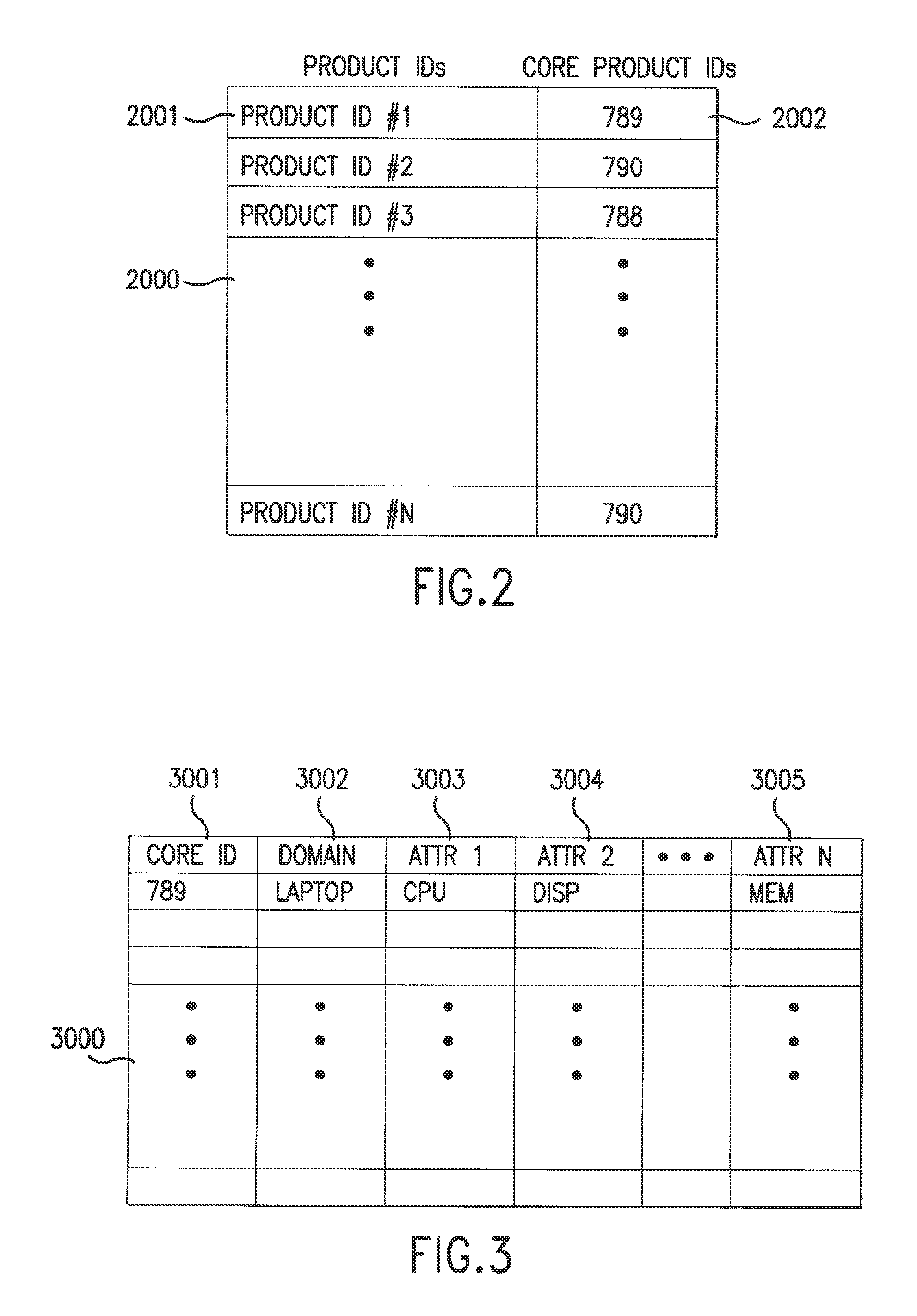
Patents
Literature
102 results about "Attribute–value pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
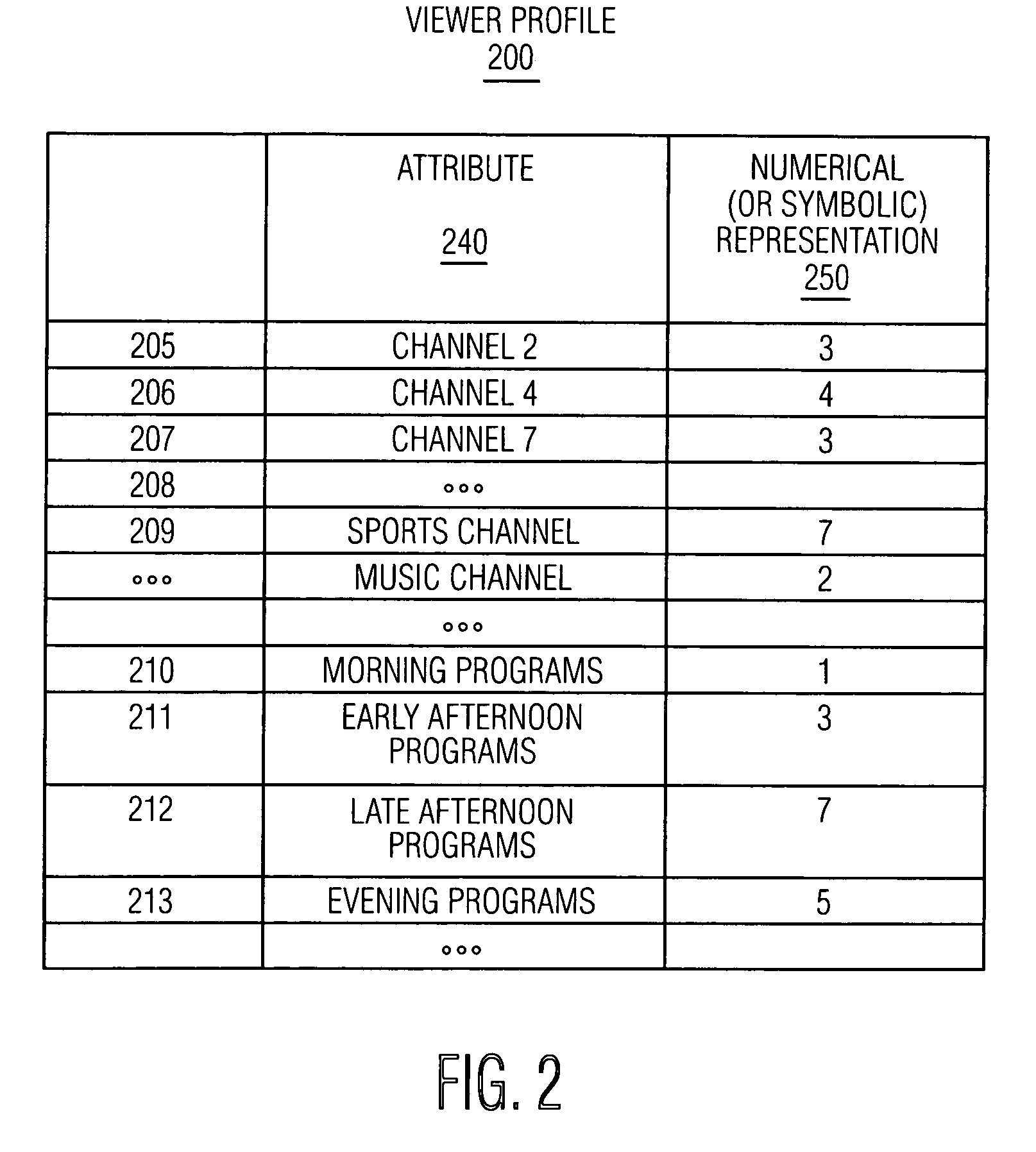
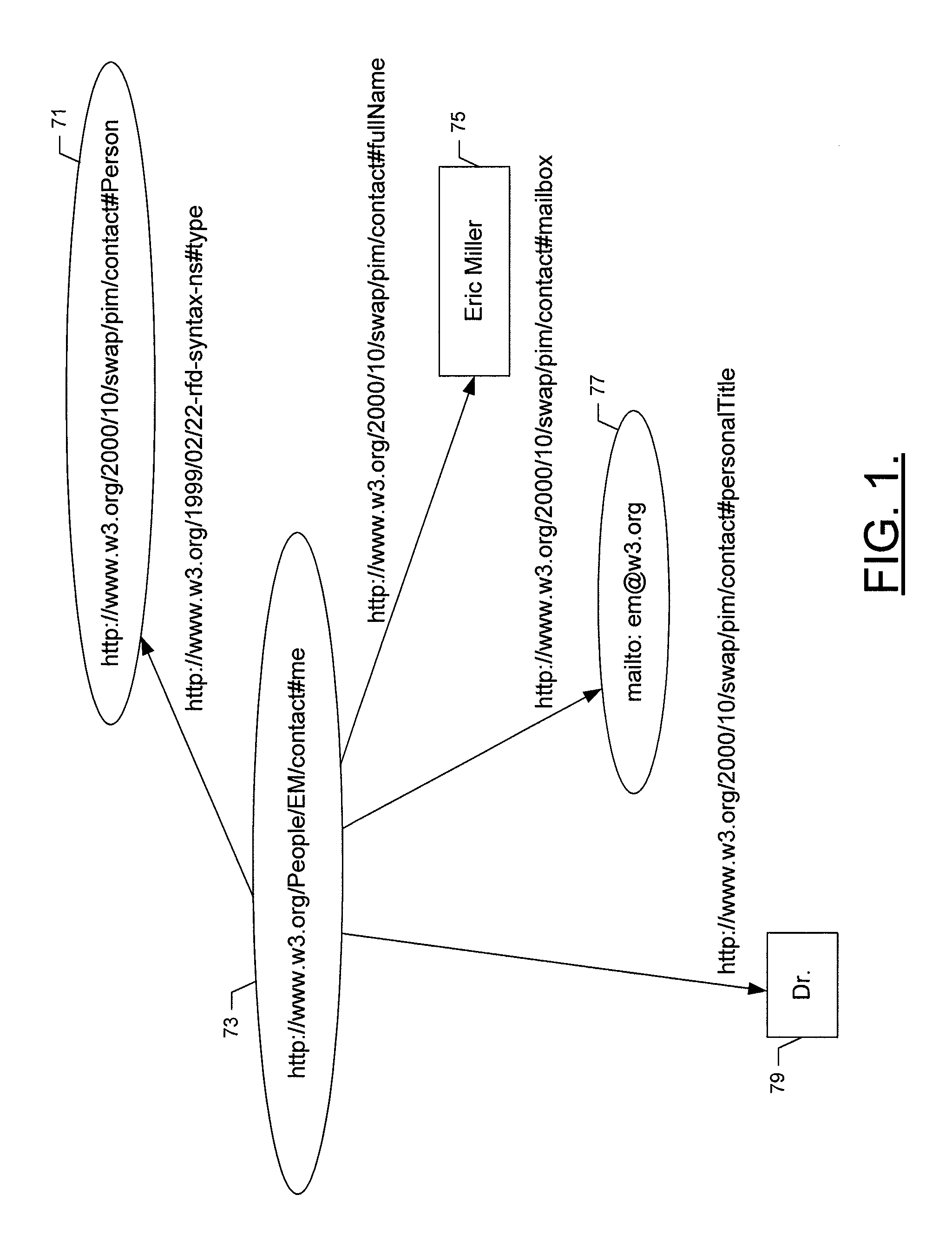
A name–value pair, key–value pair, field–value pair or attribute–value pair is a fundamental data representation in computing systems and applications. Designers often desire an open-ended data structure that allows for future extension without modifying existing code or data. In such situations, all or part of the data model may be expressed as a collection of 2-tuples in the form <attribute name, value> with each element being an attribute–value pair. Depending on the particular application and the implementation chosen by programmers, attribute names may or may not be unique.
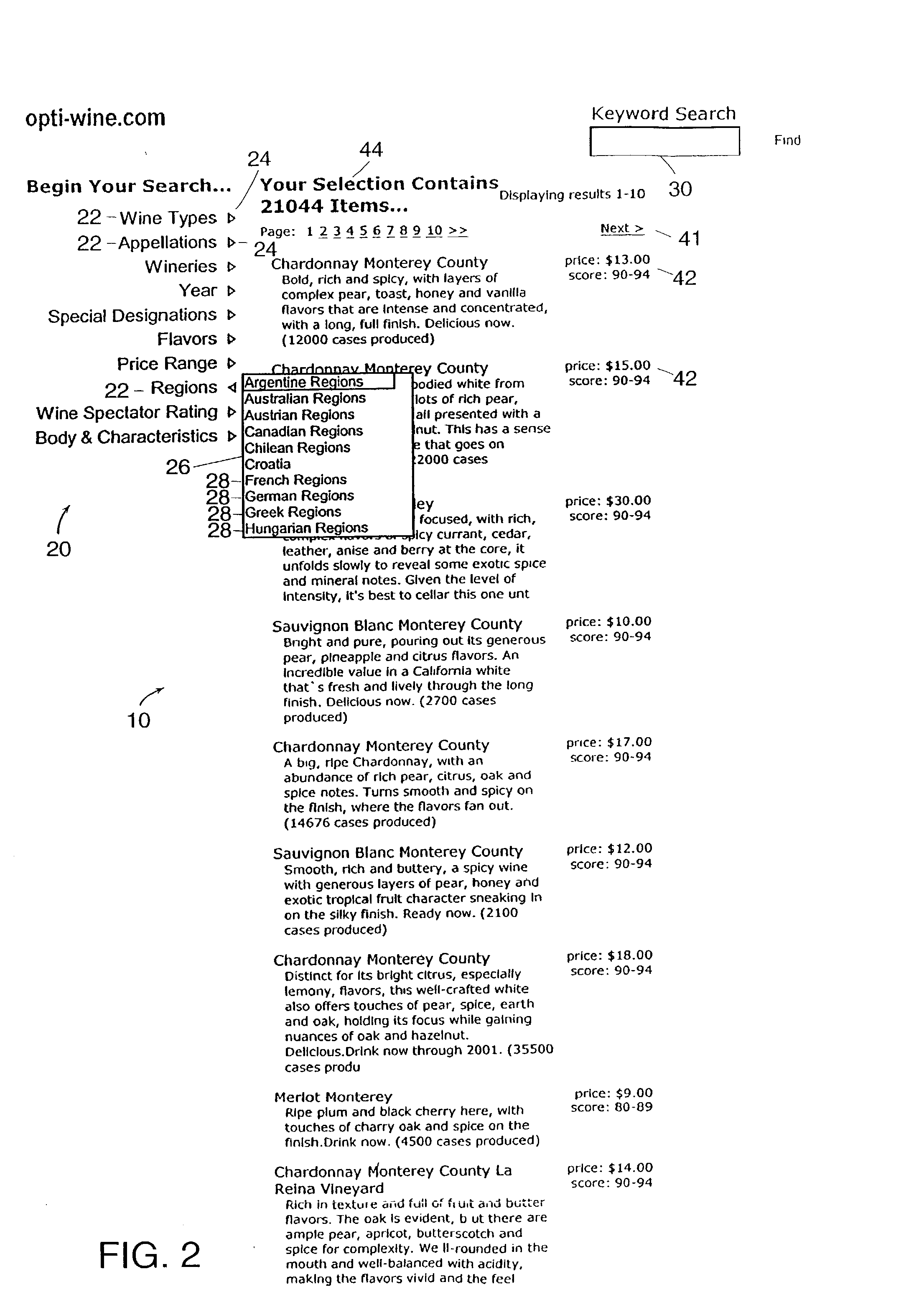
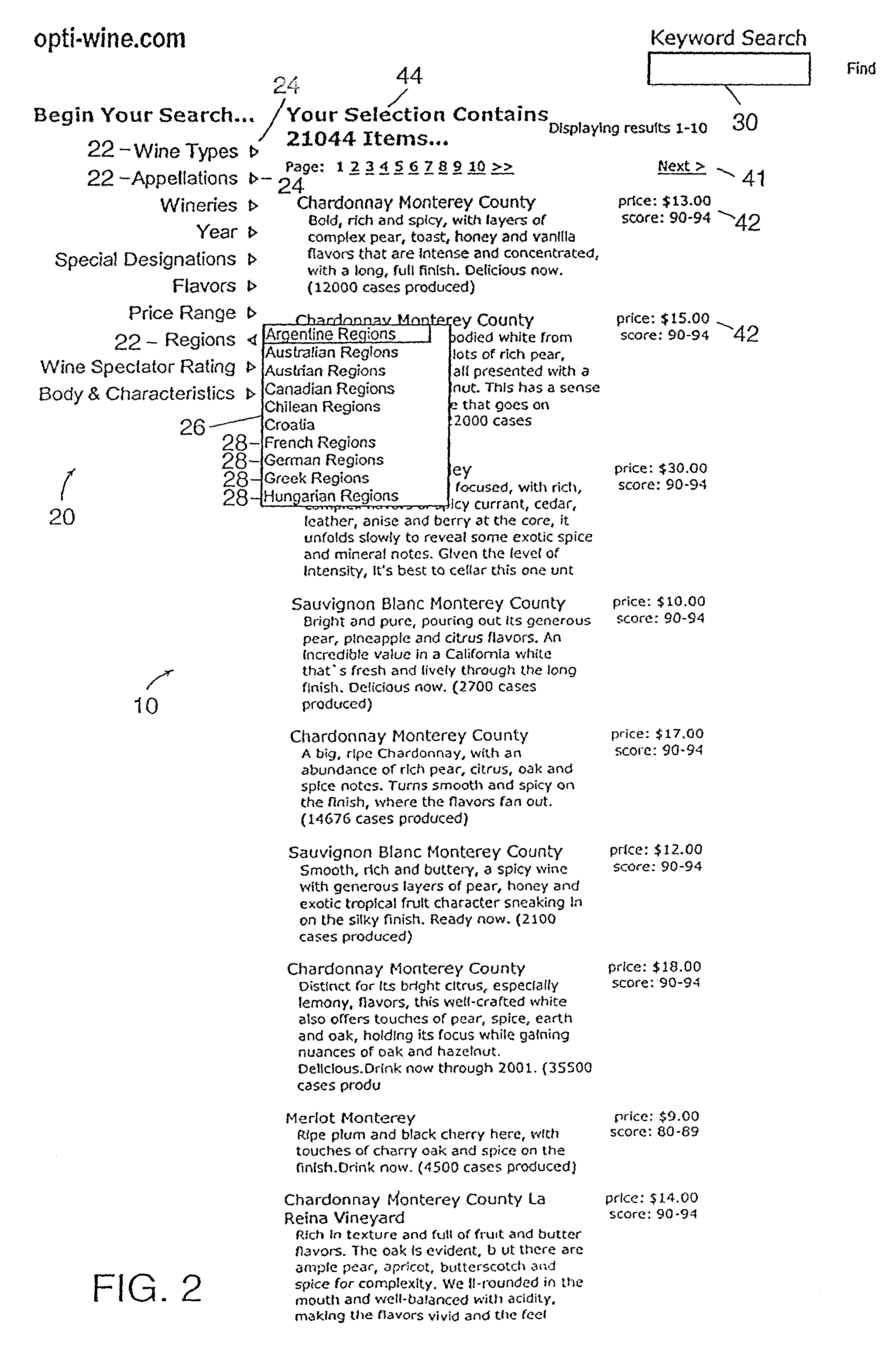
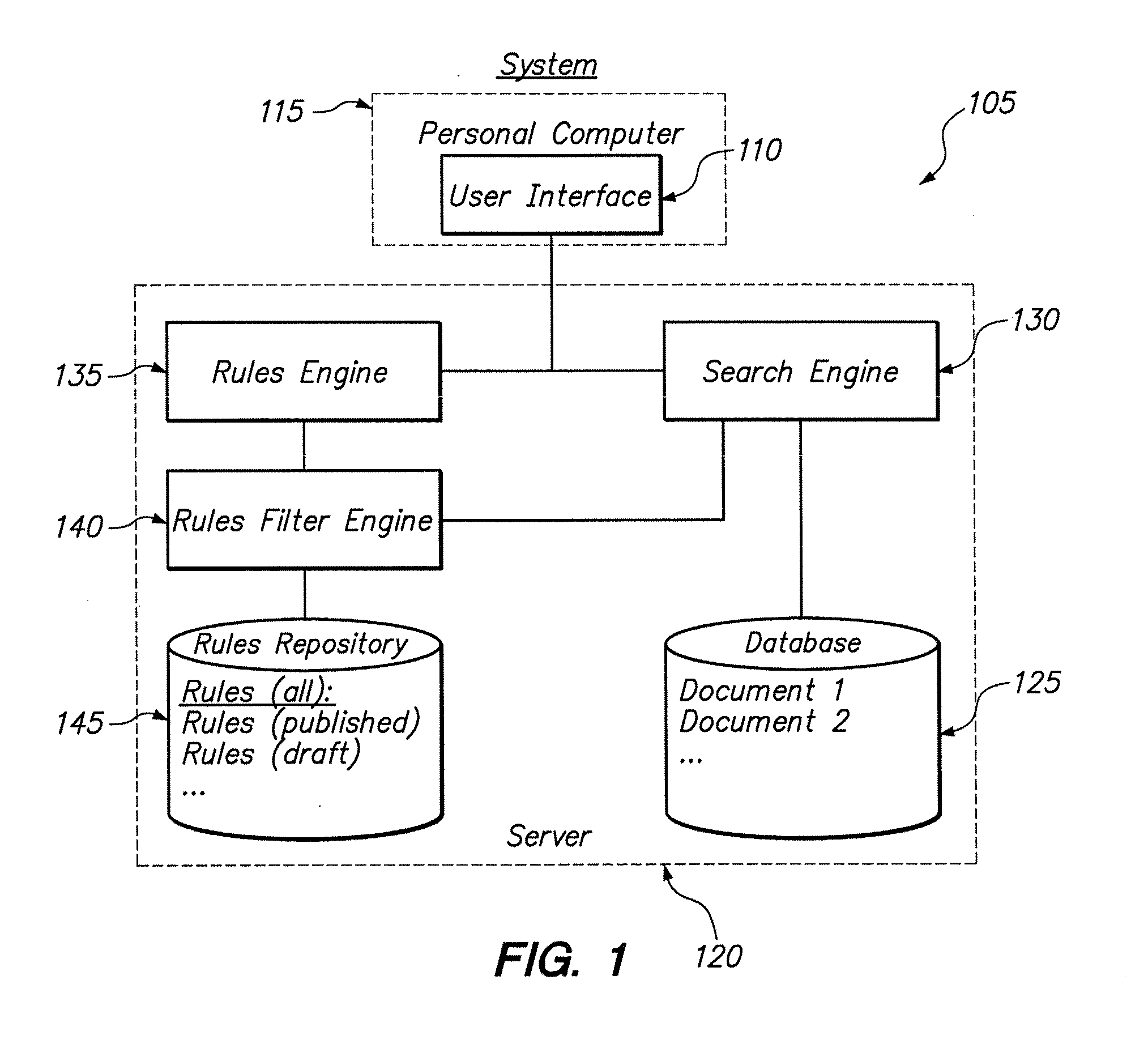
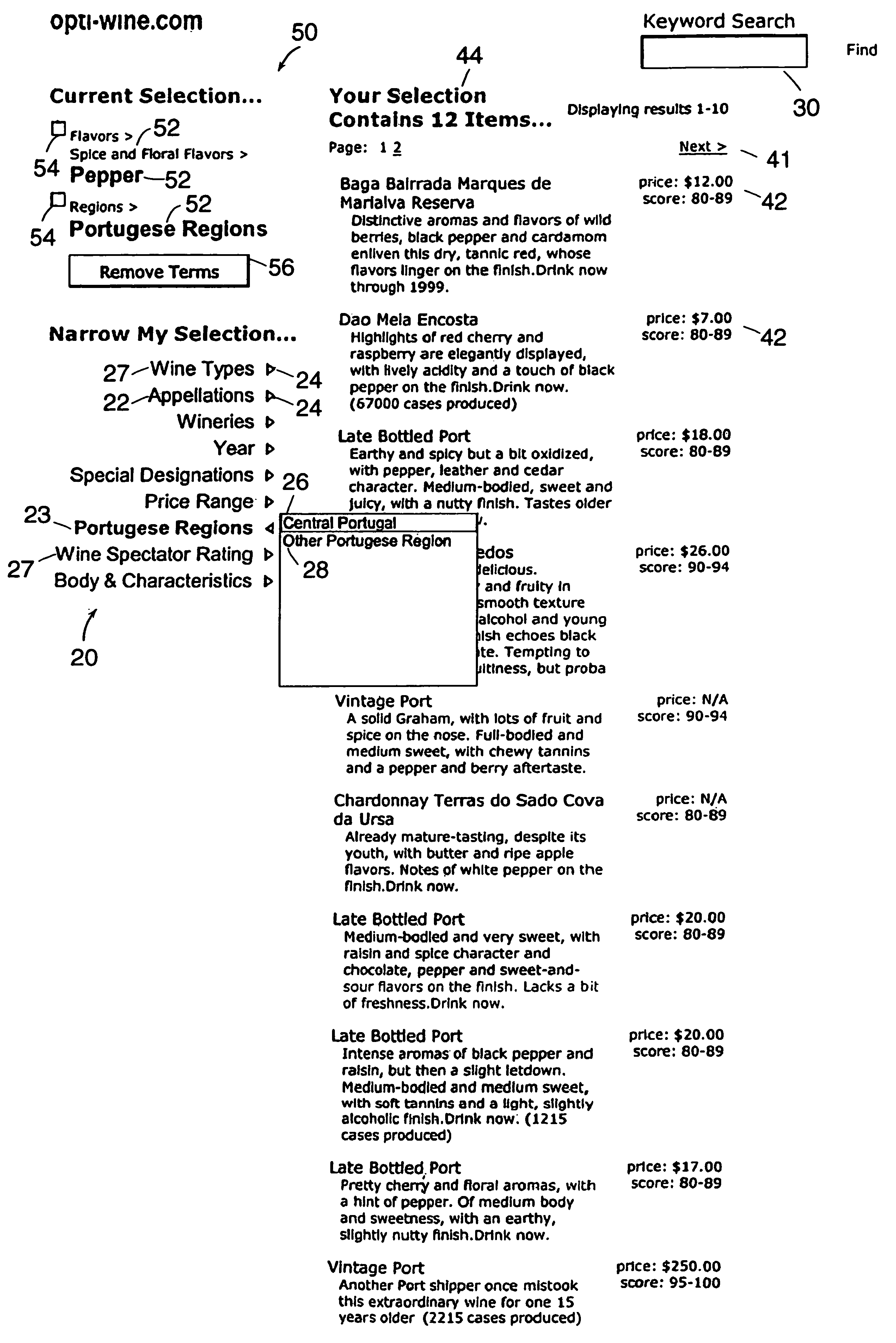
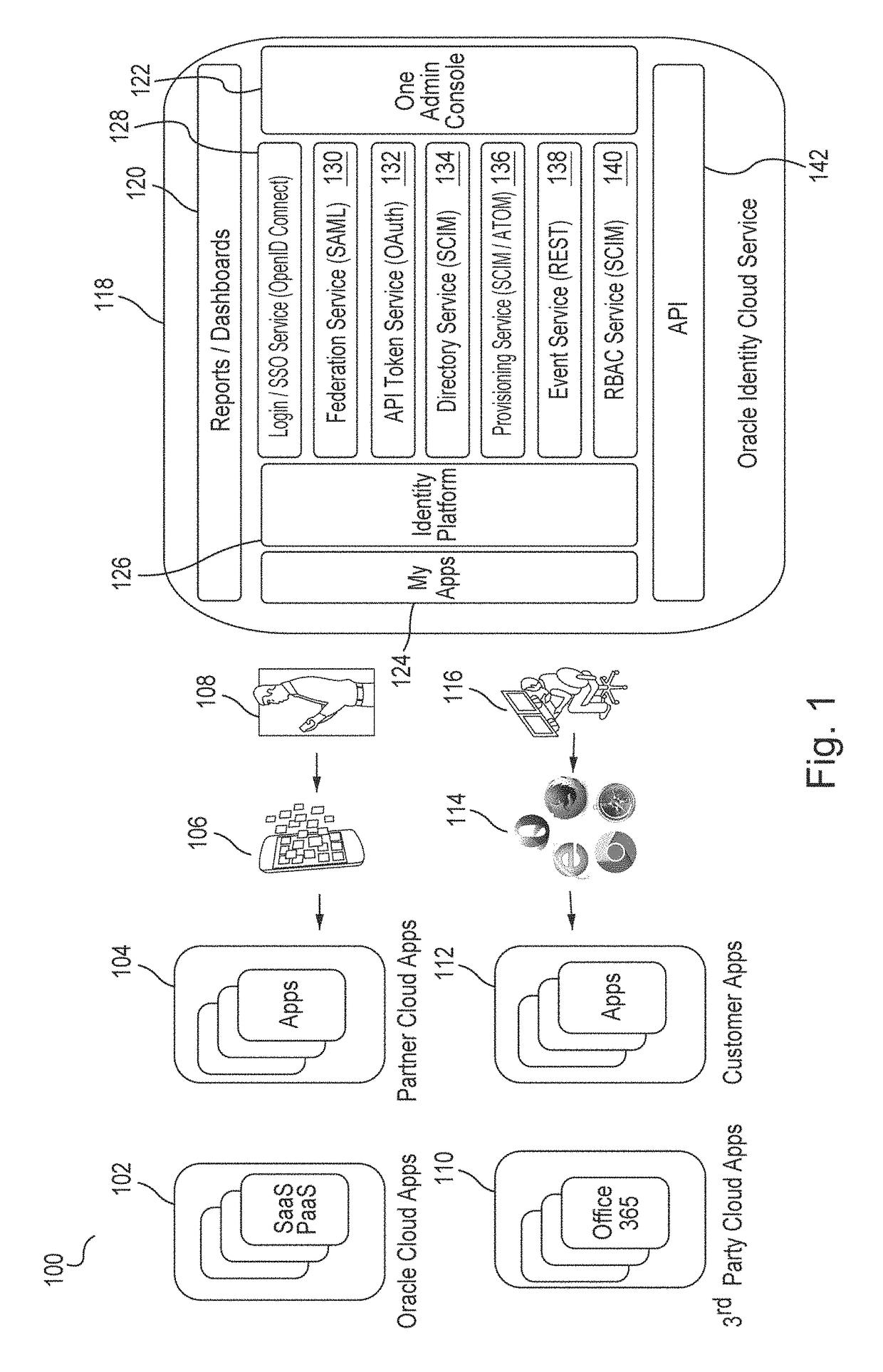
System and method for manipulating content in a hierarchical data-driven search and navigation system
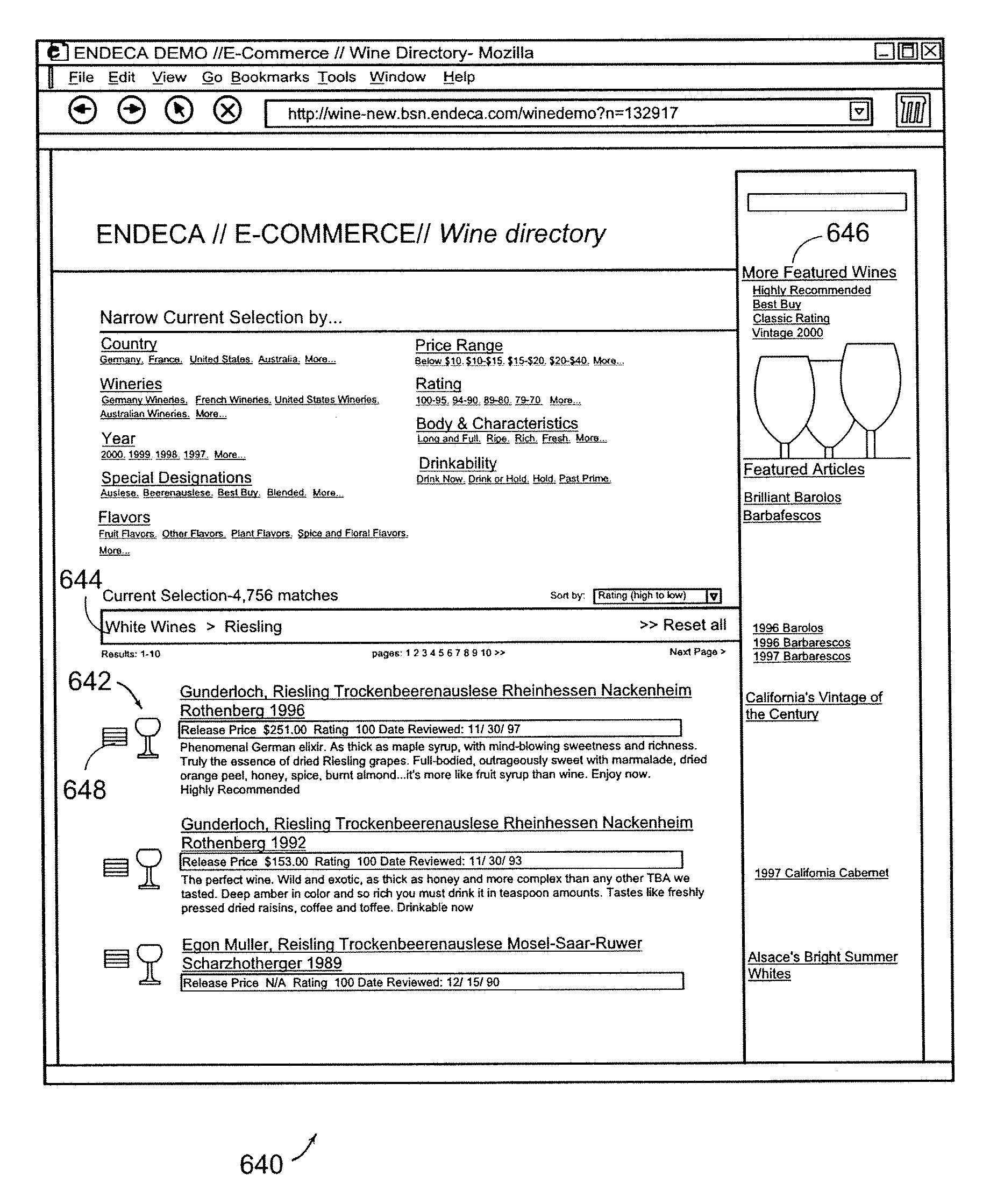
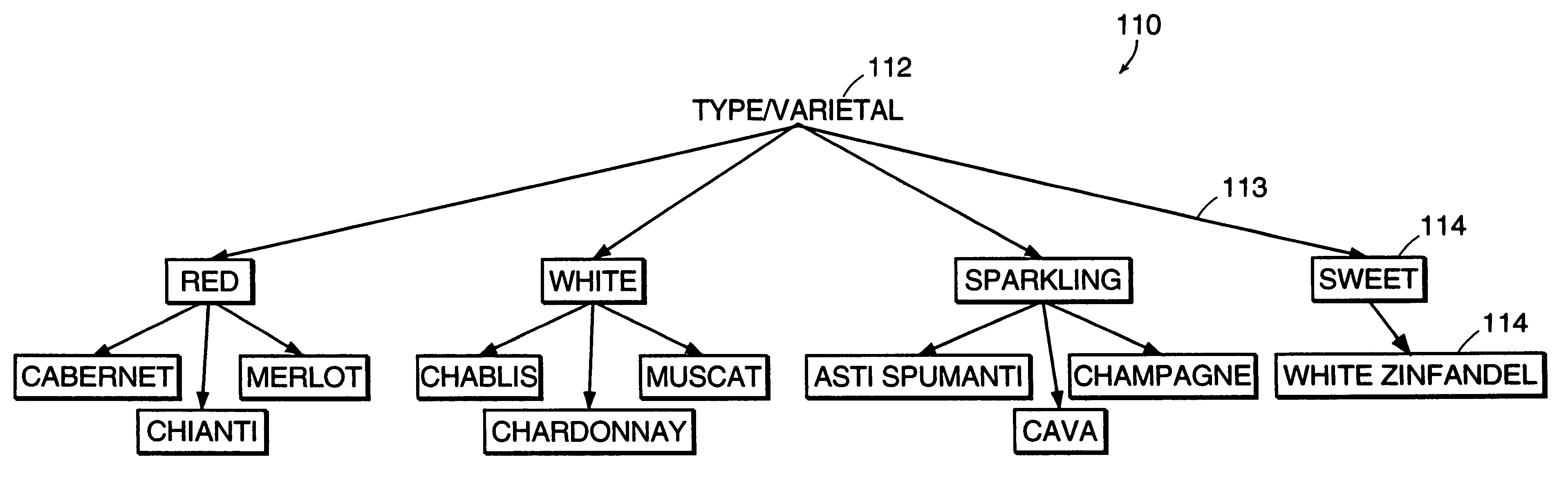
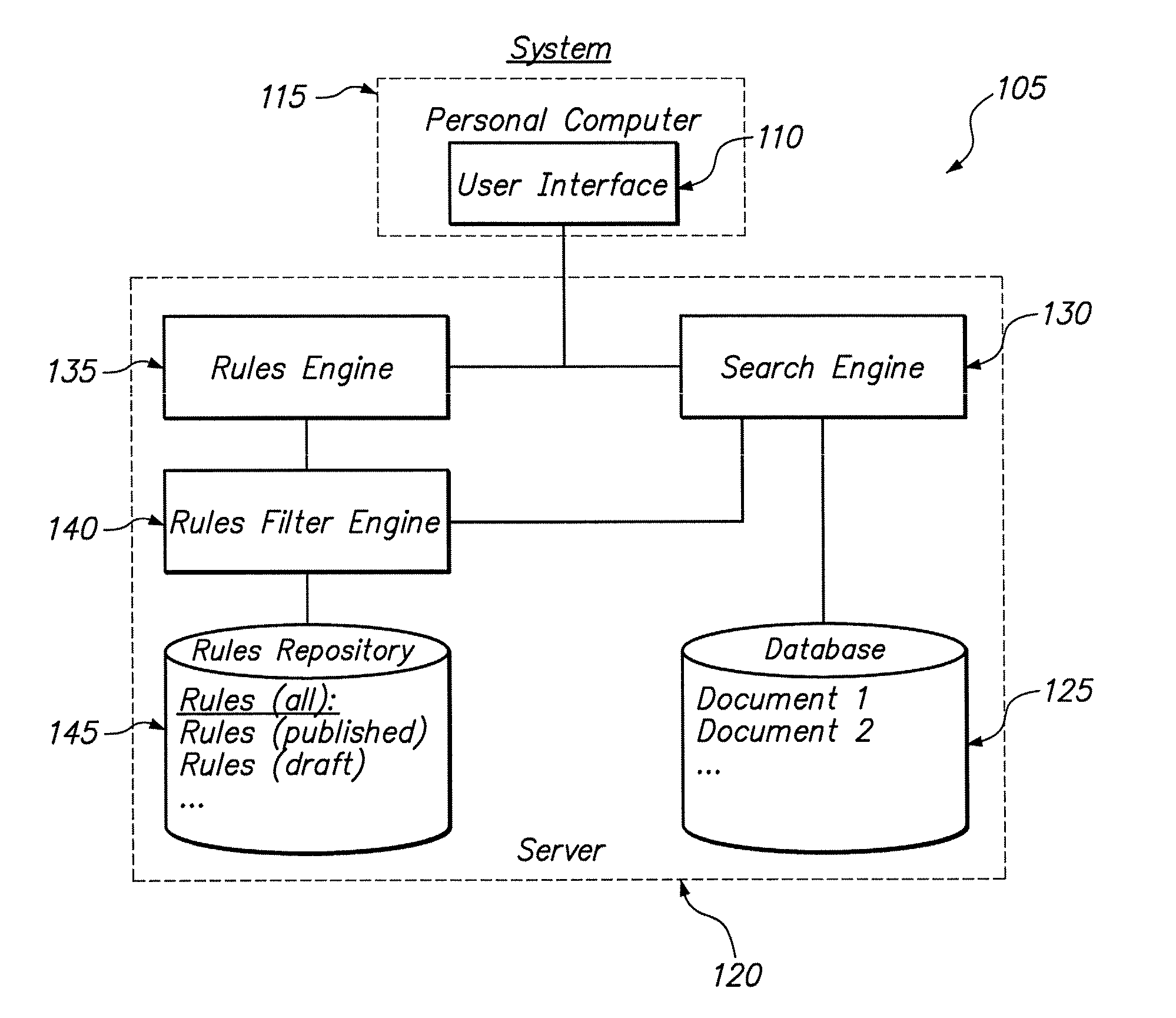
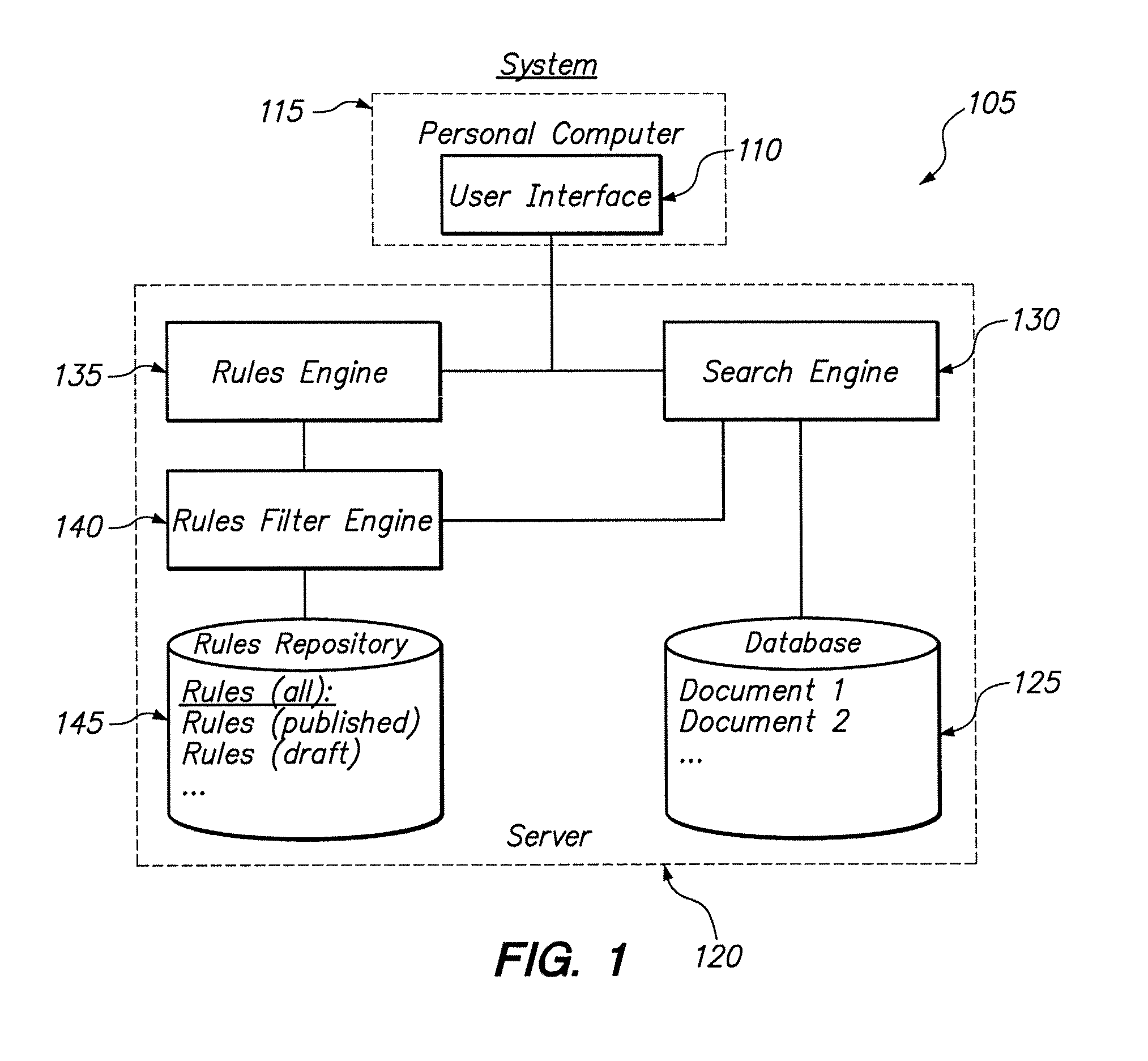
A data-driven, hierarchical information search and navigation system and method enable search and navigation of sets of materials by certain common attributes that characterize the materials. A rules engine provides for manipulation of the content displayed to the user based on the query entered by the user. The rules engine includes one or more rules with a trigger and an action. The action of a rule is performed only if the trigger is satisfied. A trigger may be specified in terms of expressions of attribute-value pairs and is evaluated against a given query or navigation state. The actions can include various techniques for content manipulation, such as supplementing content, rendering content in a particular way, and sorting content in a particular way. An action may be specified in terms of navigation states. The rules engine may include a script for processing the rules.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY
Hierarchical data-driven search and navigation system and method for information retrieval
InactiveUS7062483B2Maximize efficiencyHighly scalable, hierarchical, data-drivenData processing applicationsWeb data navigationDocument preparationApplication software
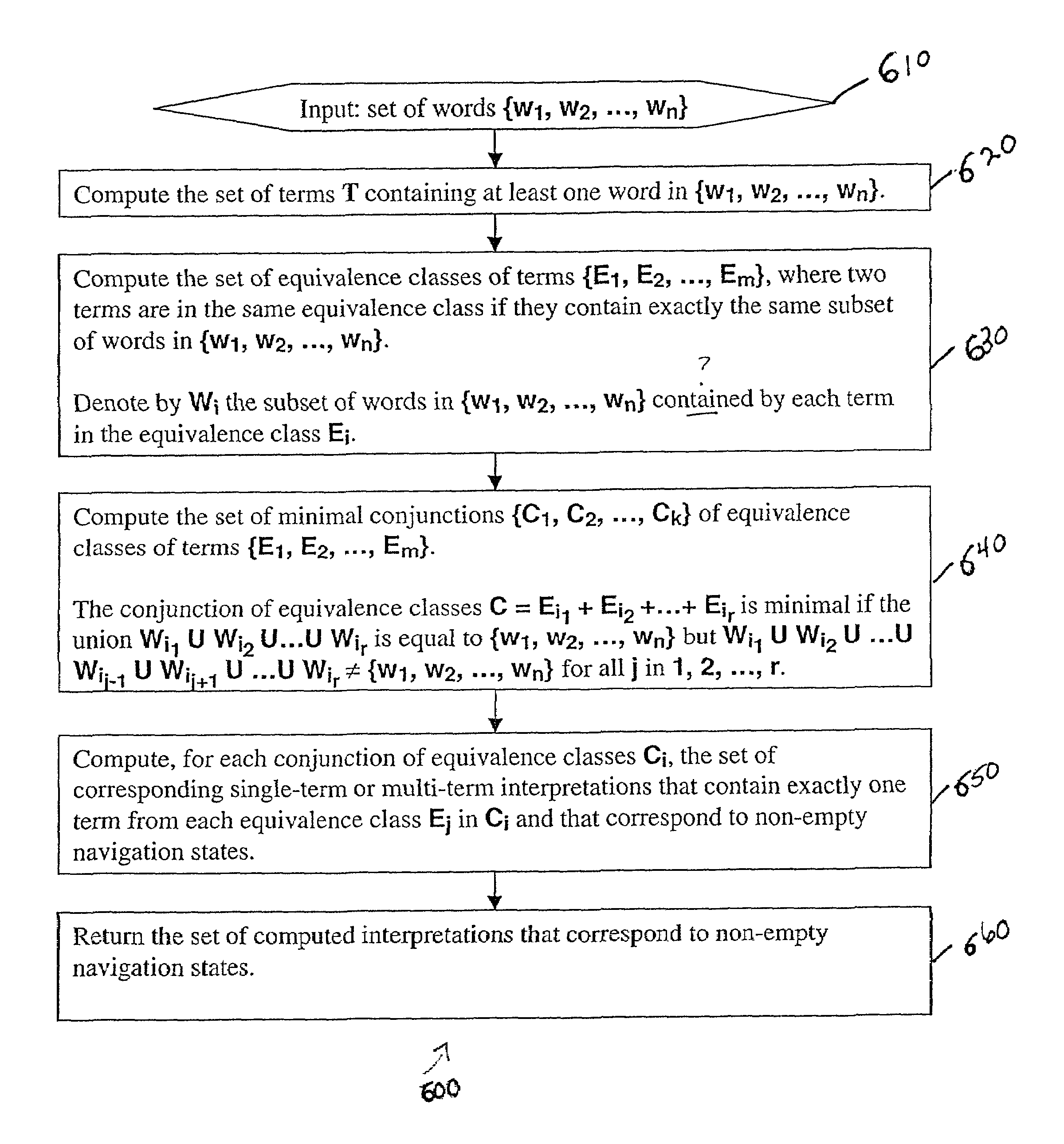
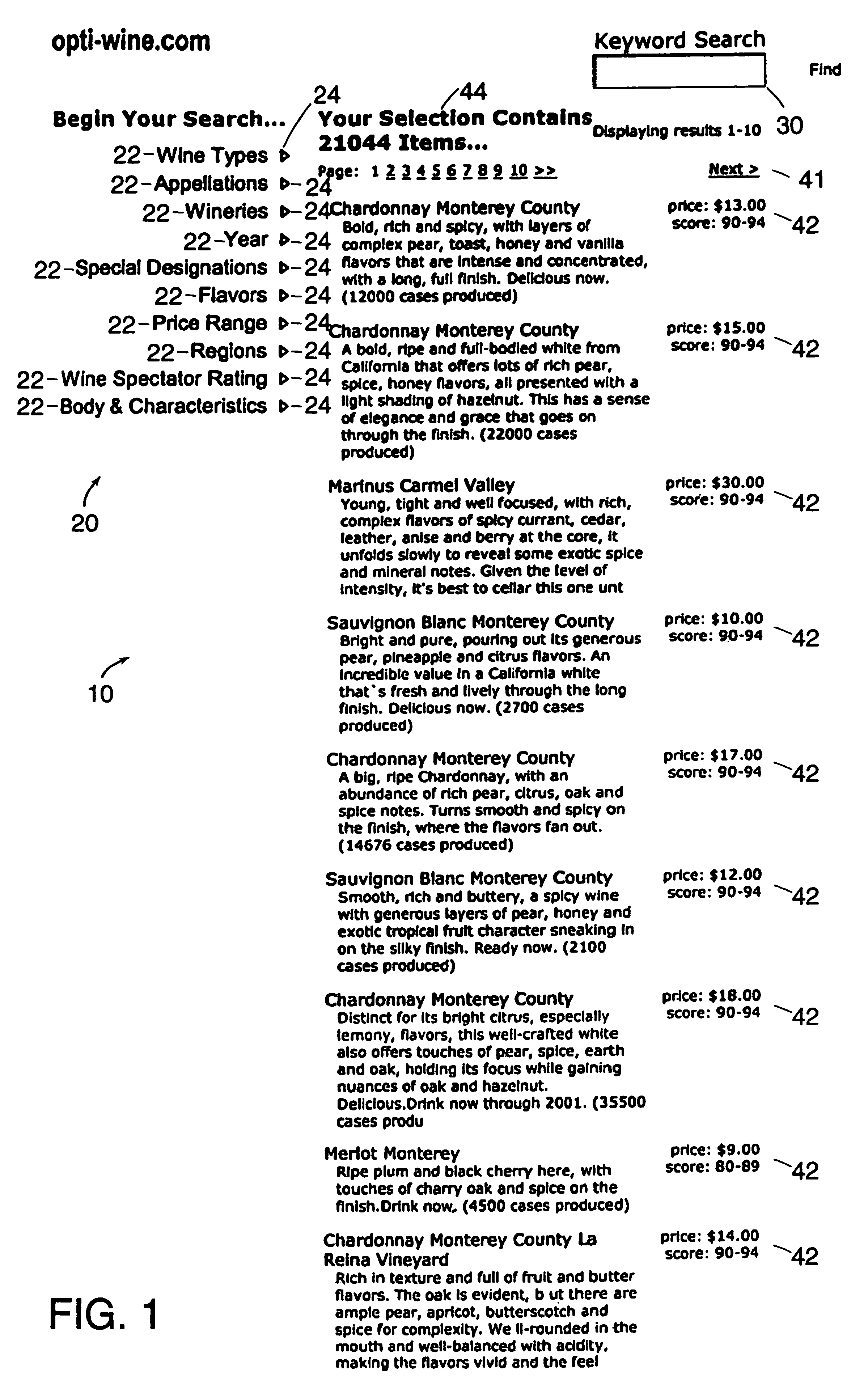
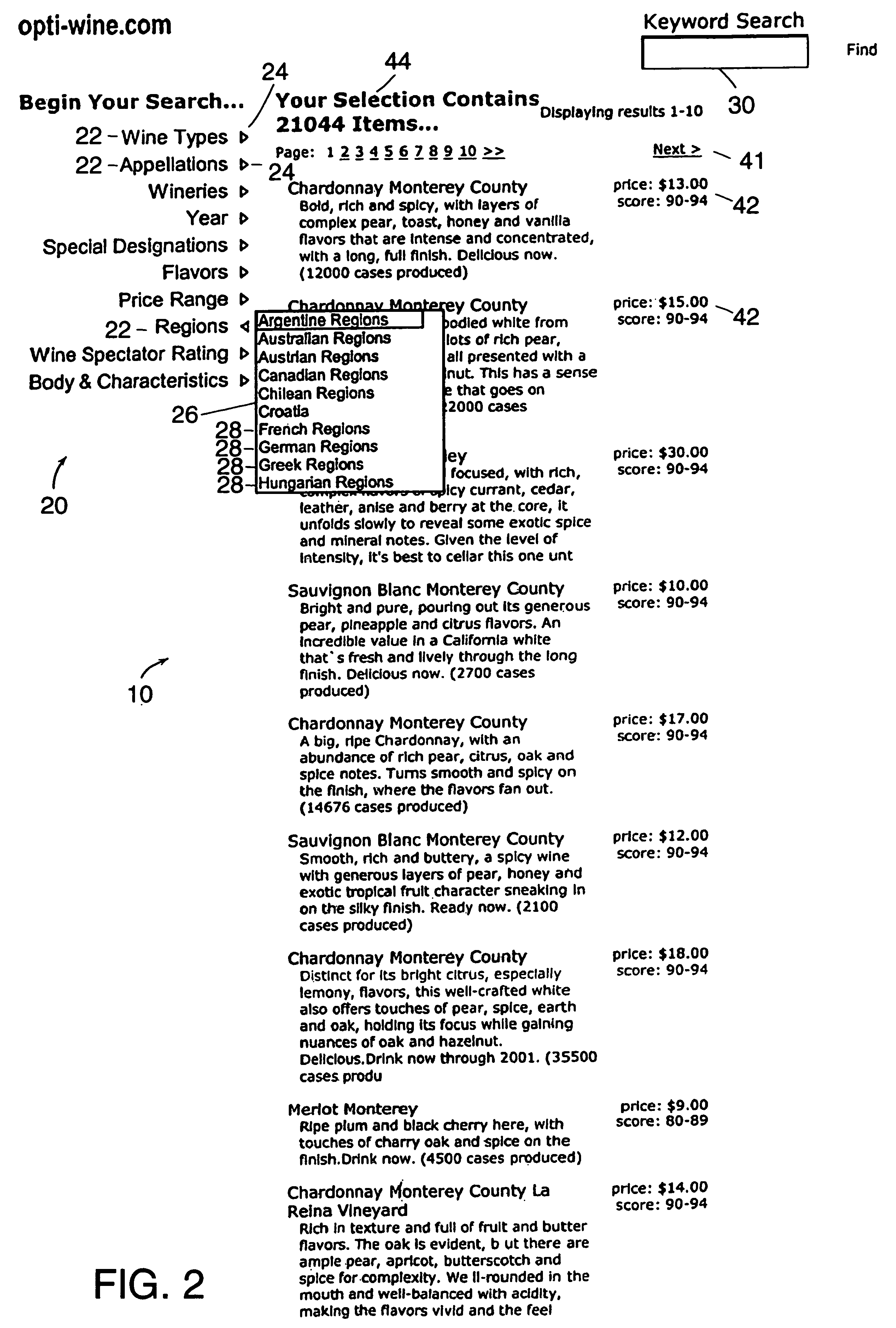
