMV replication in salivary glands, 3-week old BALB / c mice were immunized twice with IFA alone, 89pep, p458-89pep or control-89pep (FIG. 2). Three-week old, female BALB / c mice were immunized (i.f.p.) with various p...
example 3
IFNγ Secretion by 89pep-Specific T Cells Following Infection and Vaccination
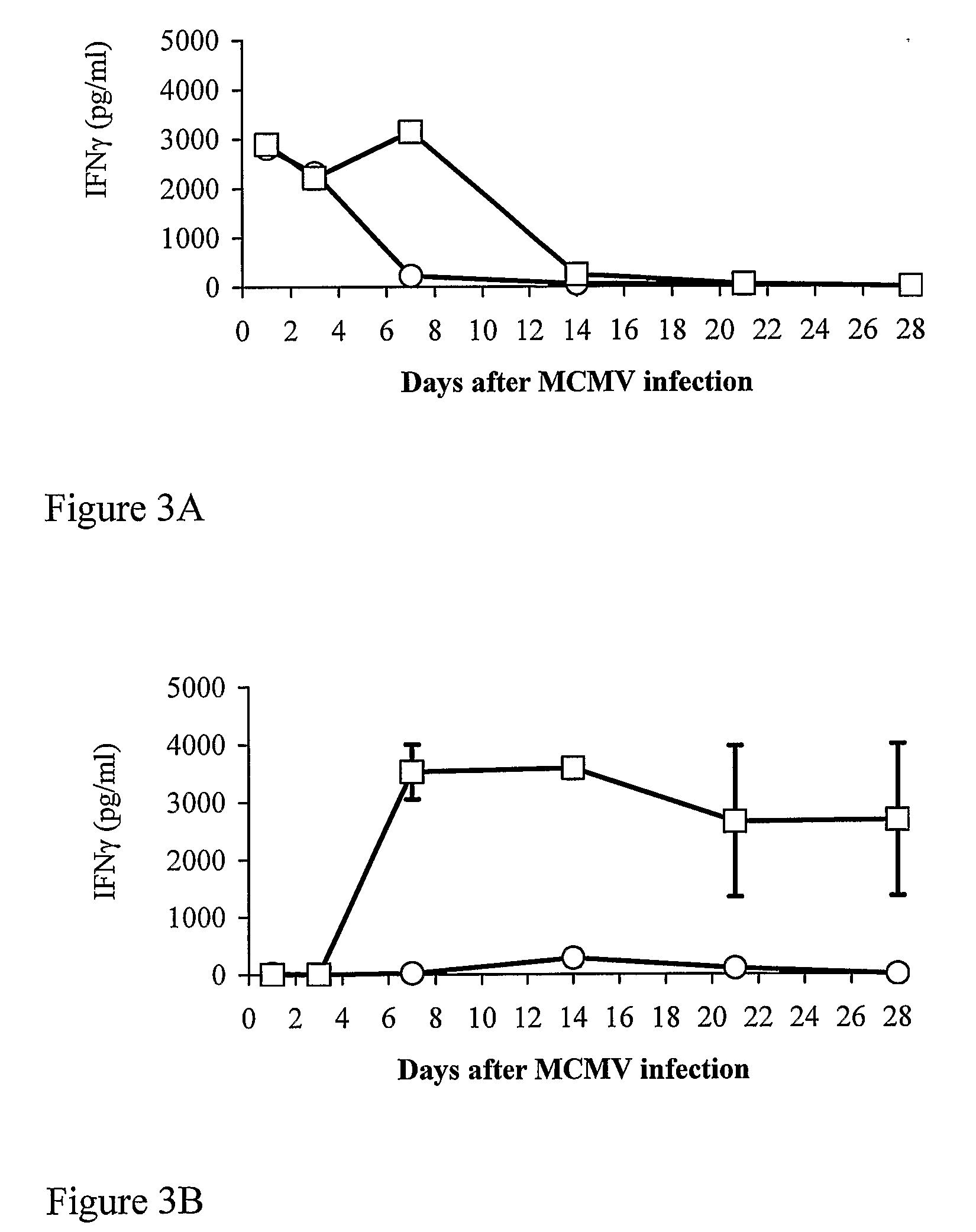
[0196]It is well established that clearance of MCMV during acute infection depends primarily on Th1 IFNγ secretion and protective CTL responses (Mercer and Spector, 1986; Reddehase et al., 1989). We tested whether IFNγ secretion was stimulated by 89pep from spleen (FIG. 3A) and salivary gland (FIG. 3B) cell cultures of MCMV-challenged mice. Cell cultures were prepared on days 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 after infection, plated for 3 d with or without 89pep, and IFNγ secretion was measured. In the absence of 89pep stimulation, secretion of IFNγ was detected only in spleen cultures from days 1 and 3 after infection. This result probably reflects NK activity in the early stages of infection. When 89pep was added to the cultures, IFNγ secretion in spleen and salivary glands was correlated with the kinetics of viral replication in these organs (FIGS. 1A and 3). It is noteworthy that no significant IL-4 secretion was ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com