Micromachined electrolyte sheet, fuel cell devices utilizing such, and micromachining method for making fuel cell devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1a
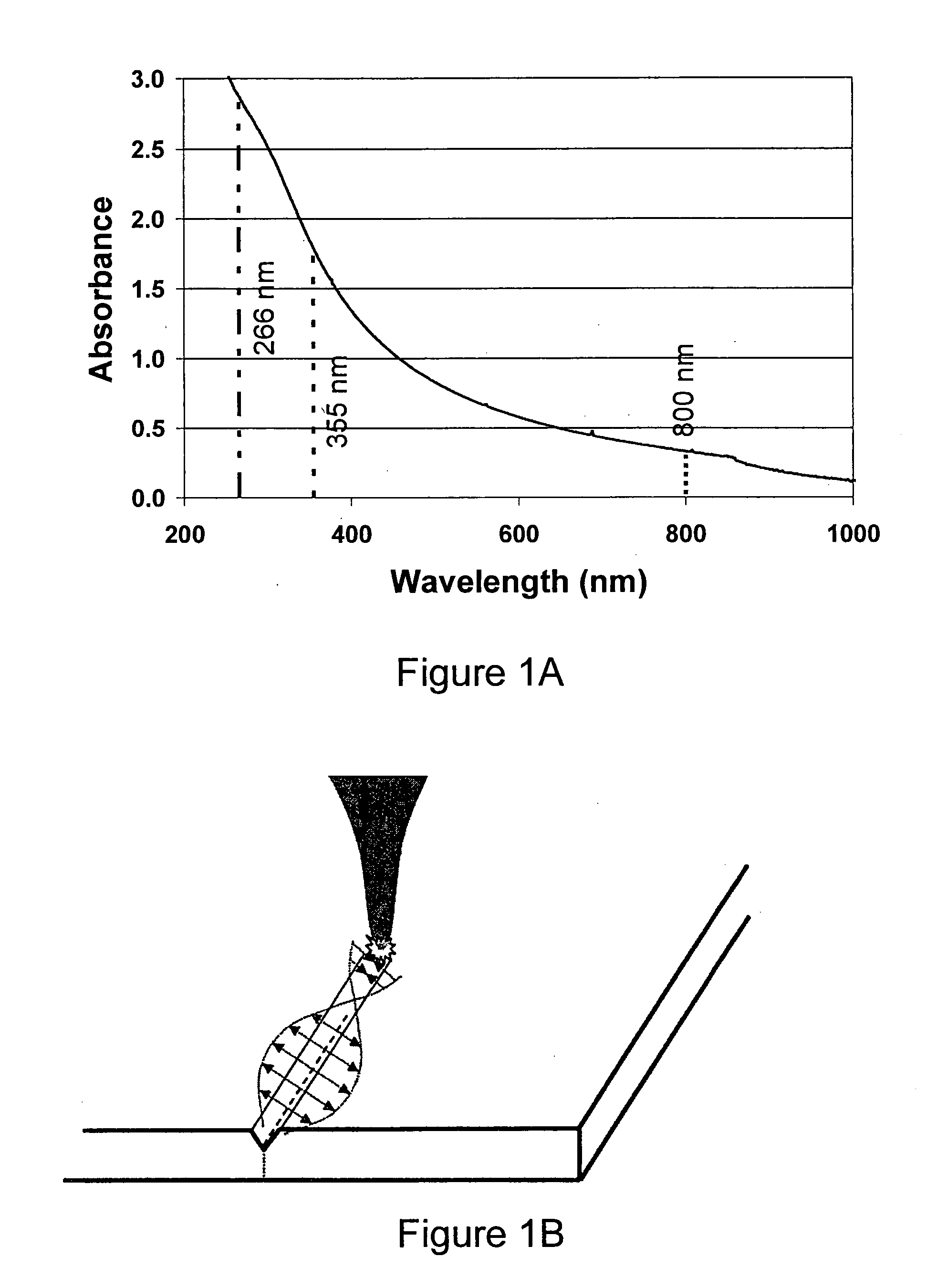
[0081]A plano-convex (PCX) lens L1 with a focal length of 10 cm was used to focus the light in proximity to the zirconia based electrolyte sheet. A simple percussion drilling technique was used. The 266 nm laser 160 had its optical power level set at 340 mW. This power level corresponds to 340 μJ per pulse. Since the diameter of the via hole of this example is about 50 μm, this gives a laser fluence level of roughly 17 J / cm2. In the experiment the hole was laser cut / drilled through the electrolyte sheet after less than 2000 pulses or 2 seconds. The minimum fluence level required to observe laser ablation effects (i.e. ablation threshold level) was less than 6 J / cm2, e.g., about 1 (0.9 to 1.1 J / cm2). The via shape produced is influenced by the laser beam shape. Laser micromachining, without generating microcracks, was also achieved using a range power levels of 100 to 600 μJ per pulse, and fluence levels of 5 to 30 J / cm2.