A data-driven, hierarchical information search and navigation system and method enable search and navigation of sets of documents or other materials by certain common attributes that characterize the materials. The invention includes several aspects of a data-driven, hierarchical search and navigation system that employs this search and navigation mode. The search and navigation system of the present invention includes features of an navigation interface, a search interface, a knowledge base and a taxonomy definition process and a classification process for generating the knowledge base, a graph-based navigable data structure and method for generating the data structure, World Wide Web-based applications of the system, and methods of implementing the system. Users are able to search or browse a particular collection of documents by selecting desired values for the attributes or by searching the attribute-value pairs. A data-driven, hierarchical information search and navigation system and method enable this navigation mode by associating terms with the materials, defining a set of hierarchical relationships among the terms, providing a guided navigation mechanism based on the relationship between the terms, and providing a search mechanism that can respond to free-text queries with single-term or multi-term interpretations. In another aspect of the invention, implementations of the invention may be scalable through parallel or distributed computation.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY
System & method for creating, editing, an on-line publication
InactiveUS20030204814A1Natural language data processingWebsite content managementQuery stringComputation process
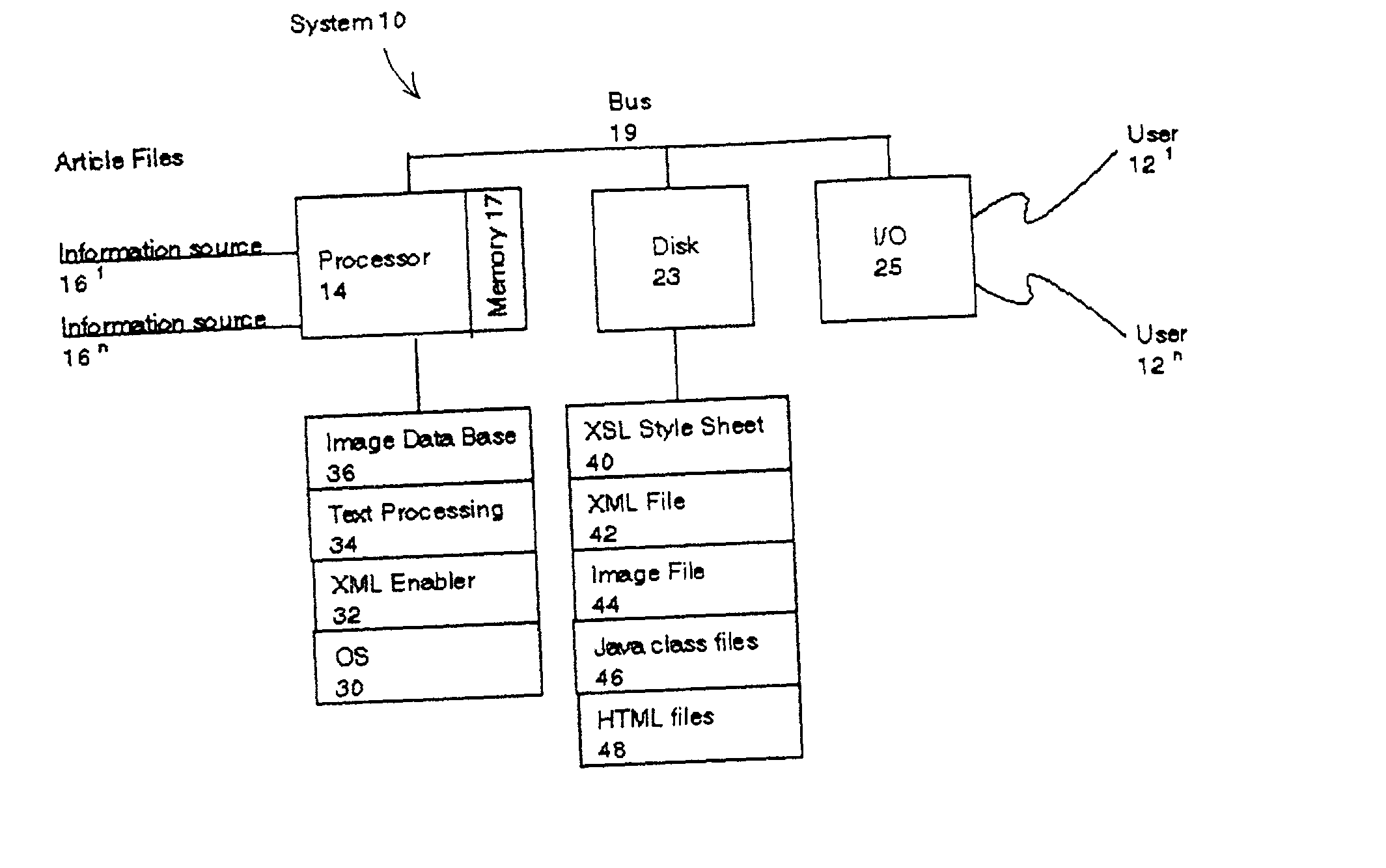
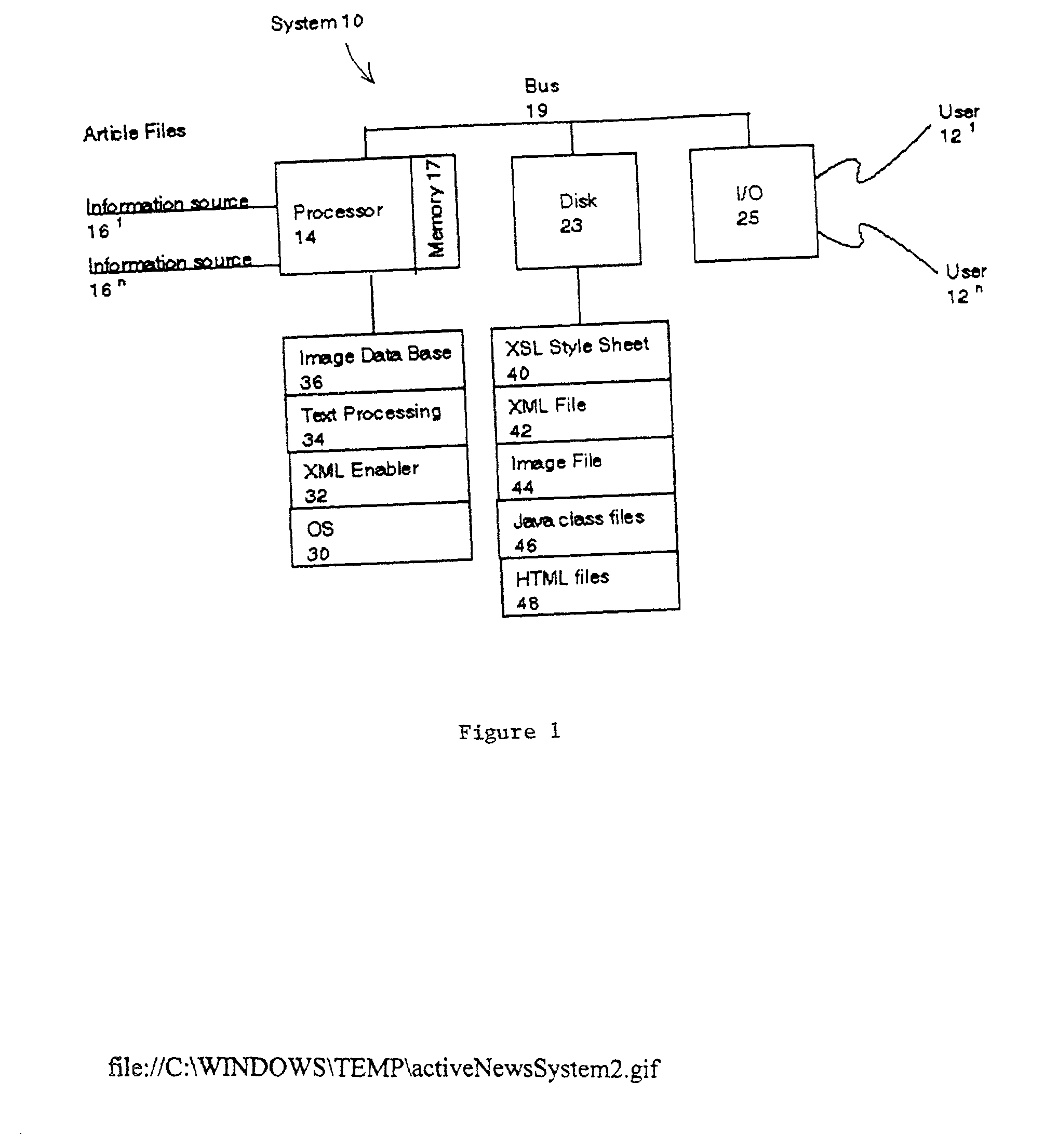
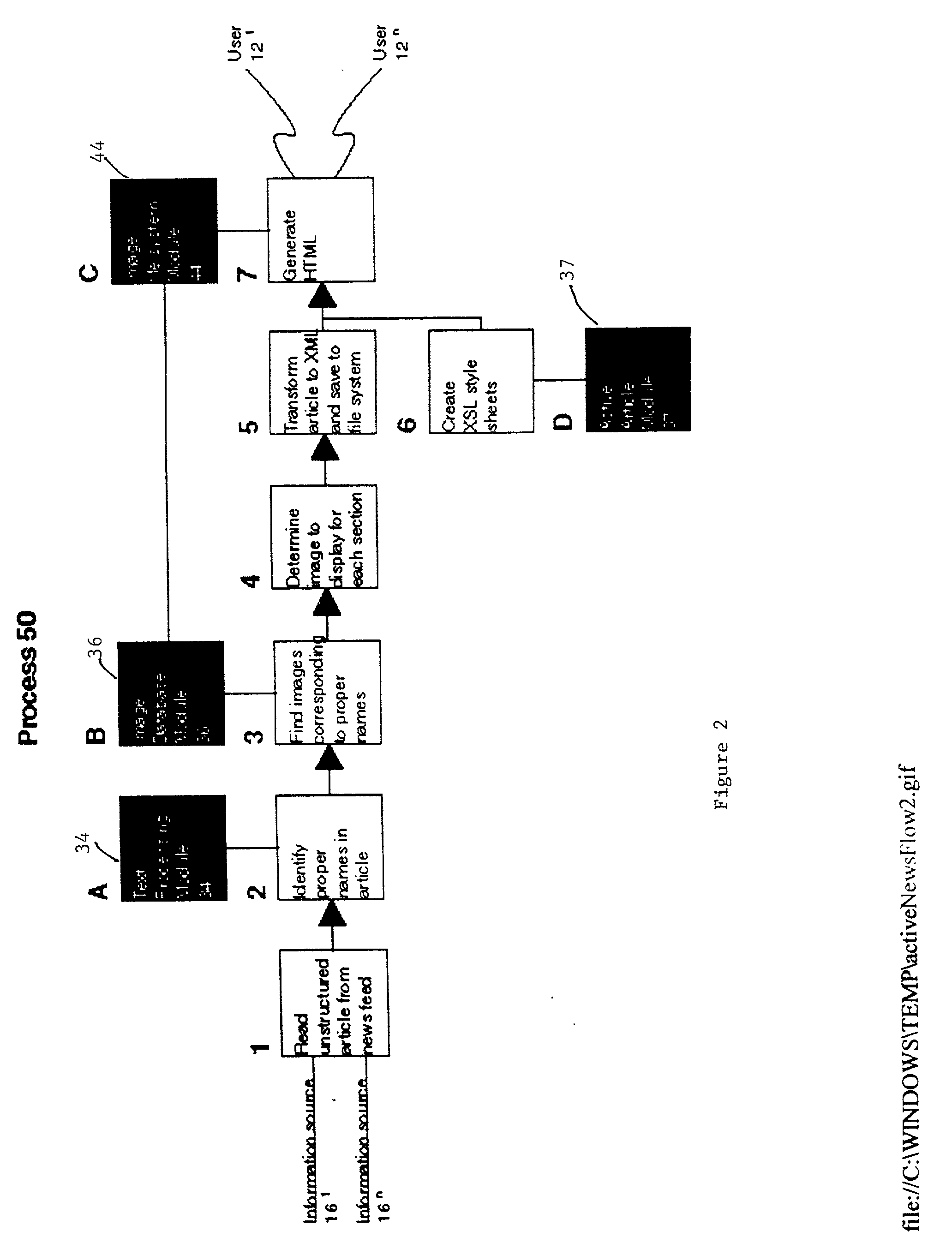
A system and method automatically generate an on-line document from raw text into an engaging, interactive form for a plurality of viewers. Unstructured articles are read from an information feed. A computation process extracts and tags proper names of people, products, organizations, and places and categorizes them. An image database is used to link these proper names with image files. The image database consists of a series of attribute-value pairs for active searching of names. A URL query string is inputted to the database to extract the location of the image in the database file system. An Extensible Markup Language (XML) file is created from the raw text of the article, the list of proper names in the processed data and the image file references. The XML file is stored in a file system. An Extensible Stylesheet Language (XSL) file provides templates containing computational relationships between the text and images. The XML and XSL style sheets are combined to generate a Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) file containing an on-line story of the unstructured articles in a Java Applet which allows the system to provide a variety of interactive behaviors for a final presentation available by a viewer from a browser.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for manipulating content in a hierarchical data-driven search and navigation system
A data-driven, hierarchical information search and navigation system and method enable search and navigation of sets of materials by certain common attributes that characterize the materials. A rules engine provides for manipulation of the content displayed to the user based on the query entered by the user. The rules engine includes one or more rules with a trigger and an action. The action of a rule is performed only if the trigger is satisfied. A trigger may be specified in terms of expressions of attribute-value pairs and is evaluated against a given query or navigation state. The actions can include various techniques for content manipulation, such as supplementing content, rendering content in a particular way, and sorting content in a particular way. An action may be specified in terms of navigation states. The rules engine may include a script for processing the rules.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY
Hierarchical data-driven search and navigation system and method for information retrieval
InactiveUS20070083505A1Highly scalable, hierarchical, data-drivenGood conditionData processing applicationsWeb data navigationPaper documentNavigation system
A data-driven, hierarchical information search and navigation system and method enable search and navigation of sets of documents or other materials by certain common attributes that characterize the materials. The invention includes several aspects of a data-driven, hierarchical search and navigation system that employs this search and navigation mode. The search and navigation system of the present invention includes features of an navigation interface, a search interface, a knowledge base and a taxonomy definition process and a classification process for generating the knowledge base, a graph-based navigable data structure and method for generating the data structure, World Wide Web-based applications of the system, and methods of implementing the system. Users are able to search or browse a particular collection of documents by selecting desired values for the attributes or by searching the attribute-value pairs. A data-driven, hierarchical information search and navigation system and method enable this navigation mode by associating terms with the materials, defining a set of hierarchical relationships among the terms, providing a guided navigation mechanism based on the relationship between the terms, and providing a search mechanism that can respond to free-text queries with single-term or multi-term interpretations. In another aspect of the invention, implementations of the invention may be scalable through parallel or distributed computation.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY