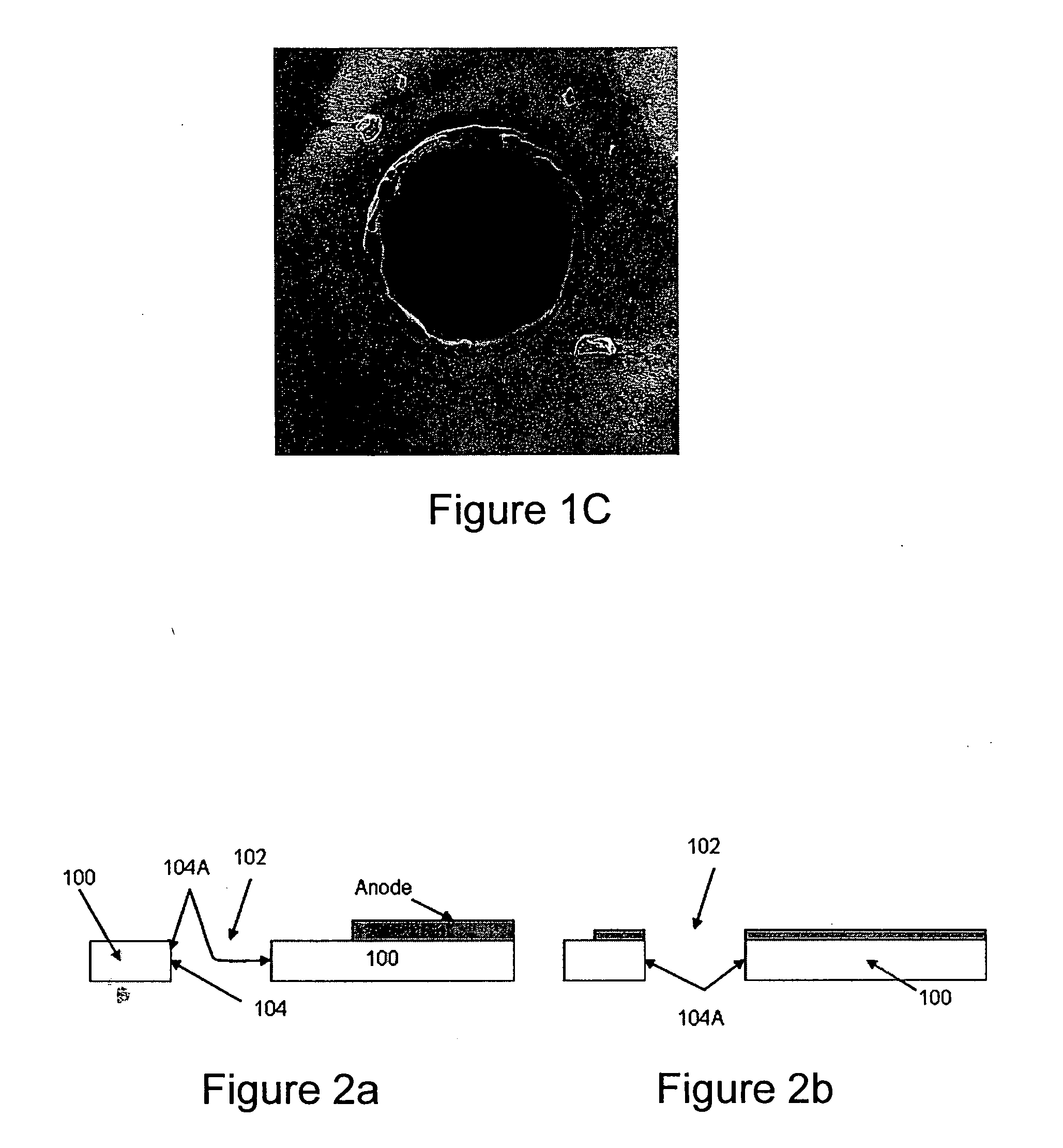
[0082]FIG. 6a and FIG. 6b are photographs taken with an optical...
example 1b
[0083]FIGS. 7a and 7b are SEM images of straight edges laser micromachined with the above described laser cutting equipment and at the same settings, using a cut speed of 1 mm / s. Cutting speeds of 0.5 to 2 mm / s can be utilized, but the cutting speed was ultimately limited by the laser repetition rate (i.e., max. speed is less than spot size diameter×repetition rate). More specifically, FIG. 7a shows a top view of the laser micromachined edge surface and FIG. 7b shows a side view of the micromachined edge surface. Redeposition 108 is seen as a discolored band near the micromachined edge on the laser incident side is also apparent (see FIG. 7a).
Examples Using ns Laser Configuration #2
examples 2 to 4f
[0084]In another embodiment of a laser micromachining system for (nanosecond) laser cutting of sintered zirconia based electrolyte sheet, a frequency-quadrupled Nd:YVO4 laser, made by Spectra-Physics (HIPPO-266QW), was utilized (Examples 2-3B). The output wavelength of this exemplary laser is 266 nm. The ns laser 160, running at a repetition rate of 30 to 120 kHz, has a peak laser power of approximately 2.5 W and a pulse duration of less than 15 ns according to the specifications from the manufacturer. A 3× optical beam expander (BE) and with a 10.3 cm focal length telecentric lens L1 were used in conjunction with the laser 160 to cut the electrolyte sheet 100. (FIG. 8). Single pulse ablation on electrolyte test samples showed that the focal spot size of the laser beam (beam waist) is about 20 μm in diameter.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com