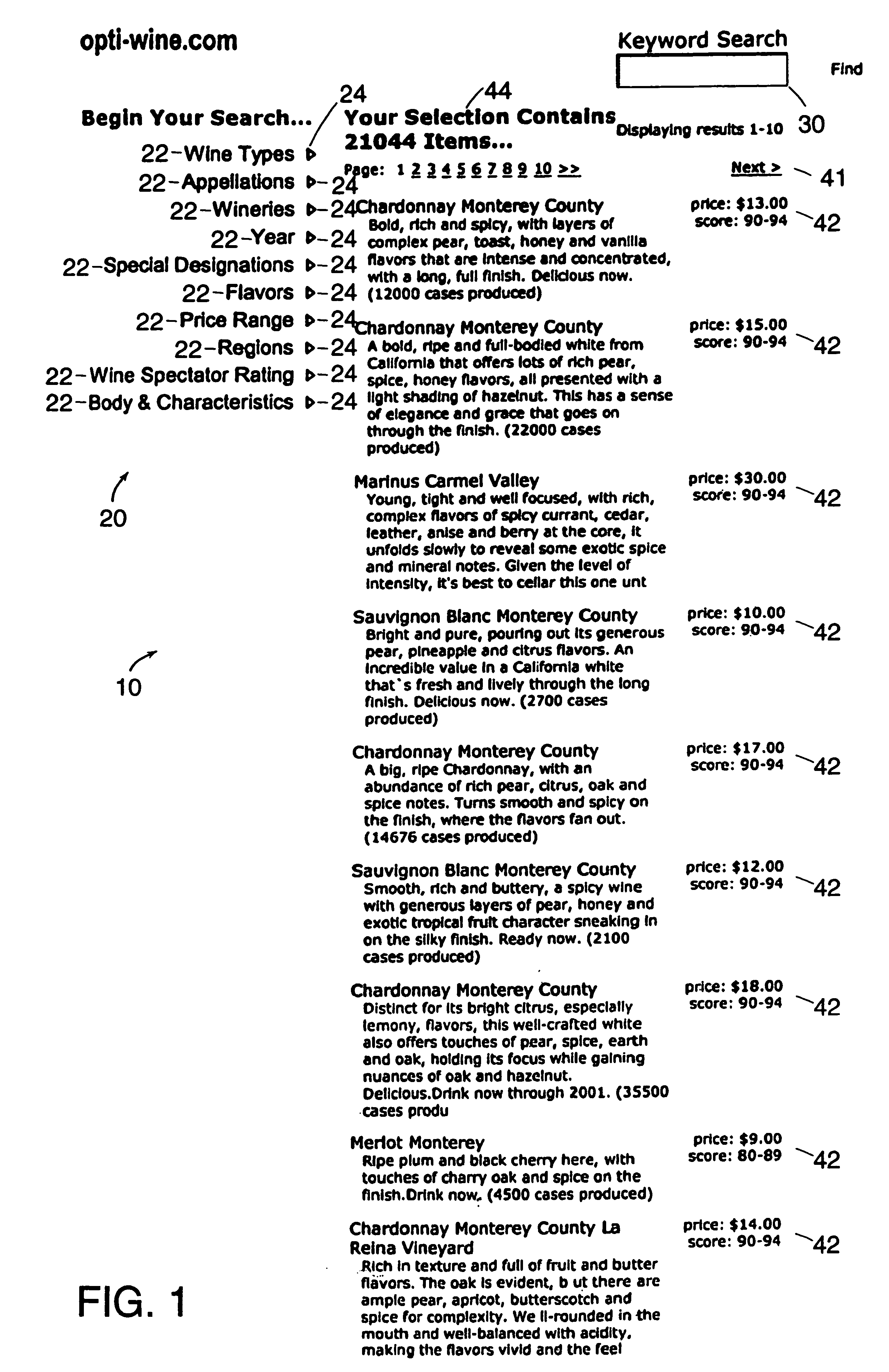
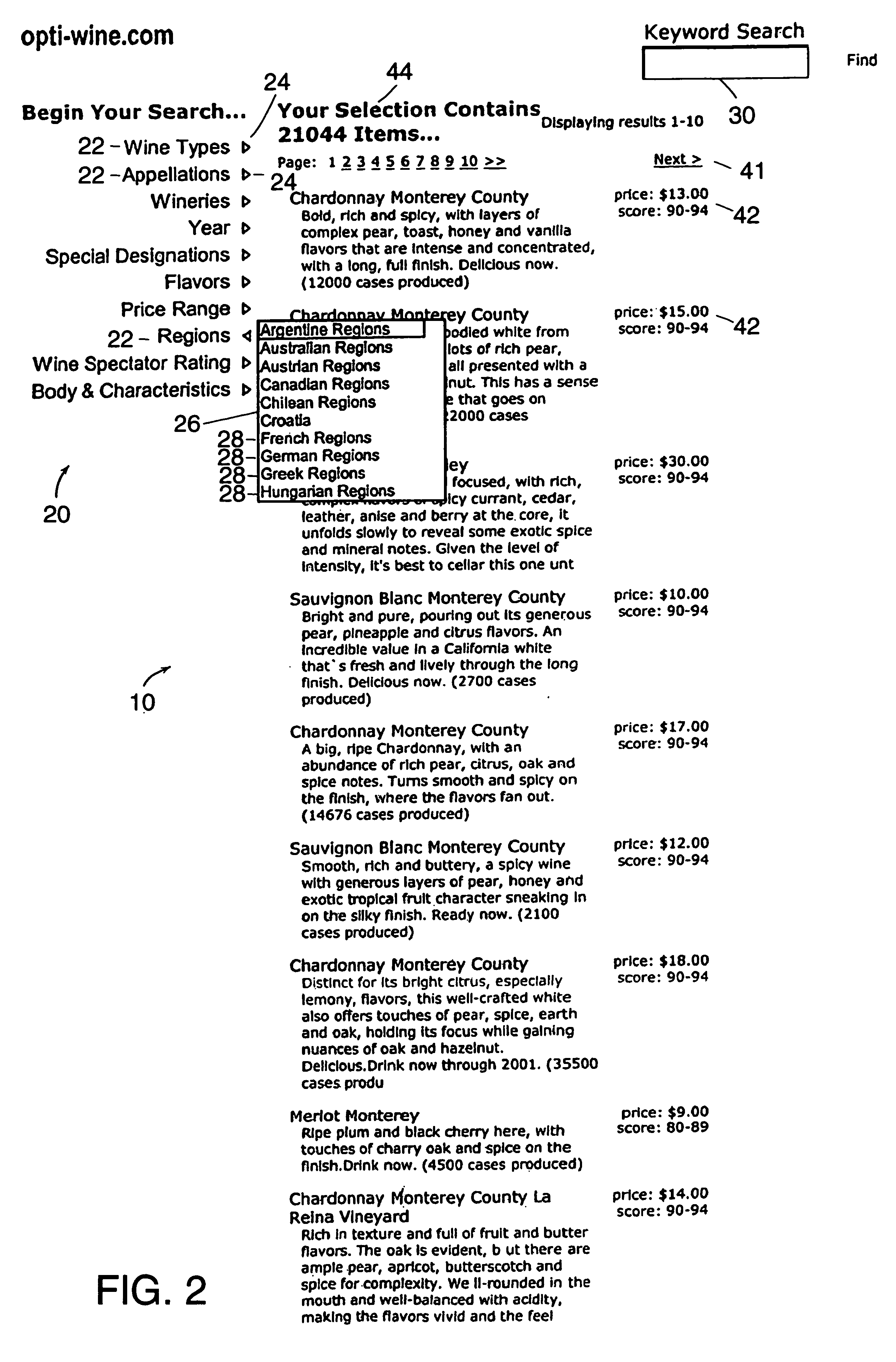
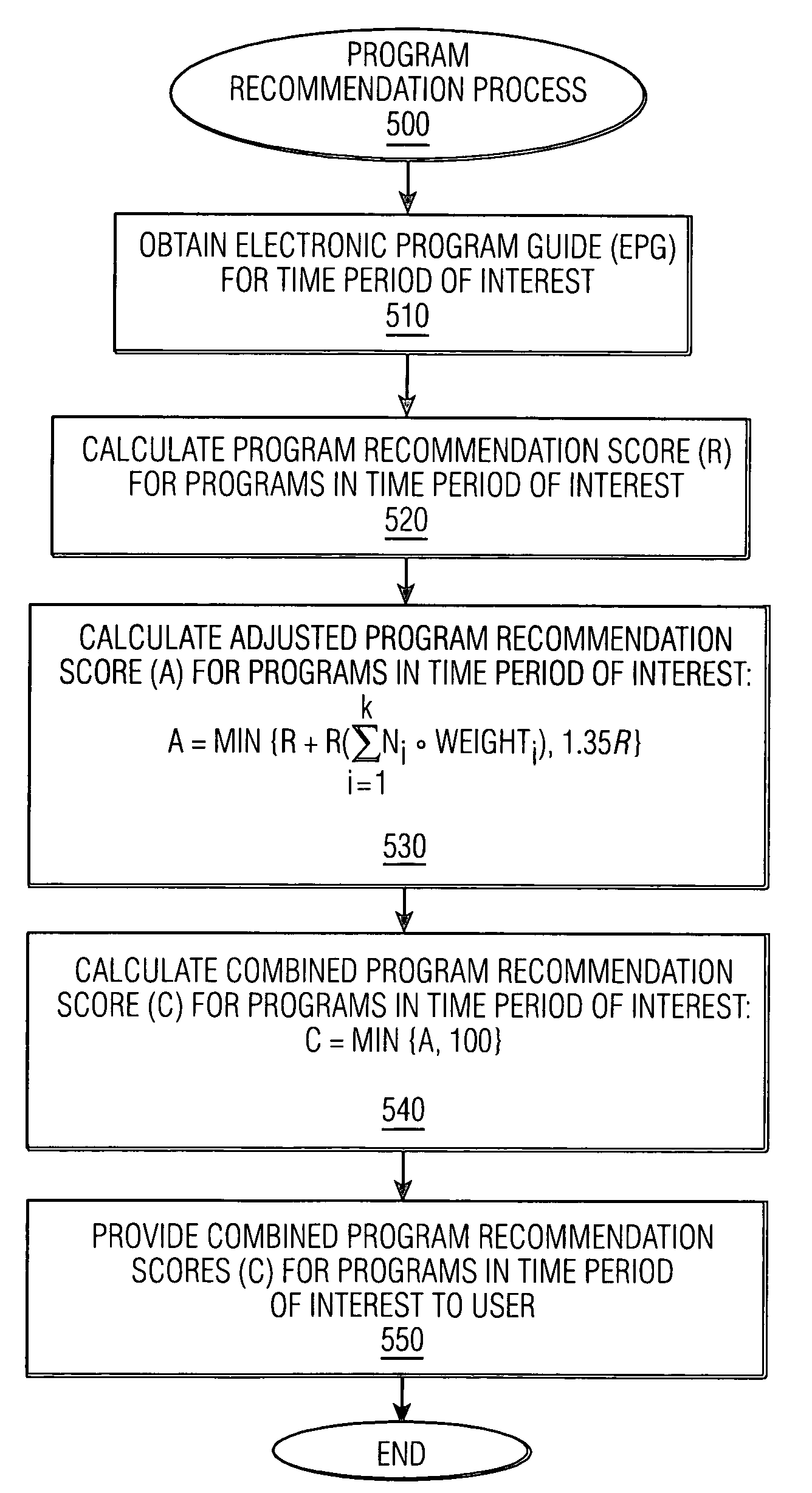
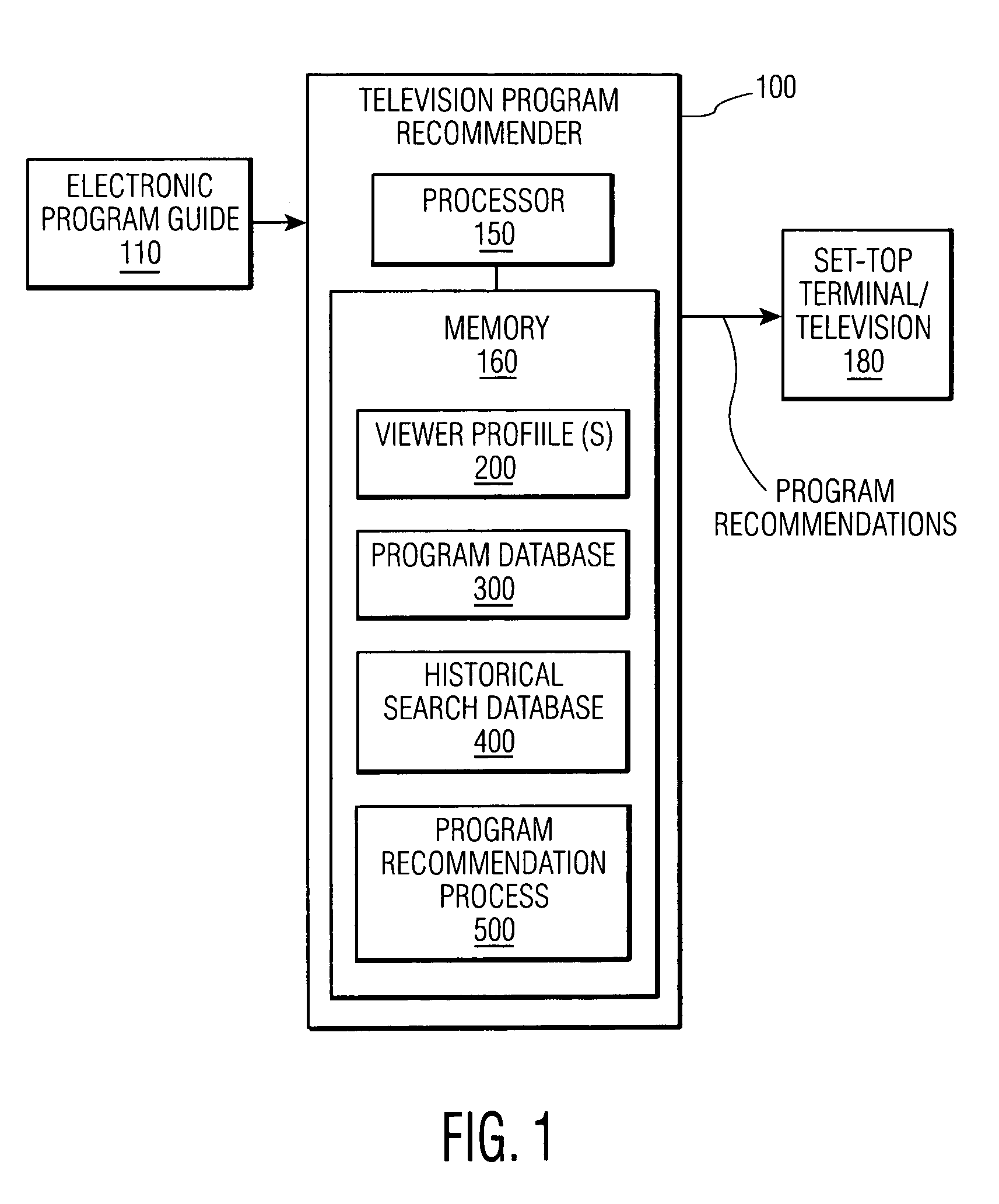
Method and apparatus for generating television program recommendations based on prior queries
ActiveUS7581237B1Television system detailsBroadcast with distributionComputer scienceElectronic program guide
A method and apparatus are disclosed that generate television program recommendations based on queries that have previously been performed by a user on an electronic program guide. A conventional program recommender score for a given program is adjusted according to the degree of correlation between the attribute-value pairs that define the program and the attribute-value pairs that have previously been searched by the user. A historical search database indicates the number of times each attribute-value pair appears in a user query and provides additional information regarding the preferences of the user. Higher frequency counts for certain attribute-value pairs imply the user's preference for programs conforming to such criteria.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
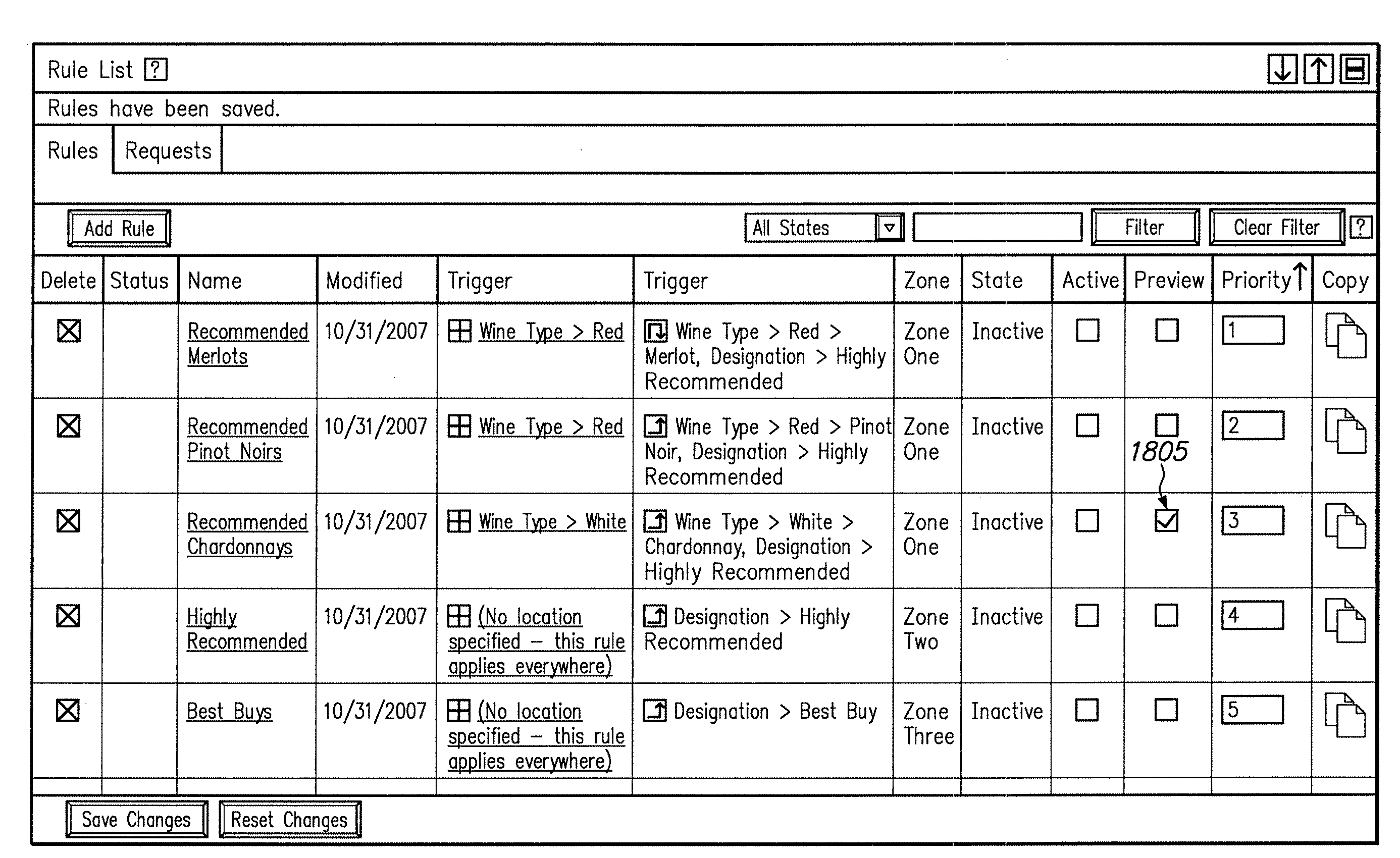
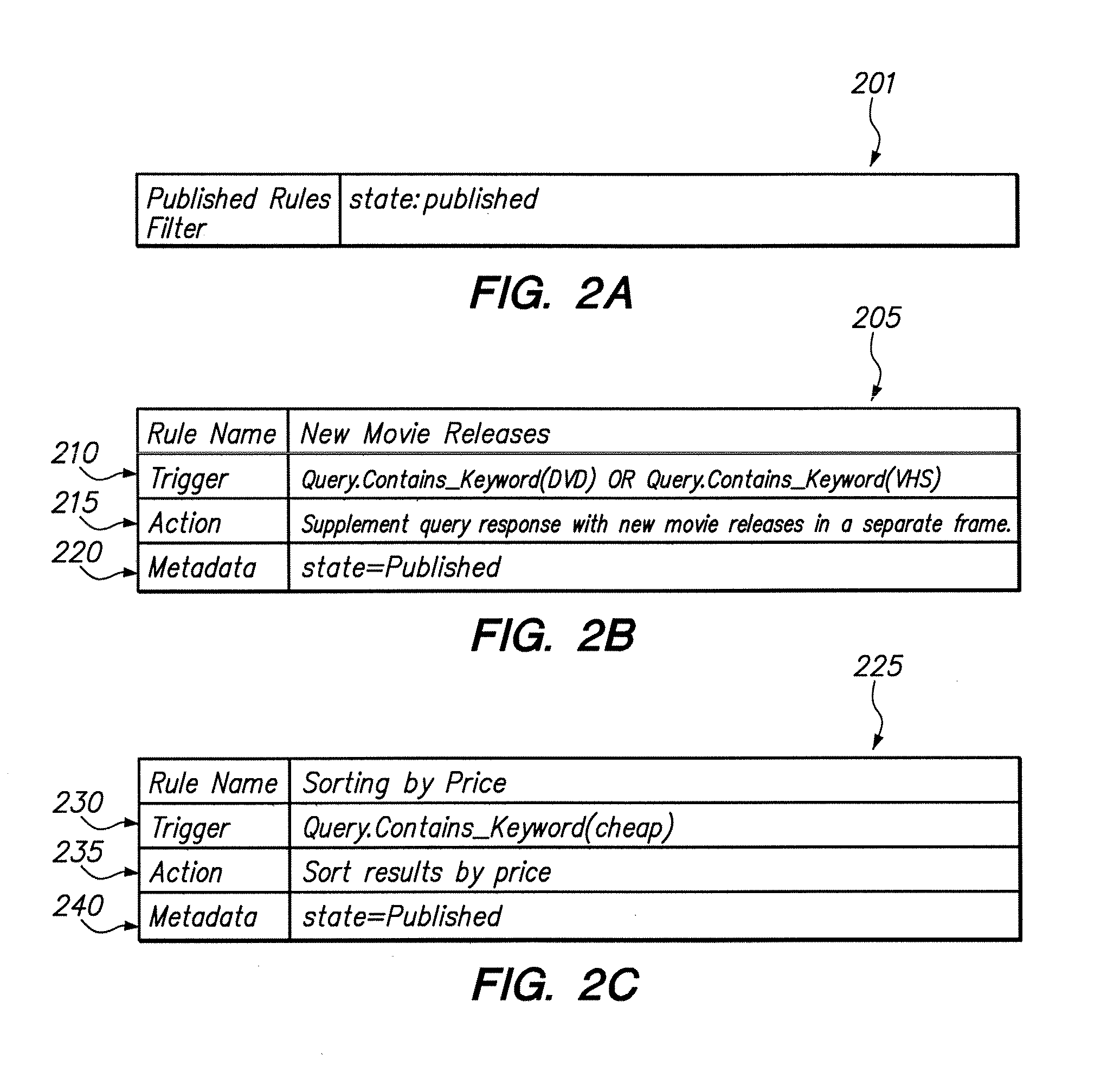
System and method for filtering rules for manipulating search results in a hierarchical search and navigation system
ActiveUS20090125482A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsFiltering rulesNavigation system
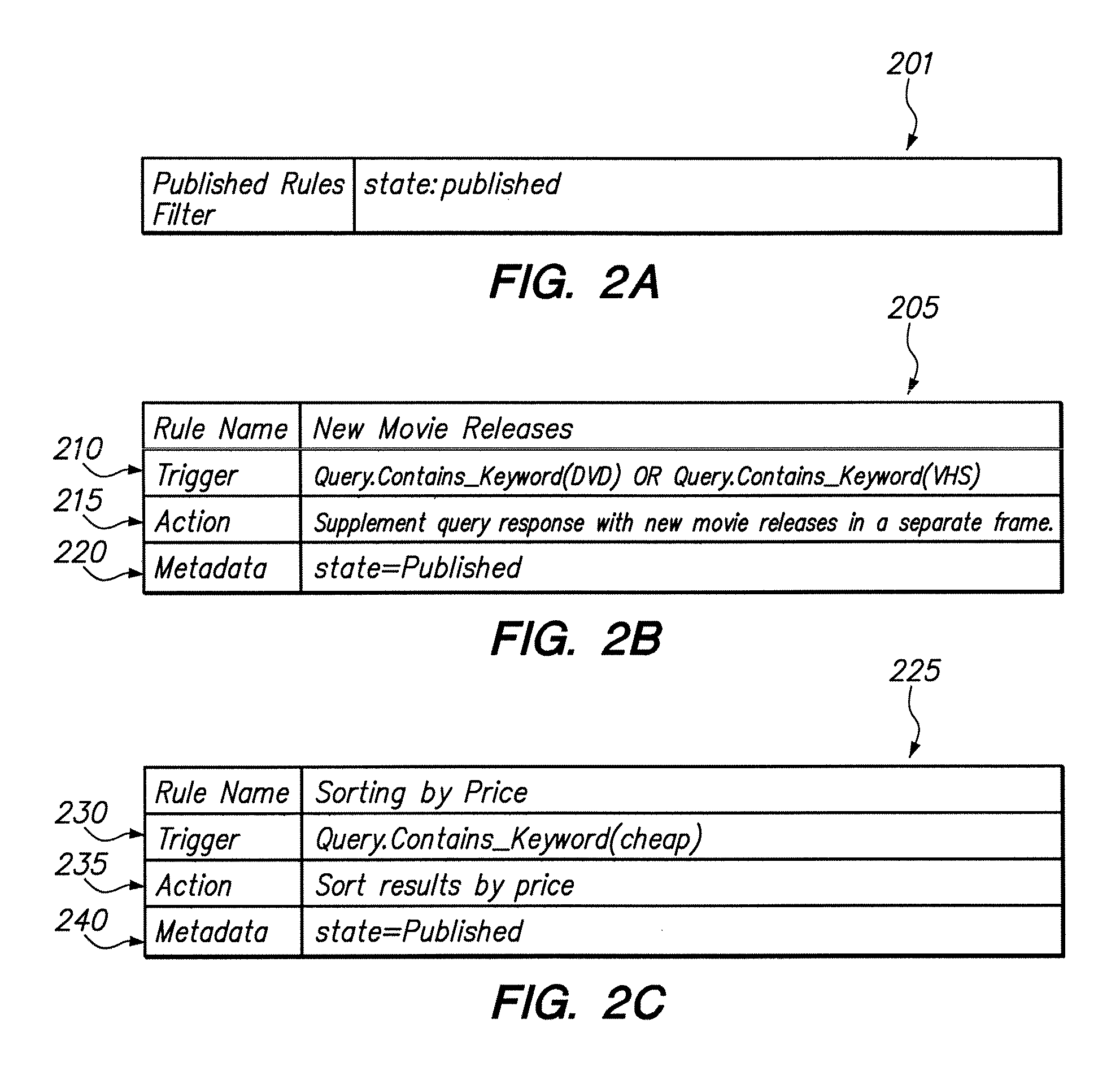
A method is disclosed for modifying the results of a search performed in a collection of items by a search and navigation system. The method includes receiving a query from a user interface and determining a navigation state, defined by expressions of attribute-value pairs, based on the received query. The user interface accepts both selecting and deselecting of any of the attribute-value pairs in an expression corresponding to a navigation state to obtain an expression corresponding to a different navigation state, and each selection and deselection forms a new query. The method further includes retrieving, from the collection, items associated with the navigation state to form a set of unmodified search results, the set of unmodified search results having an arrangement for presentation to the user. A rule filter that includes a metadata expression is applied to a set of rules, each rule having a trigger, an action, and metadata. The application of the rule filter to the set of rules includes evaluating the metadata expression of the rule filter based on the metadata of each rule and passing rules for which the metadata expression of the rule filter evaluates as logical true. The trigger of each rule passed by the rule filter is evaluated, and the action of each rule for which the trigger of the rule evaluates as logical true is executed to modify the unmodified search results to form modified search results.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY
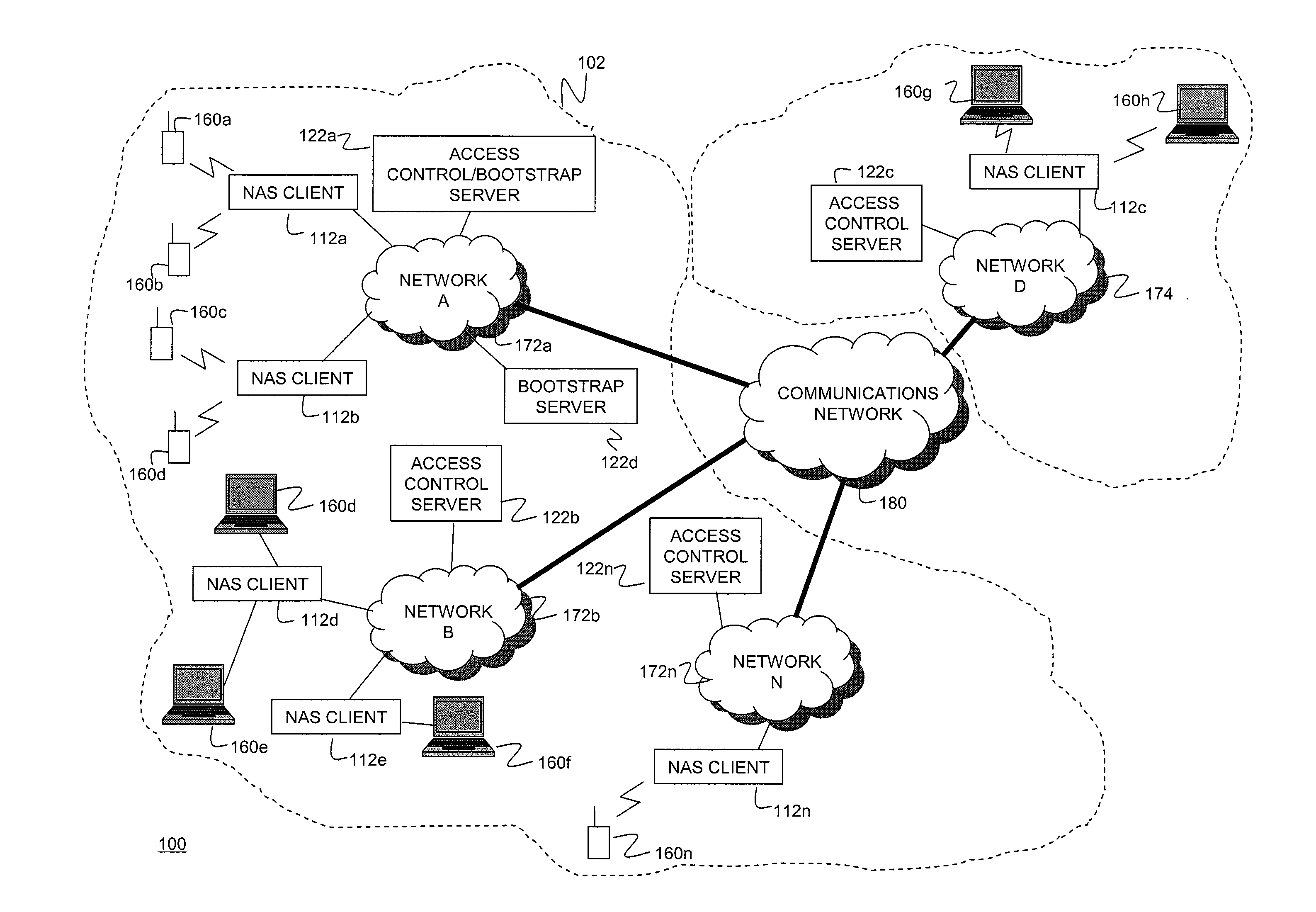
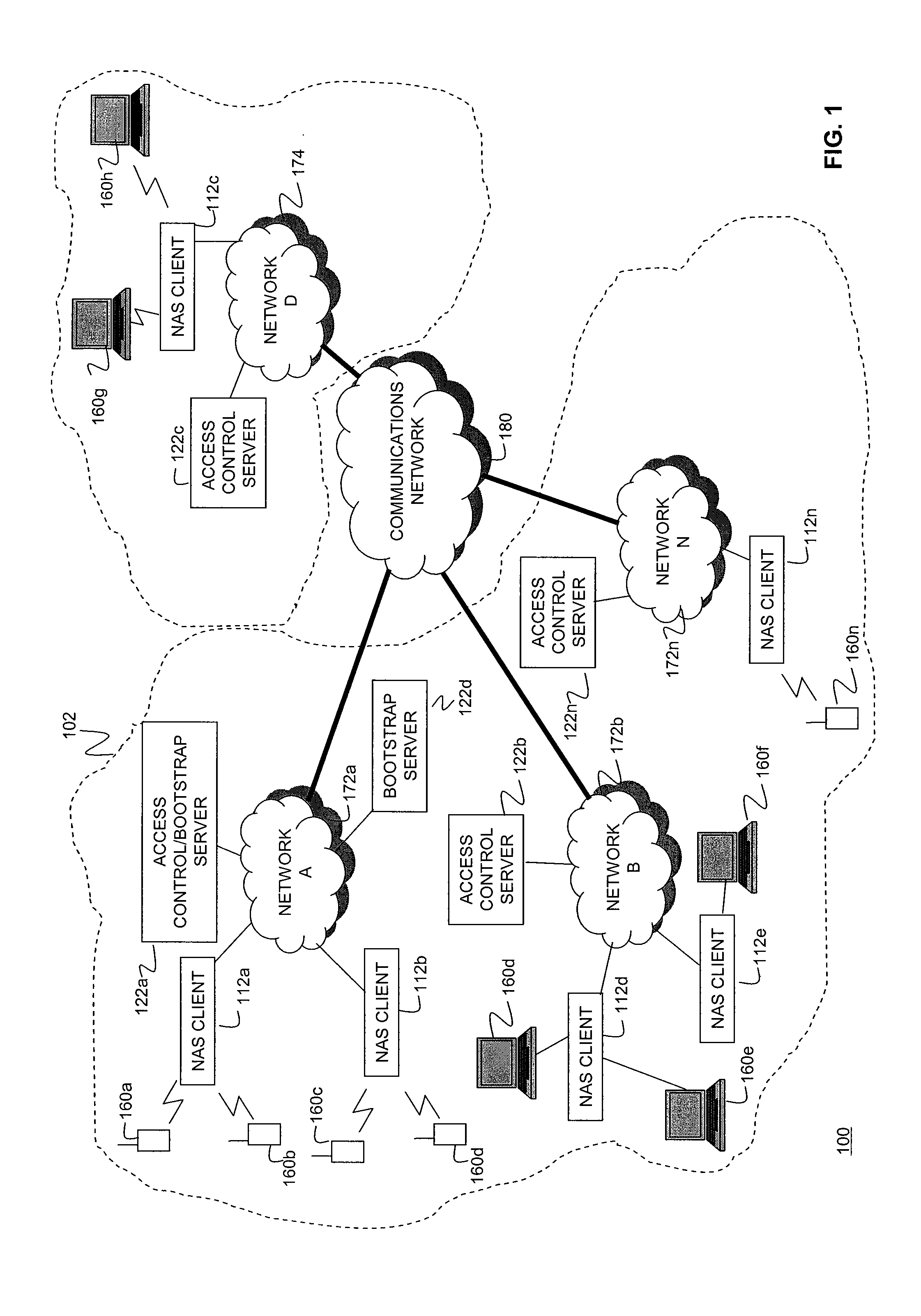
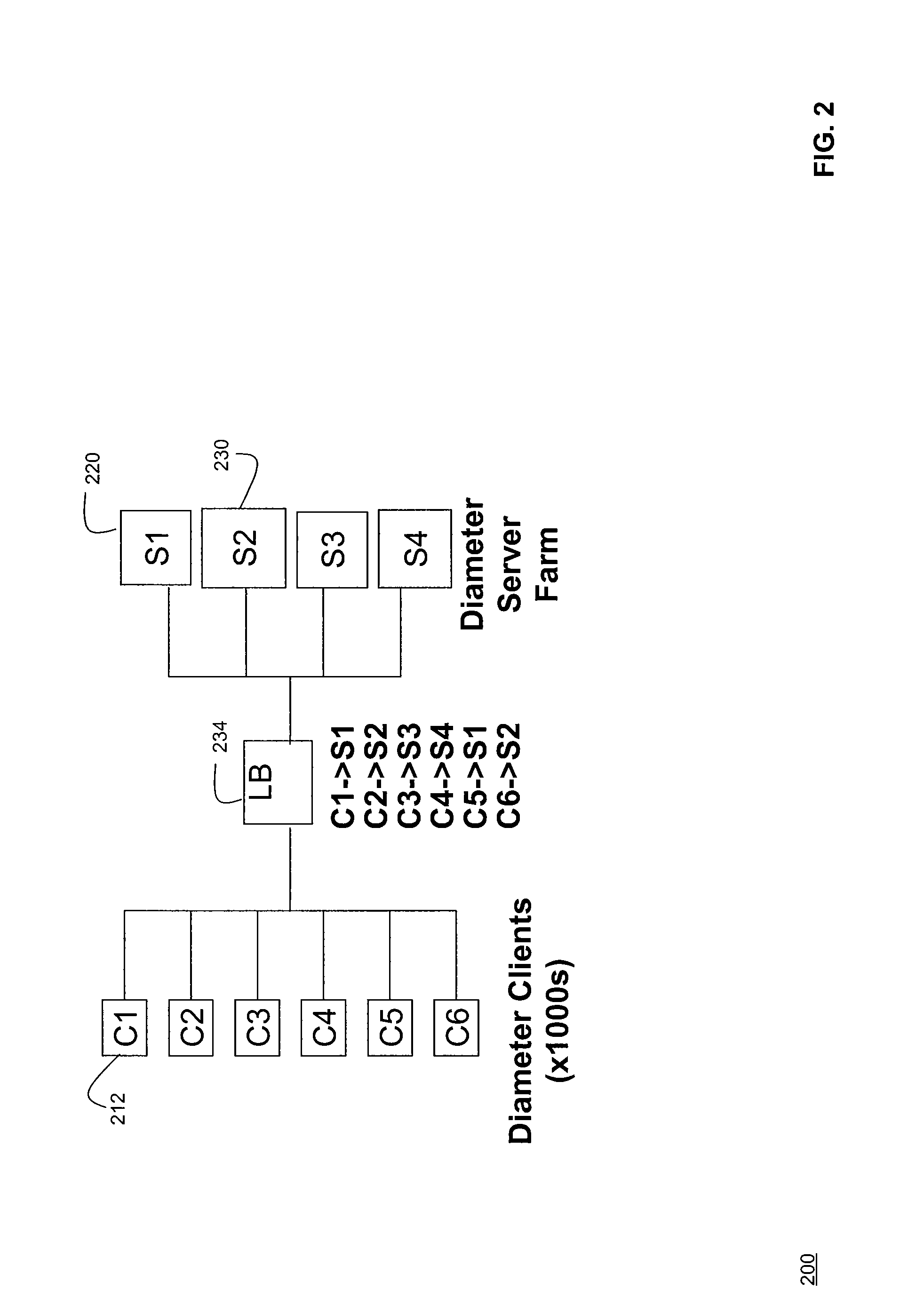
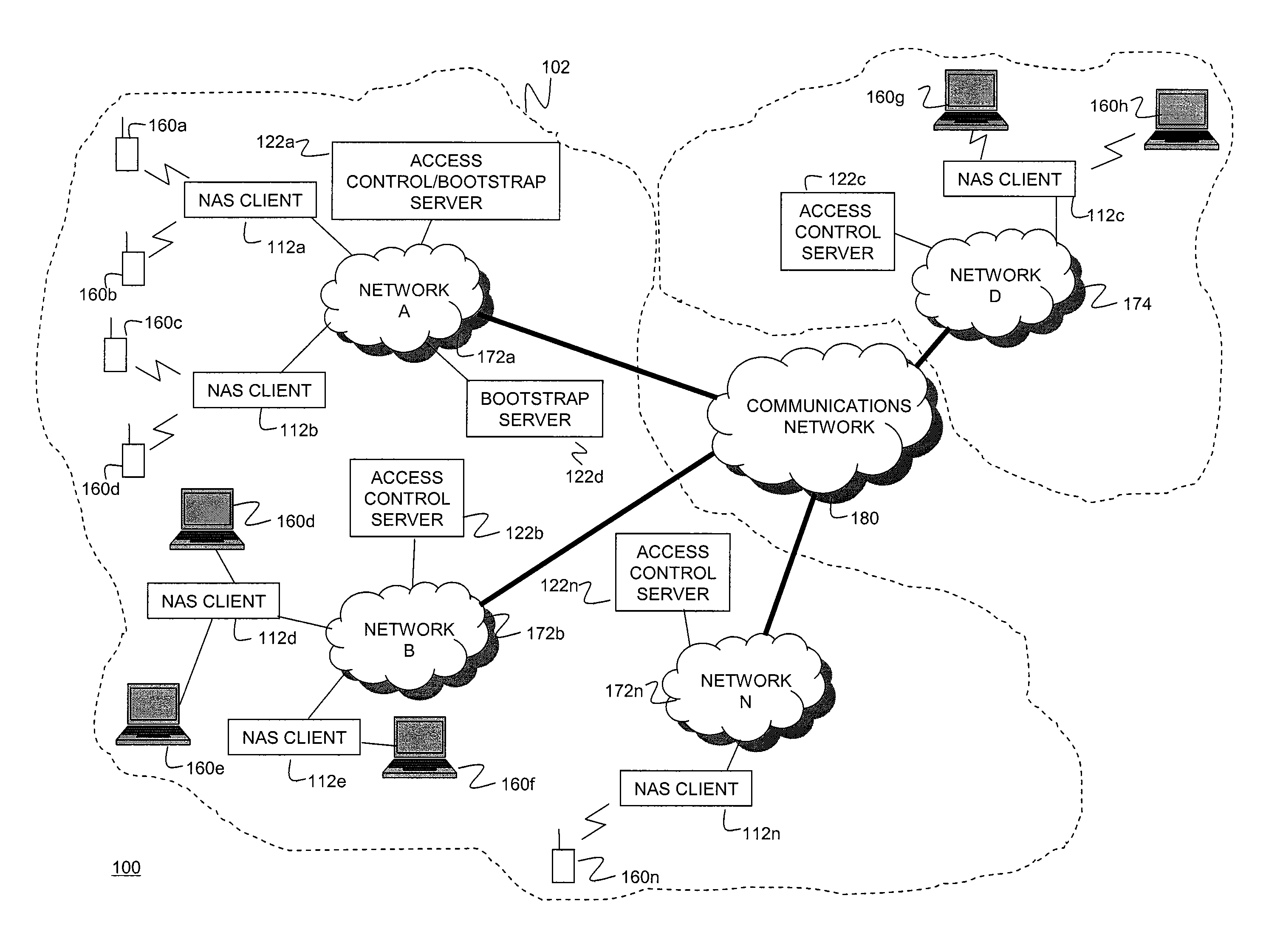
Systems and Methods for Server Load Balancing Using Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting Protocols
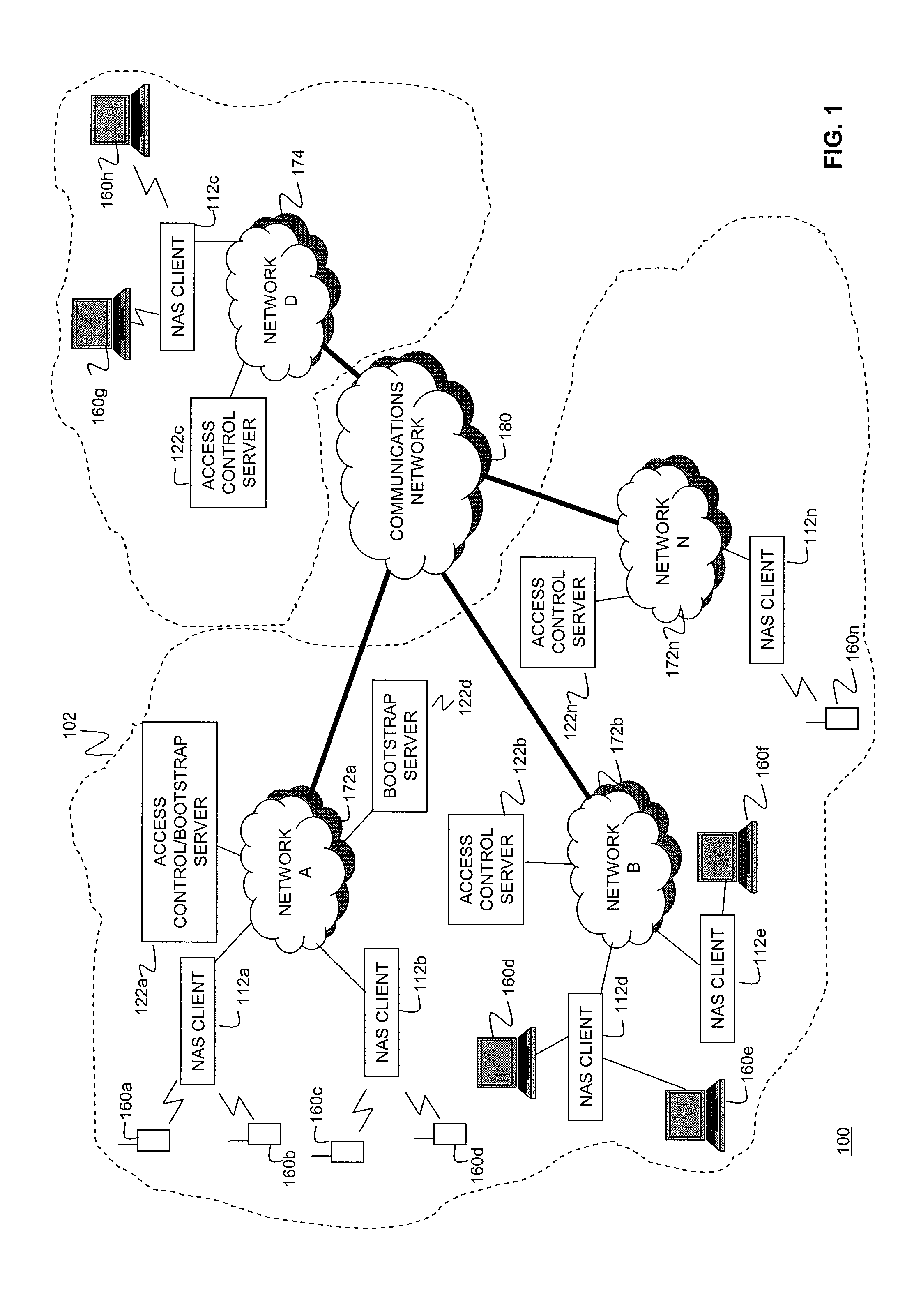
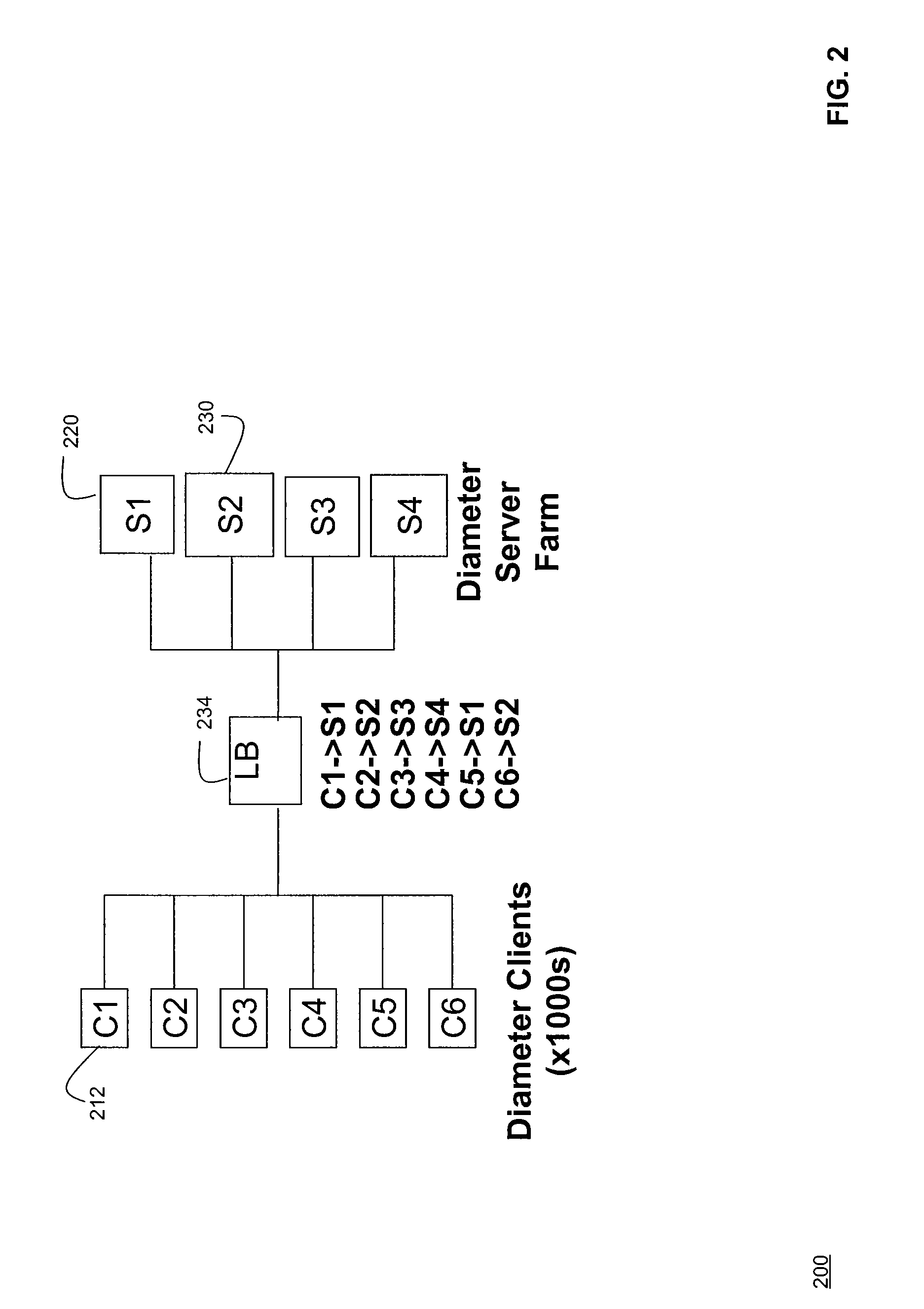
InactiveUS20090083861A1Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsServer allocationClient-side
Systems and methods for dynamically load-balancing clients across available servers without the need for a load balancer in front of a network are provided. Exemplary methods assign servers to clients in wireless and wireline networks based on server load. Methods and systems for using the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) protocols to load-balance network servers are provided. The load-balancing systems and methods further include using the Diameter AAA protocol routing attribute value pairs (AVPs) to implement bootstrap functionality and load balancing. Methods and systems using the Diameter protocol to manage client assignments are disclosed. Methods and systems for dynamically load-balancing clients across available servers using an AAA protocol are further described. Methods and systems to redirect clients to available servers with the least load are disclosed.
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
Systems and methods for server load balancing using authentication, authorization, and accounting protocols
InactiveUS8201219B2Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsServer allocationClient-side
Systems and methods for dynamically load-balancing clients across available servers without the need for a load balancer in front of a network are provided. Exemplary methods assign servers to clients in wireless and wireline networks based on server load. Methods and systems for using the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) protocols to load-balance network servers are provided. The load-balancing systems and methods further include using the Diameter AAA protocol routing attribute value pairs (AVPs) to implement bootstrap functionality and load balancing. Methods and systems using the Diameter protocol to manage client assignments are disclosed. Methods and systems for dynamically load-balancing clients across available servers using an AAA protocol are further described. Methods and systems to redirect clients to available servers with the least load are disclosed.
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
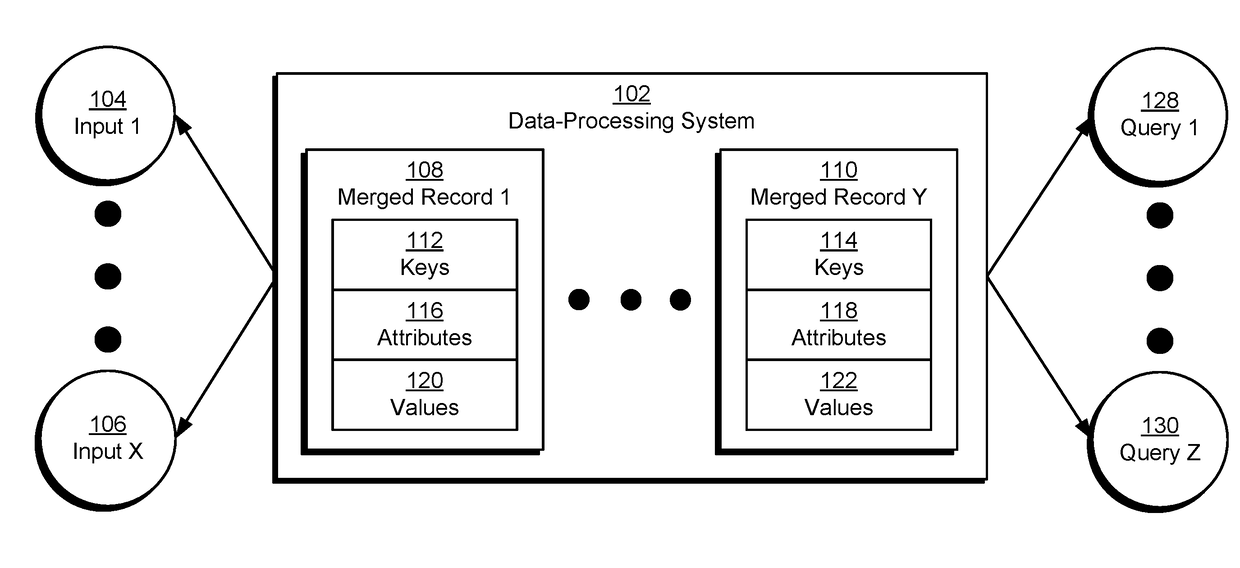
Efficient consolidation of high-volume metrics
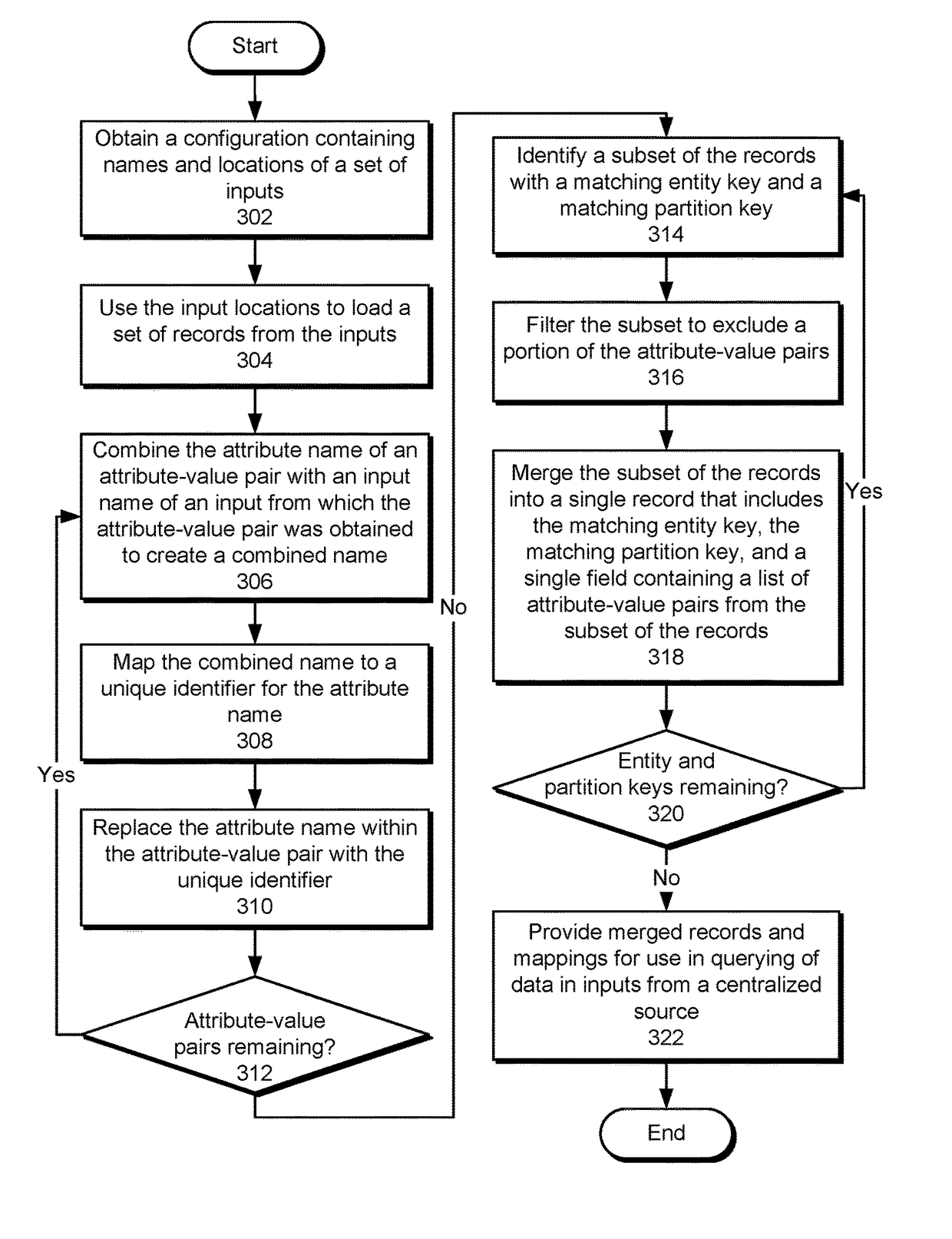
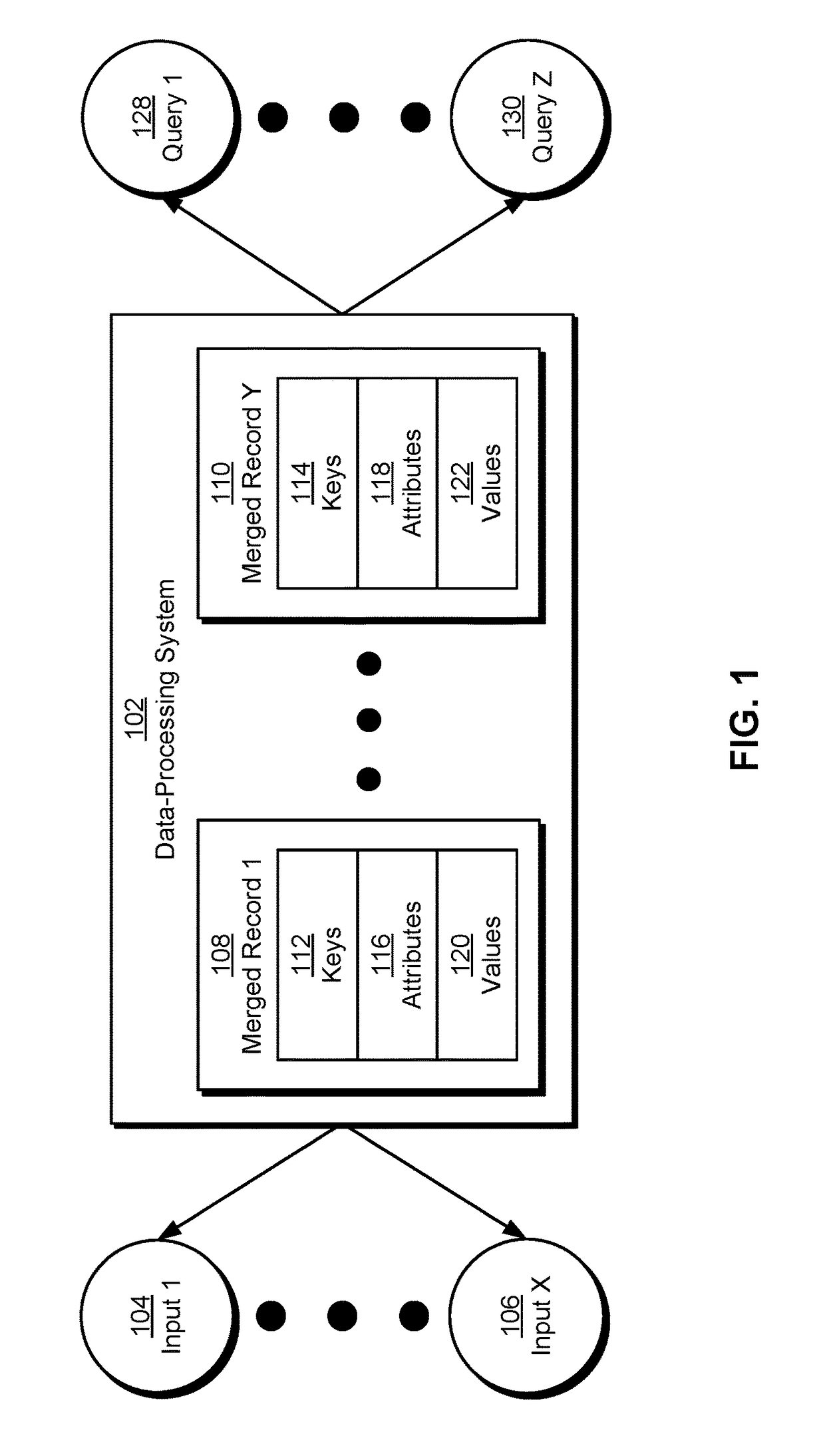
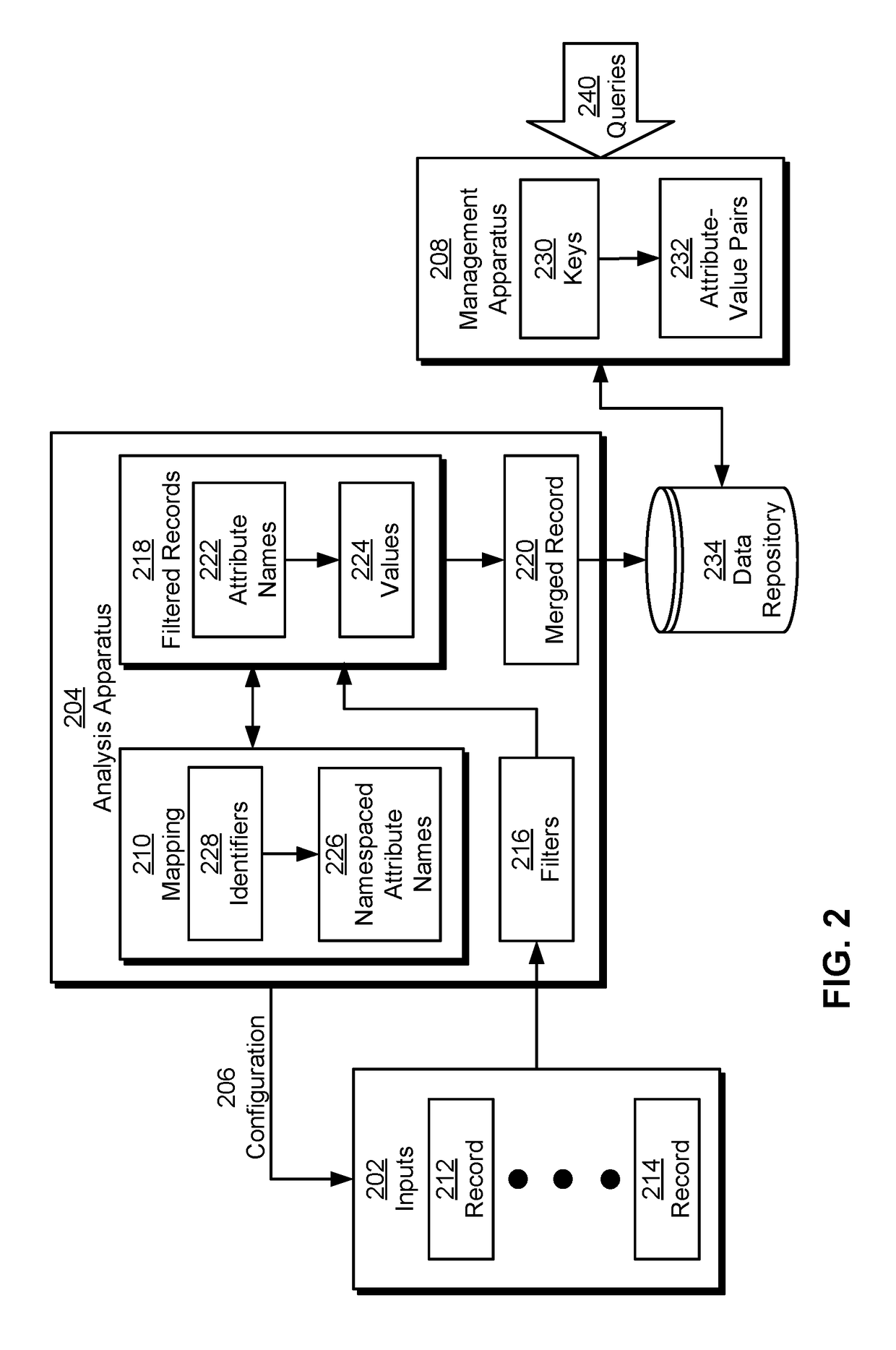
InactiveUS20170154057A1Database queryingSpecial data processing applicationsUnique identifierData mining
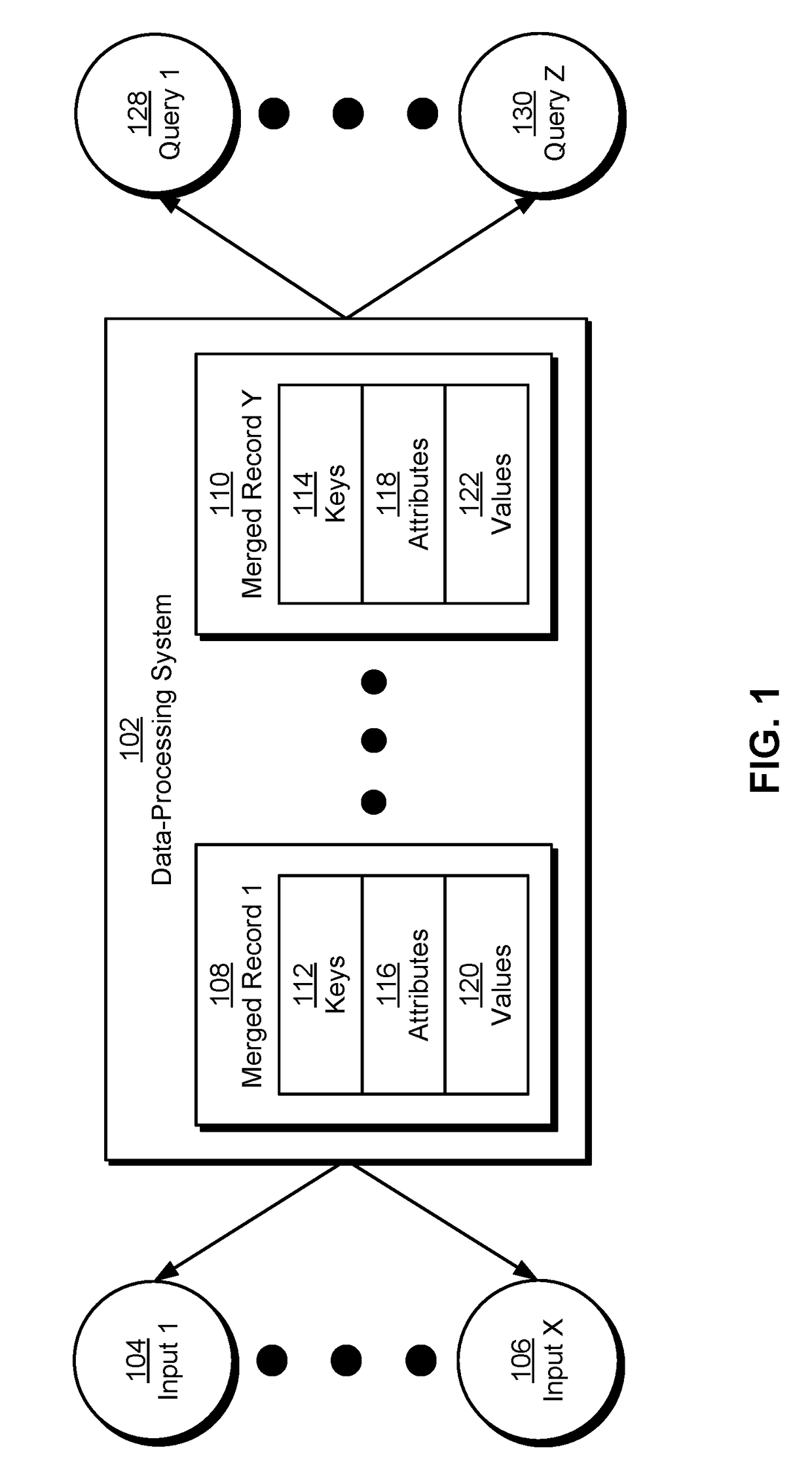
The disclosed embodiments provide a system for processing data. During operation, the system obtains a set of records from a set of inputs, with each record containing an entity key, a partition key, and one or more attribute-value pairs. For each attribute-value pair in the records, the system maps an attribute name in the attribute-value pair to a unique identifier for the attribute name and replaces the attribute name with the unique identifier. The system then identifies a subset of the records with a matching entity key and a matching partition key and merges the subset of the records into a single record that includes the matching entity key, the matching partition key, and a single field containing a list of attribute-value pairs from the subset of the records. Finally, the system provides the single record and the mapping for use in querying from a centralized source.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for filtering rules for manipulating search results in a hierarchical search and navigation system
ActiveUS7856434B2Web data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsFiltering rulesNavigation system
A method is disclosed for modifying the results of a search performed in a collection of items by a search and navigation system. The method includes receiving a query from a user interface and determining a navigation state, defined by expressions of attribute-value pairs, based on the received query. The user interface accepts both selecting and deselecting of any of the attribute-value pairs in an expression corresponding to a navigation state to obtain an expression corresponding to a different navigation state, and each selection and deselection forms a new query. The method further includes retrieving, from the collection, items associated with the navigation state to form a set of unmodified search results, the set of unmodified search results having an arrangement for presentation to the user. A rule filter that includes a metadata expression is applied to a set of rules, each rule having a trigger, an action, and metadata. The application of the rule filter to the set of rules includes evaluating the metadata expression of the rule filter based on the metadata of each rule and passing rules for which the metadata expression of the rule filter evaluates as logical true. The trigger of each rule passed by the rule filter is evaluated, and the action of each rule for which the trigger of the rule evaluates as logical true is executed to modify the unmodified search results to form modified search results.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY LLC
Hierarchical data-driven search and navigation system and method for information retrieval
InactiveUS7567957B2Highly scalable, hierarchical, data-drivenGood conditionData processing applicationsWeb data navigationDocument preparationApplication software
A data-driven, hierarchical information search and navigation system and method enable search and navigation of sets of documents or other materials by certain common attributes that characterize the materials. The invention includes several aspects of a data-driven, hierarchical search and navigation system that employs this search and navigation mode. The search and navigation system of the present invention includes features of an navigation interface, a search interface, a knowledge base and a taxonomy definition process and a classification process for generating the knowledge base, a graph-based navigable data structure and method for generating the data structure, World Wide Web-based applications of the system, and methods of implementing the system. Users are able to search or browse a particular collection of documents by selecting desired values for the attributes or by searching the attribute-value pairs. A data-driven, hierarchical information search and navigation system and method enable this navigation mode by associating terms with the materials, defining a set of hierarchical relationships among the terms, providing a guided navigation mechanism based on the relationship between the terms, and providing a search mechanism that can respond to free-text queries with single-term or multi-term interpretations. In another aspect of the invention, implementations of the invention may be scalable through parallel or distributed computation.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY LLC
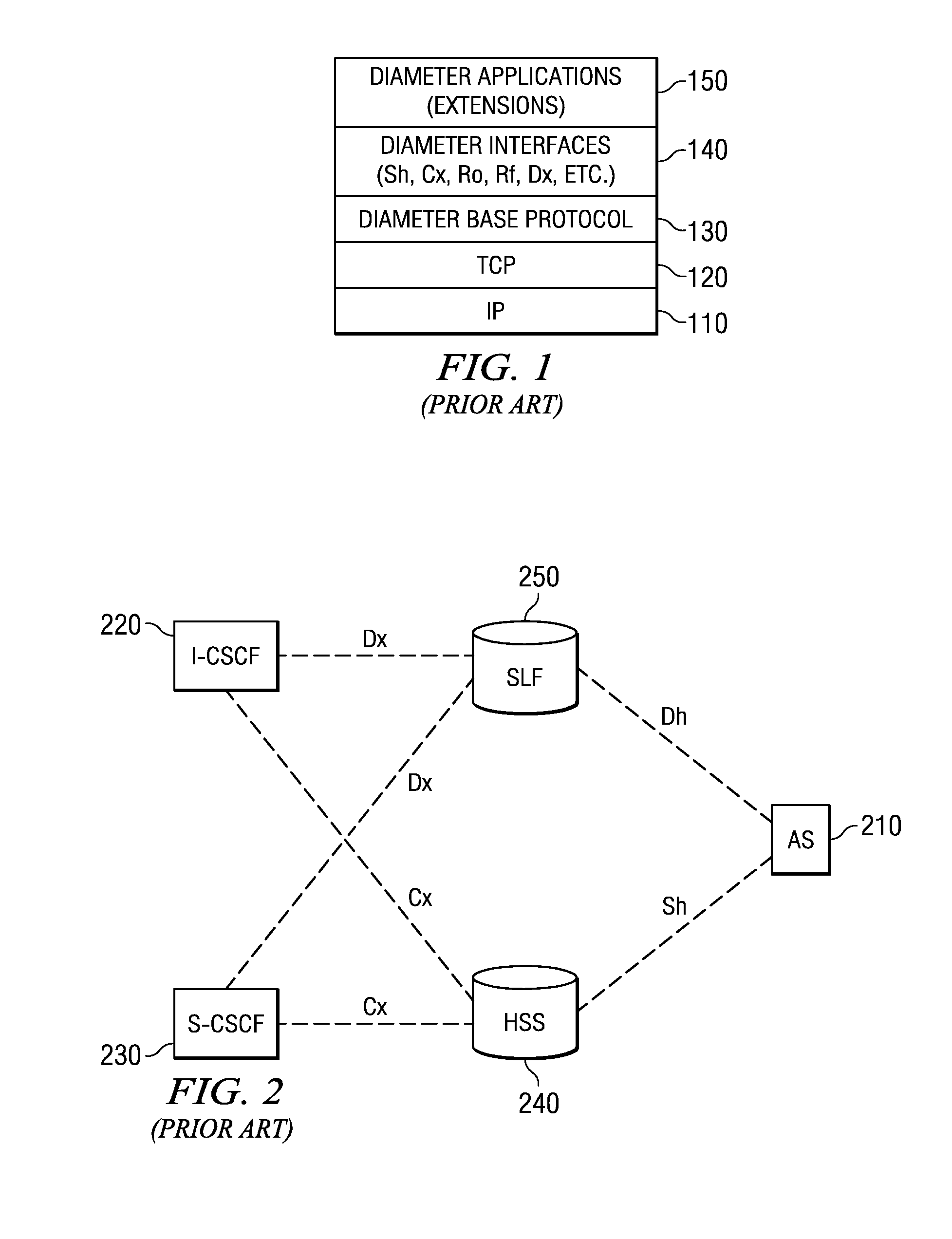
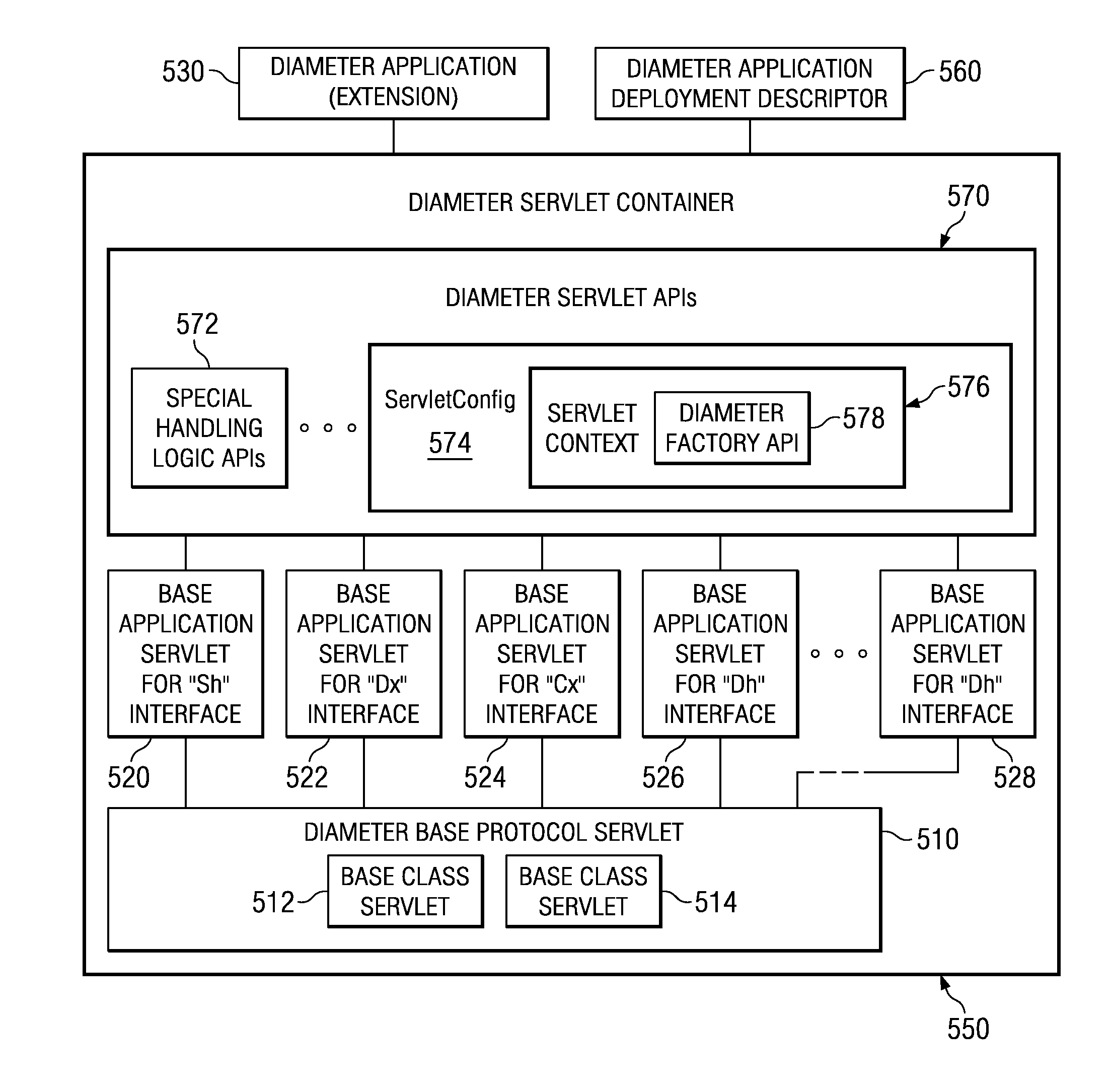
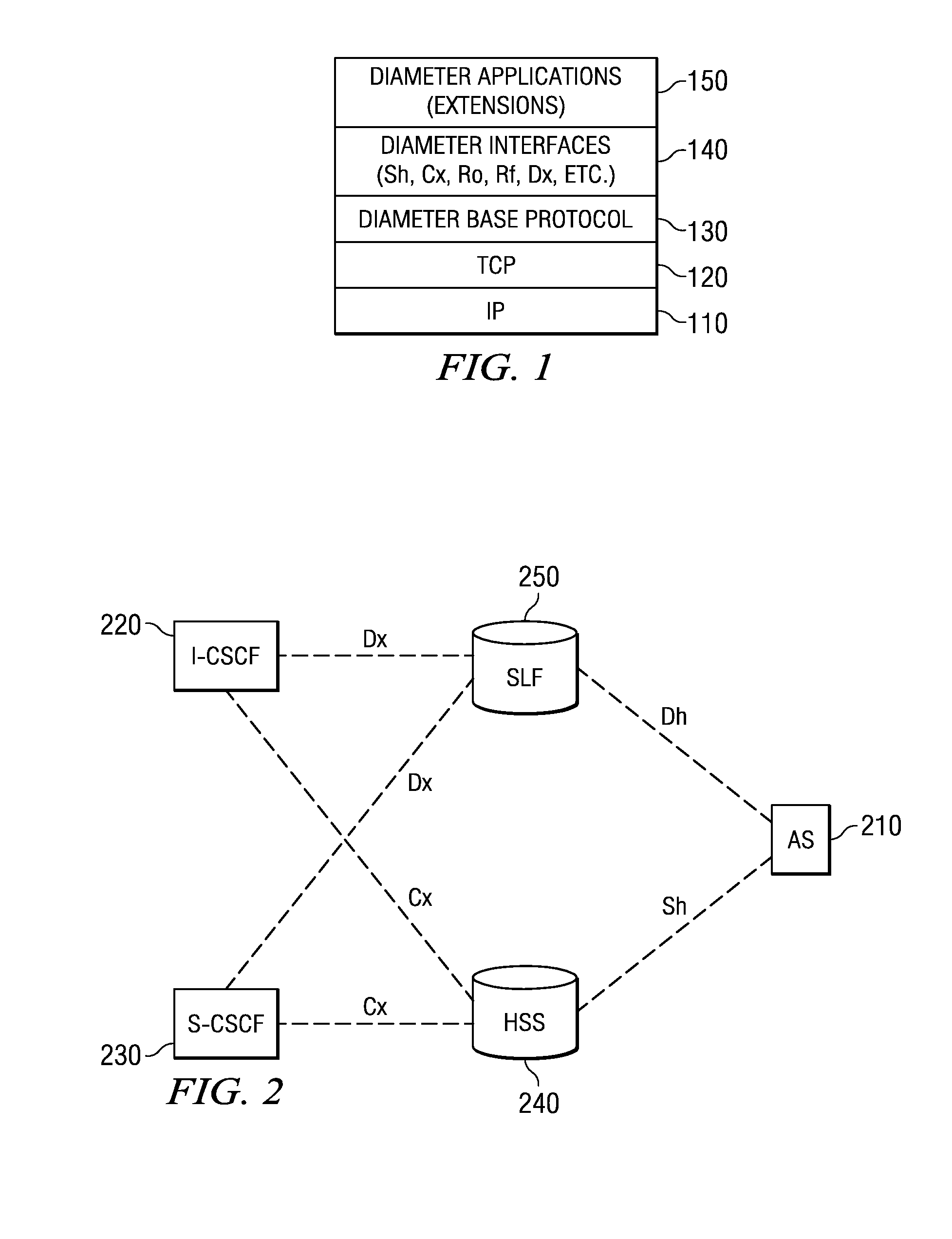
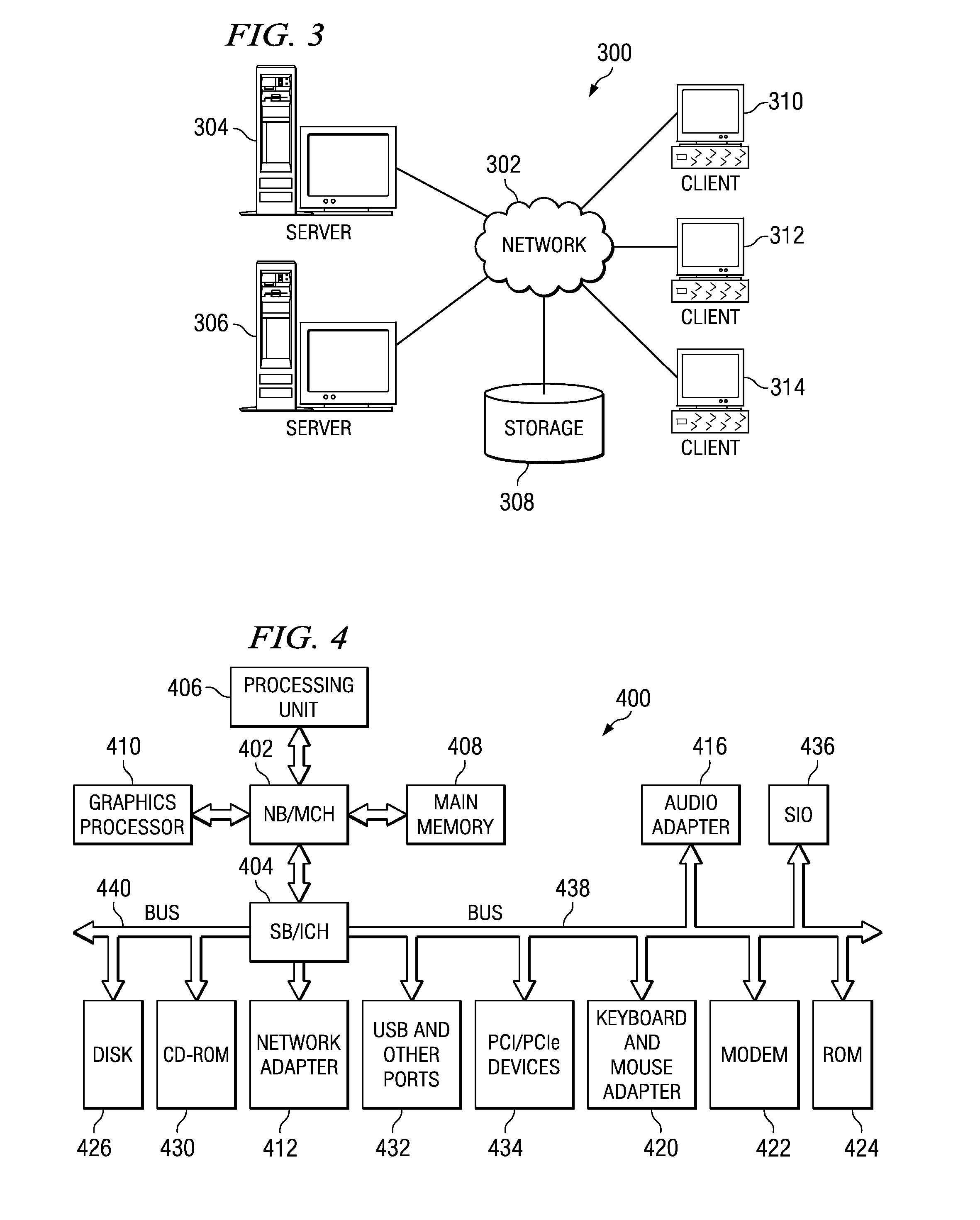
System and Method for Developing Diameter Applications
ActiveUS20080195742A1Improve usabilityFacilitate communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication serverBase class
A system and method for developing Diameter applications are provided. The system and method extend the application server servlet model to support Diameter applications. A “base protocol” servlet is provided that handles the basic Diameter protocol functionality. Base application servlets are provided for each Diameter interface (for example, an “Sh” base servlet for the IMS “Sh” interface). These servlets are base classes for application code. The base application servlets implement additional semantics on top of the base protocol servlet to support additional attribute-value pair semantics. With the system and method, Diameter servlets share the same ServletContext as HTTP and SIP servlets. This mechanism facilitates communication between the various application entities and facilitates generation of converged applications.
Owner:SNAPCHAT
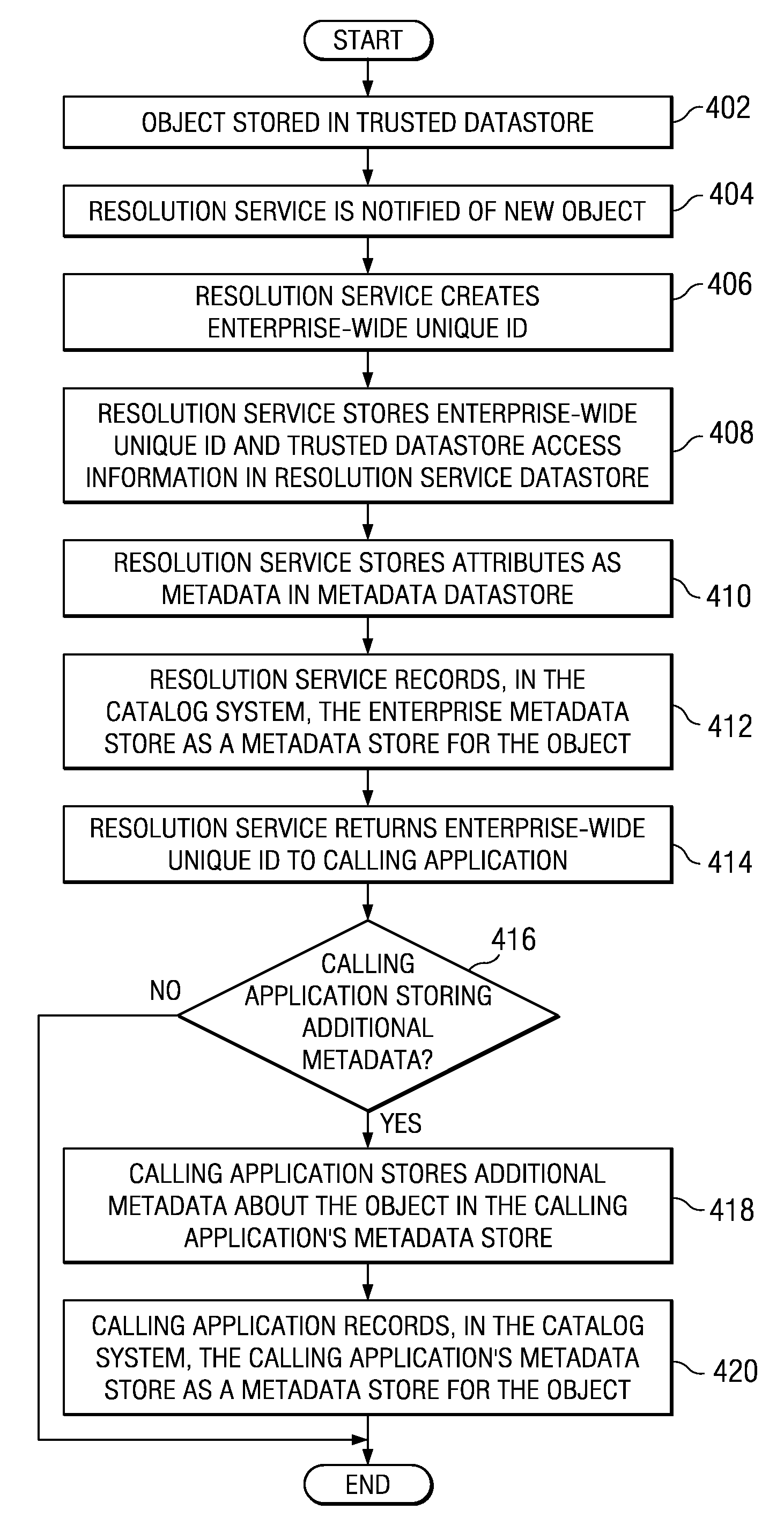
Flexible and resilient information collaboration management infrastructure
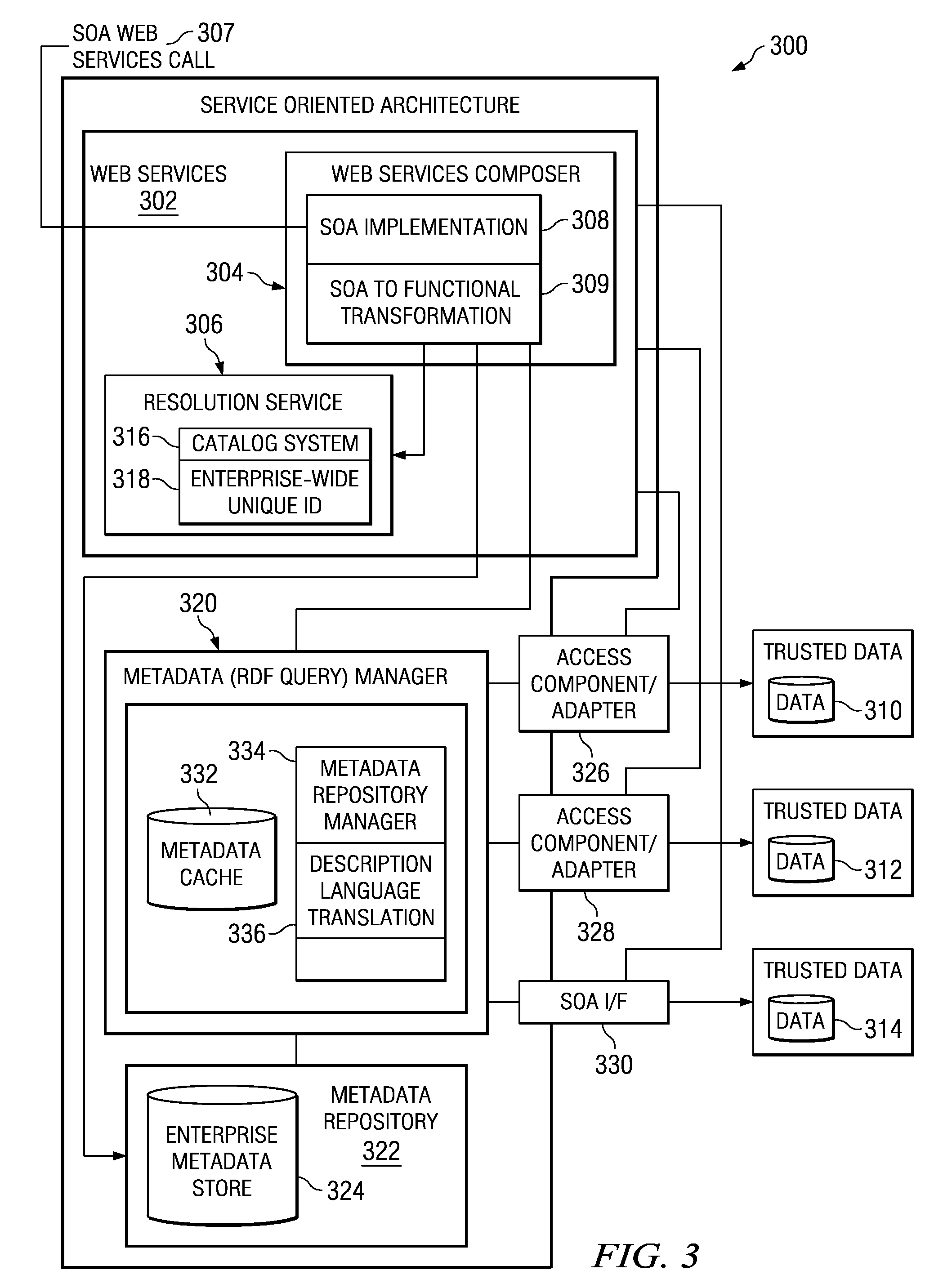
InactiveUS20090234883A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData retrievalUnique identifier
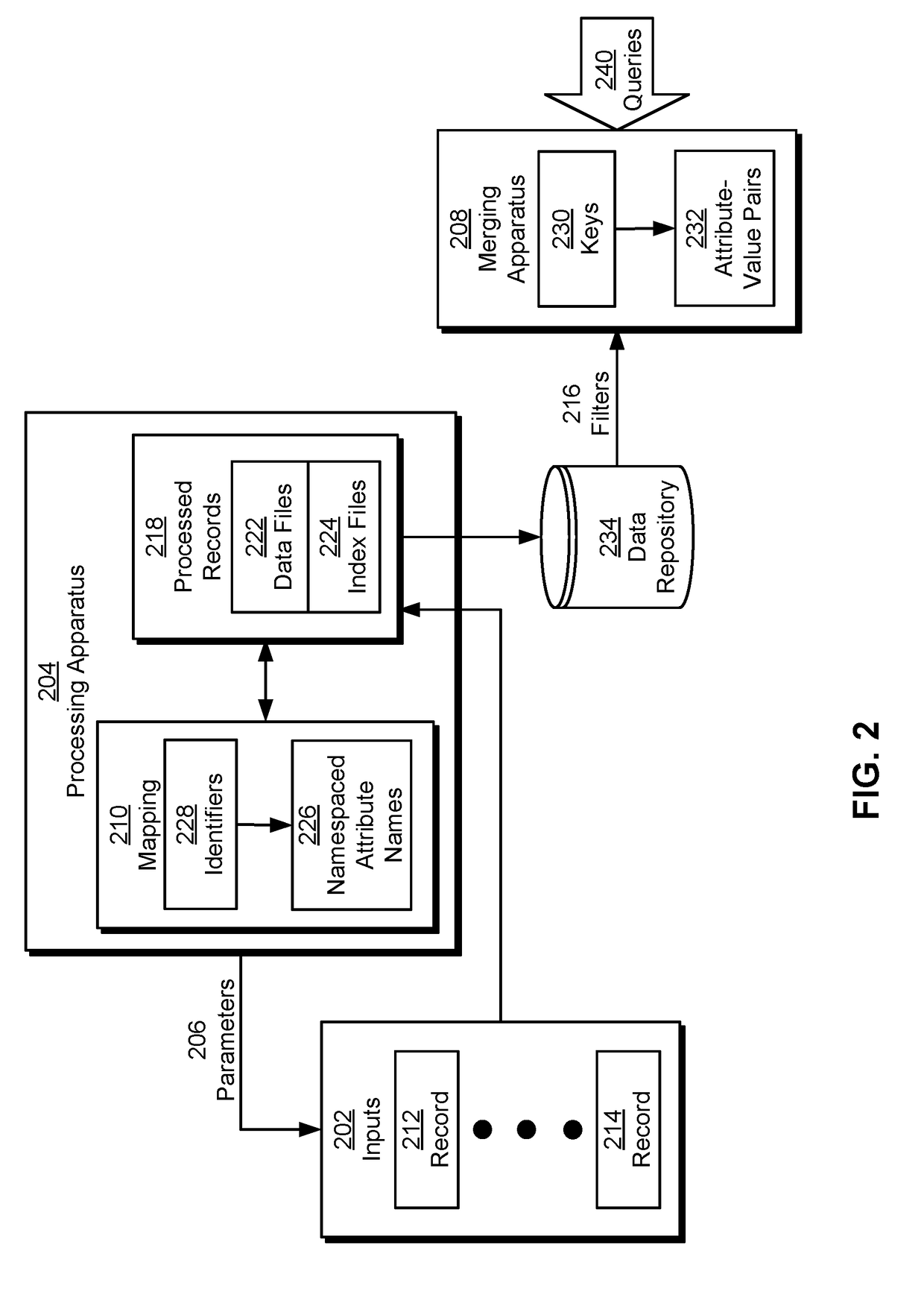
A computer-implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for cross-silo query and data retrieval. A request to access a data object in a trusted database is received, wherein the request includes an enterprise-wide unique identifier of a data object or one or more metadata attribute value pairs. If the request comprises one or more metadata attribute value pairs, one or more enterprise-wide unique identifiers associated with the metadata attribute value pairs are identified. Using the enterprise-wide unique identifiers, metadata about the data object stored in one or more enterprise-level data stores or the trusted database is retrieved. The metadata about the data object is queried to identify related data objects in disparate trusted databases in the enterprise system. The data object and the related data objects are provided to the application.
Owner:IBM CORP
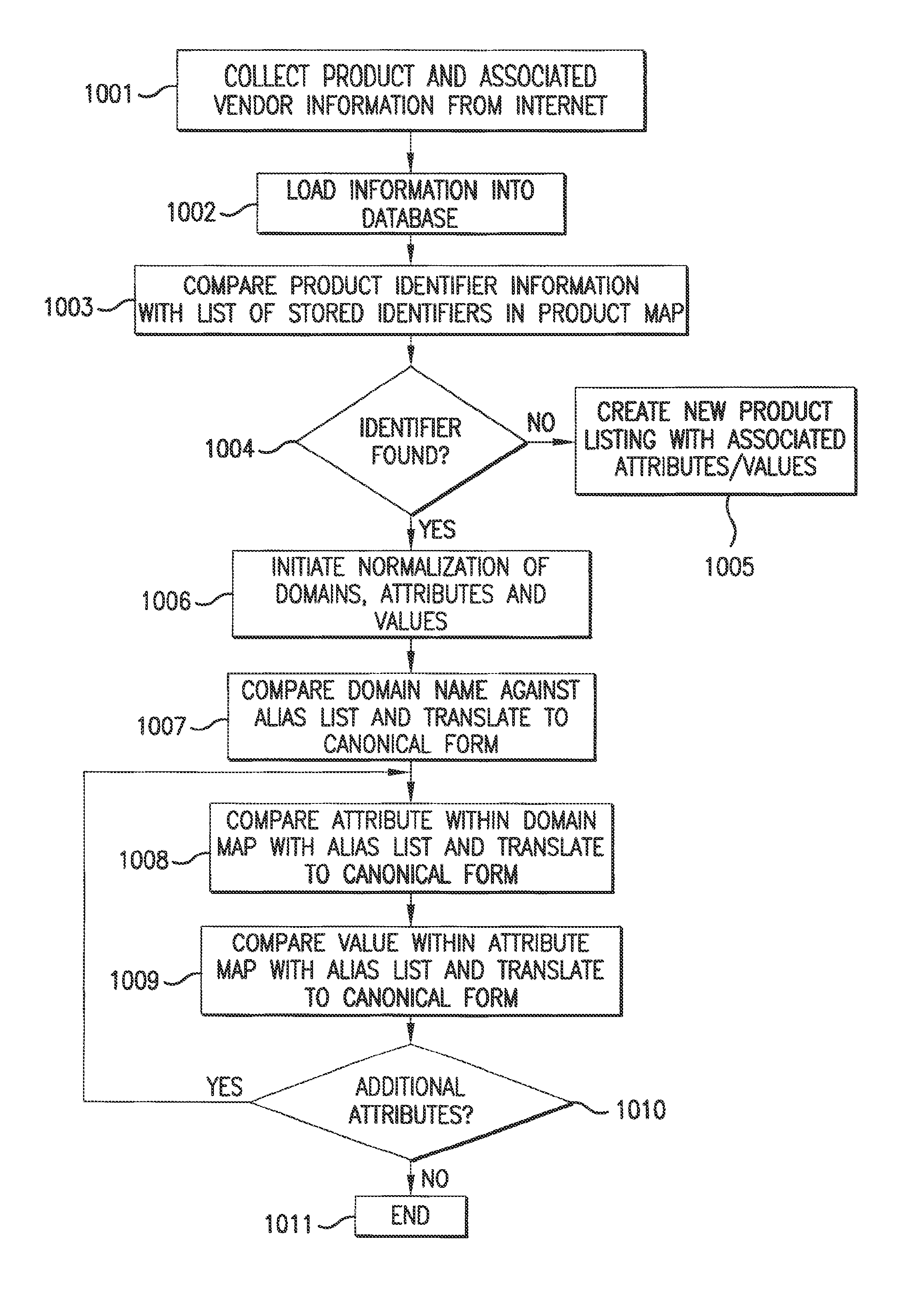
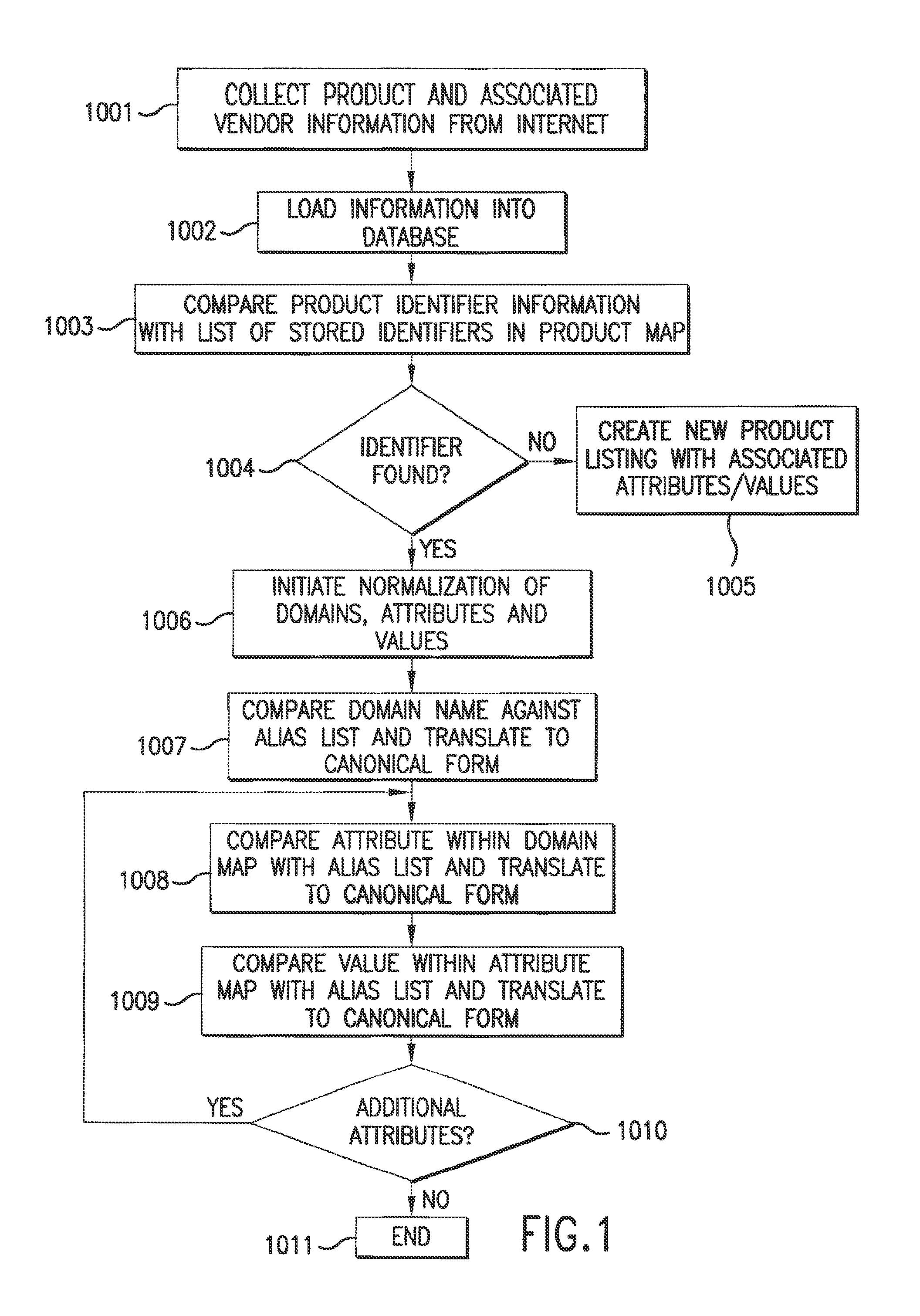
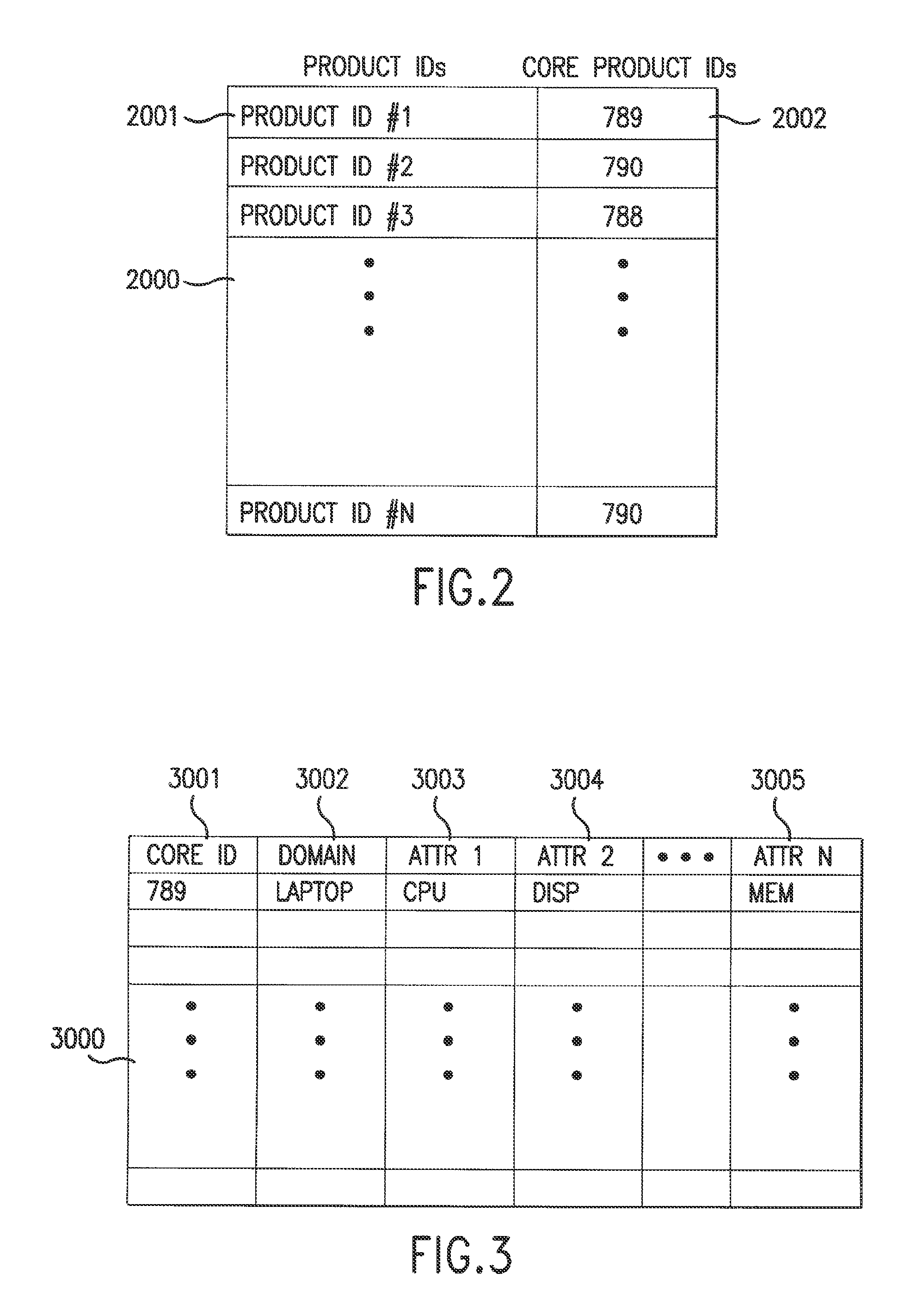
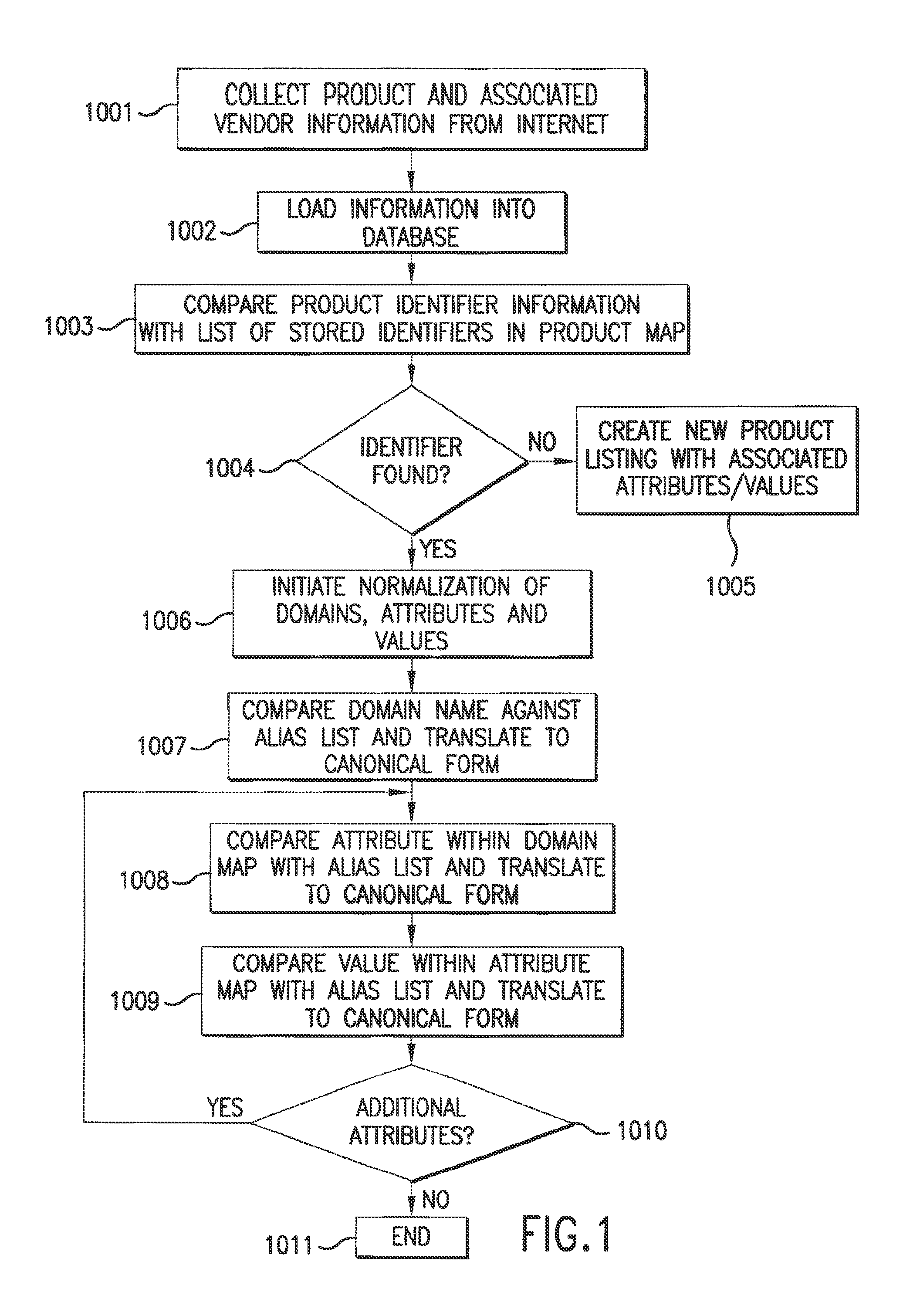
System and method for retrieving and normalizing product information
InactiveUS20130198183A1Shorten the timeWeb data retrievalDigital data processing detailsWorld Wide WebStandardization
Owner:PAYPAL INC
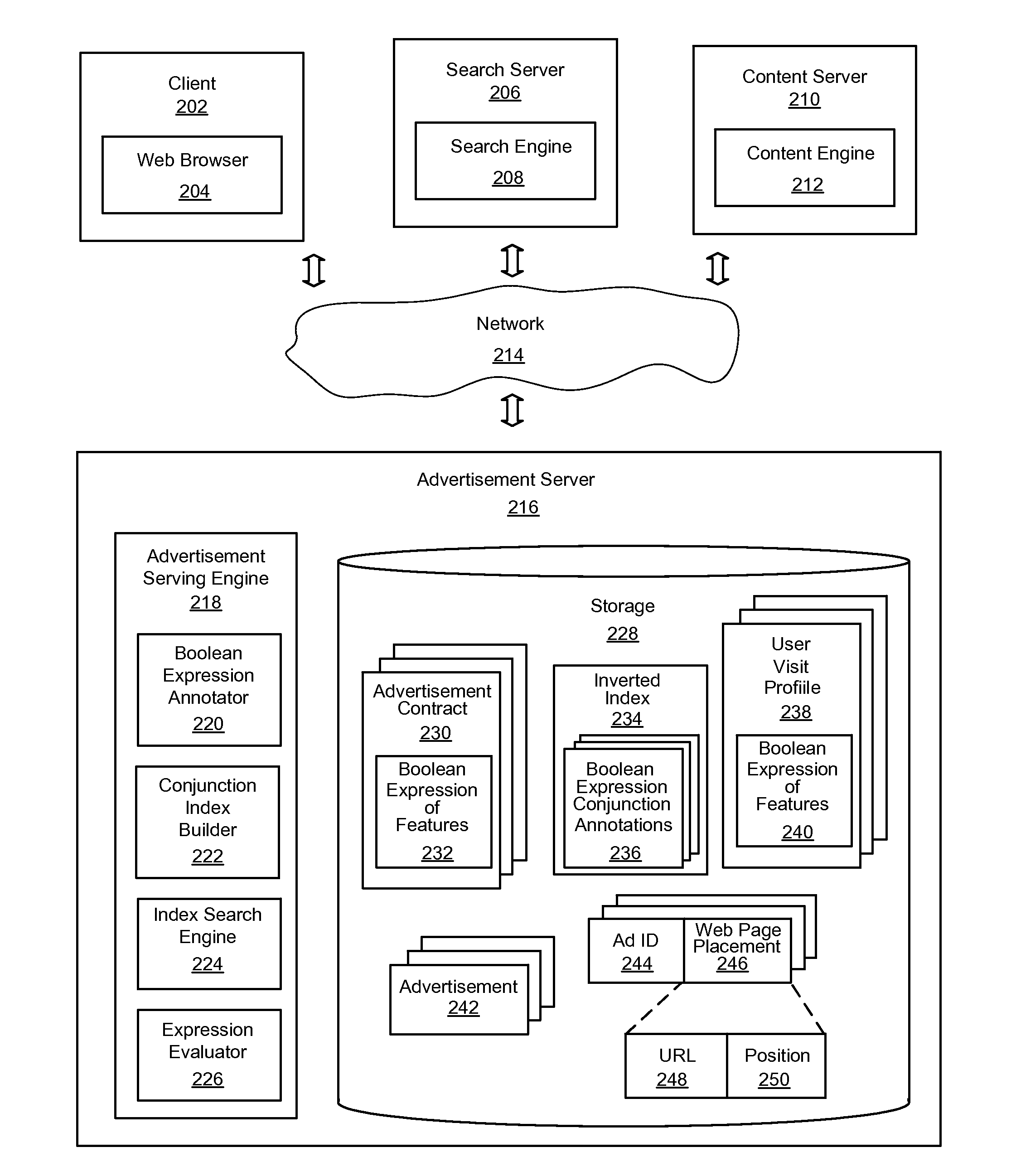
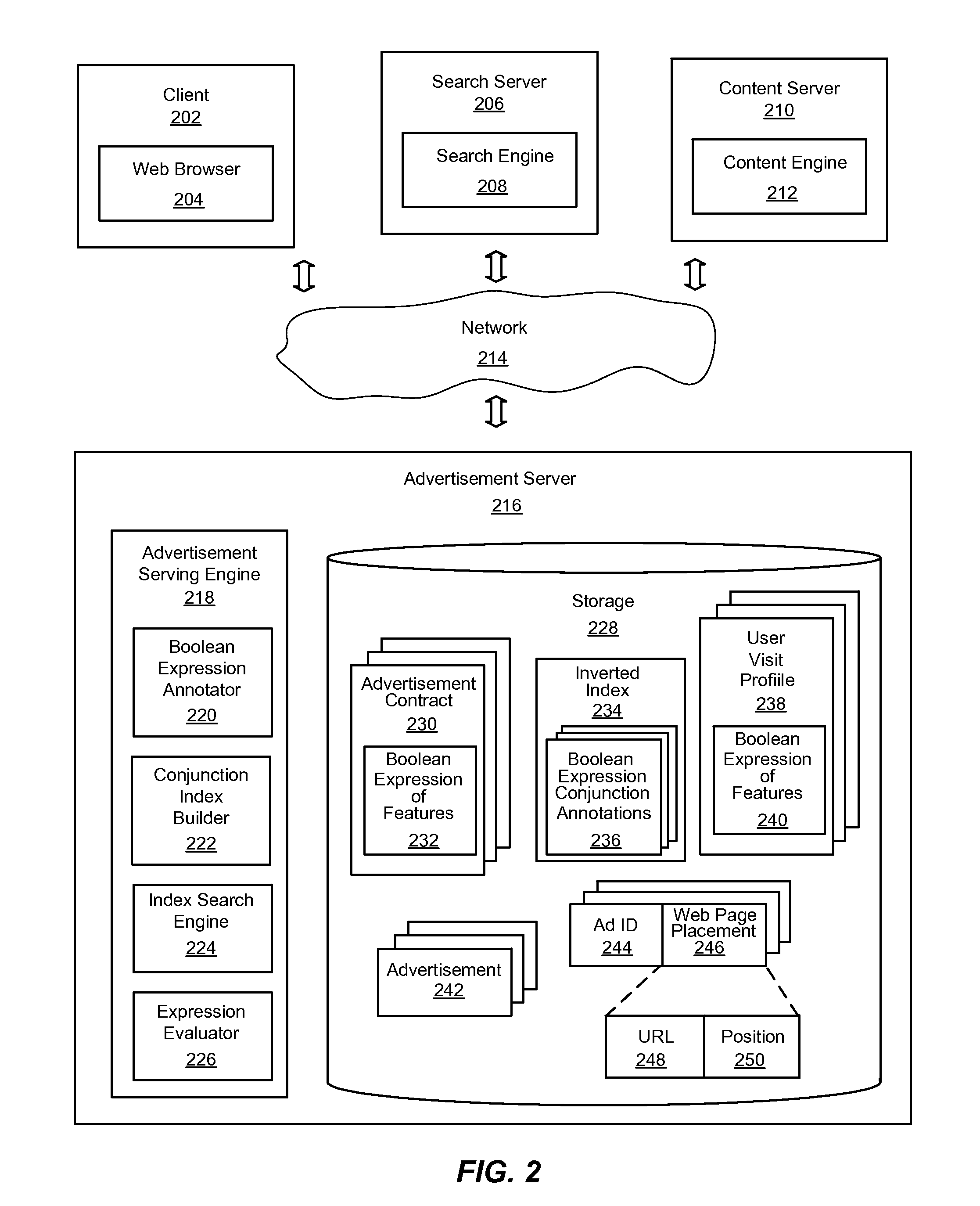
System and Method for Efficiently Evaluating Complex Boolean Expressions
InactiveUS20110225038A1Effective evaluationImprove indexing speedDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceInverted index
An improved system and method for efficiently evaluating complex Boolean expressions is provided. Leaf nodes of Boolean expression trees for objects represented by Boolean expressions of attribute-value pairs may be assigned a positional identifier that indicates the position of a node in the Boolean expression tree. The positional identifiers of each object may be indexed by attribute-value pairs of the leaf nodes of the Boolean expression trees in an inverted index. Given an input set of attribute-value pairs, a list of positional identifiers for leaf nodes of virtual Boolean expression trees may be found in the index matching the attribute-value pairs of the input set. The list of positional identifiers of leaf nodes may be sorted in order by positional identifier for each contract. An expression evaluator may then verify whether a virtual Boolean expression tree for each contract is satisfied by the list of positional identifiers.
Owner:YAHOO INC
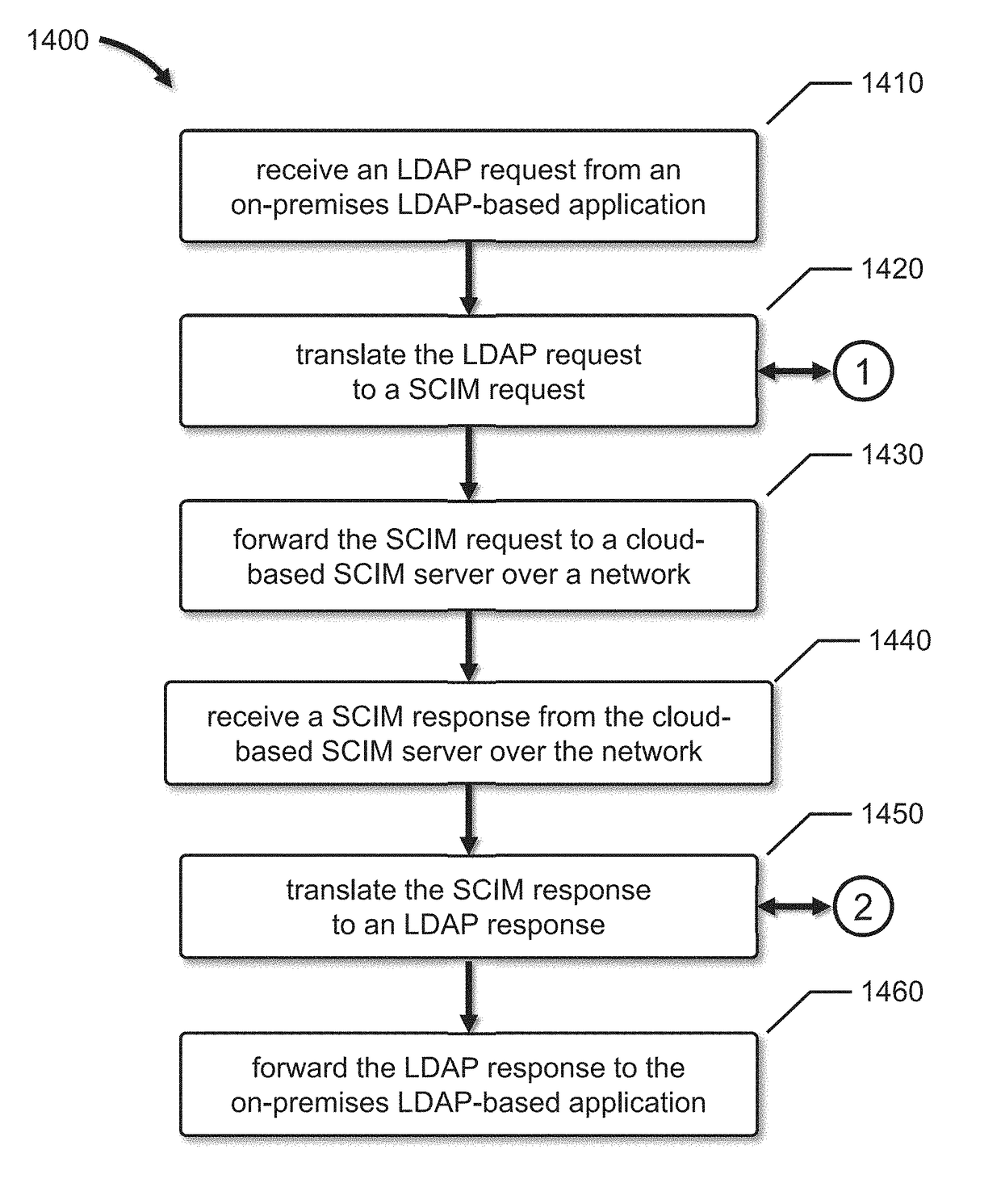
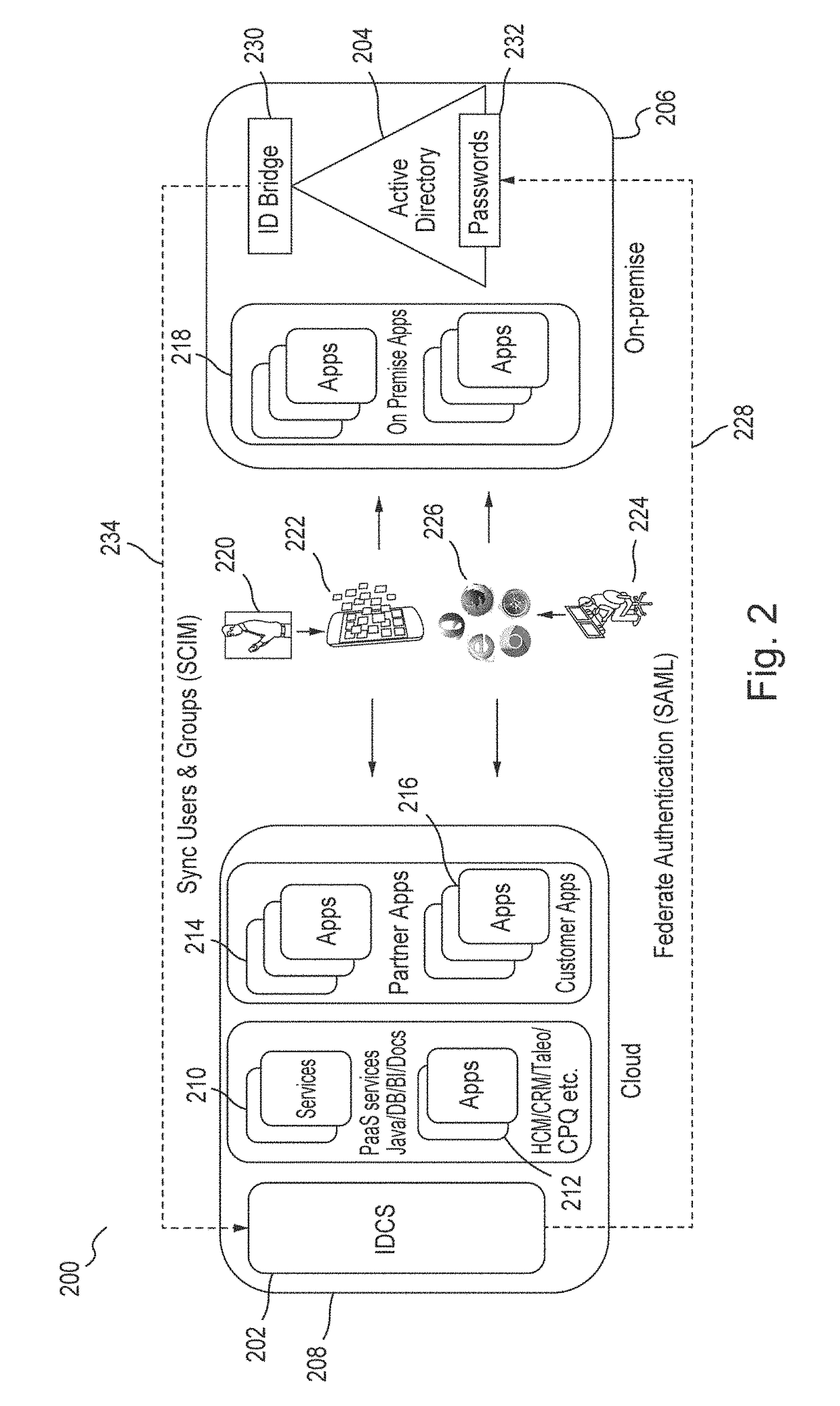
SCIM to LDAP Mapping Using Subtype Attributes
ActiveUS20180083915A1Digital data information retrievalTransmissionDirectory information treeData mining
A method for mapping SCIM resources to LDAP entries is provided. An LDAP Directory Information Tree (DIT), including a plurality of LDAP DIT entries that describe LDAP containers, users and groups, is provided. Each LDAP DIT entry includes a Distinguished Name and a plurality of LDAP attribute-value pairs, each of which include an attribute name and one or more attribute values. A SCIM directory, including a plurality of SCIM resource entries, is also provided. Each SCIM resource entry includes a plurality of SCIM attributes, each of which includes a name and one or more values. The plurality of SCIM resource entries are converted to corresponding LDAP DIT entries, and, for each SCIM resource entry that has a SCIM CMVA, the SCIM CMVA is mapped to a plurality of LDAP attributes in the corresponding LDAP DIT entry using LDAP attribute subtypes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
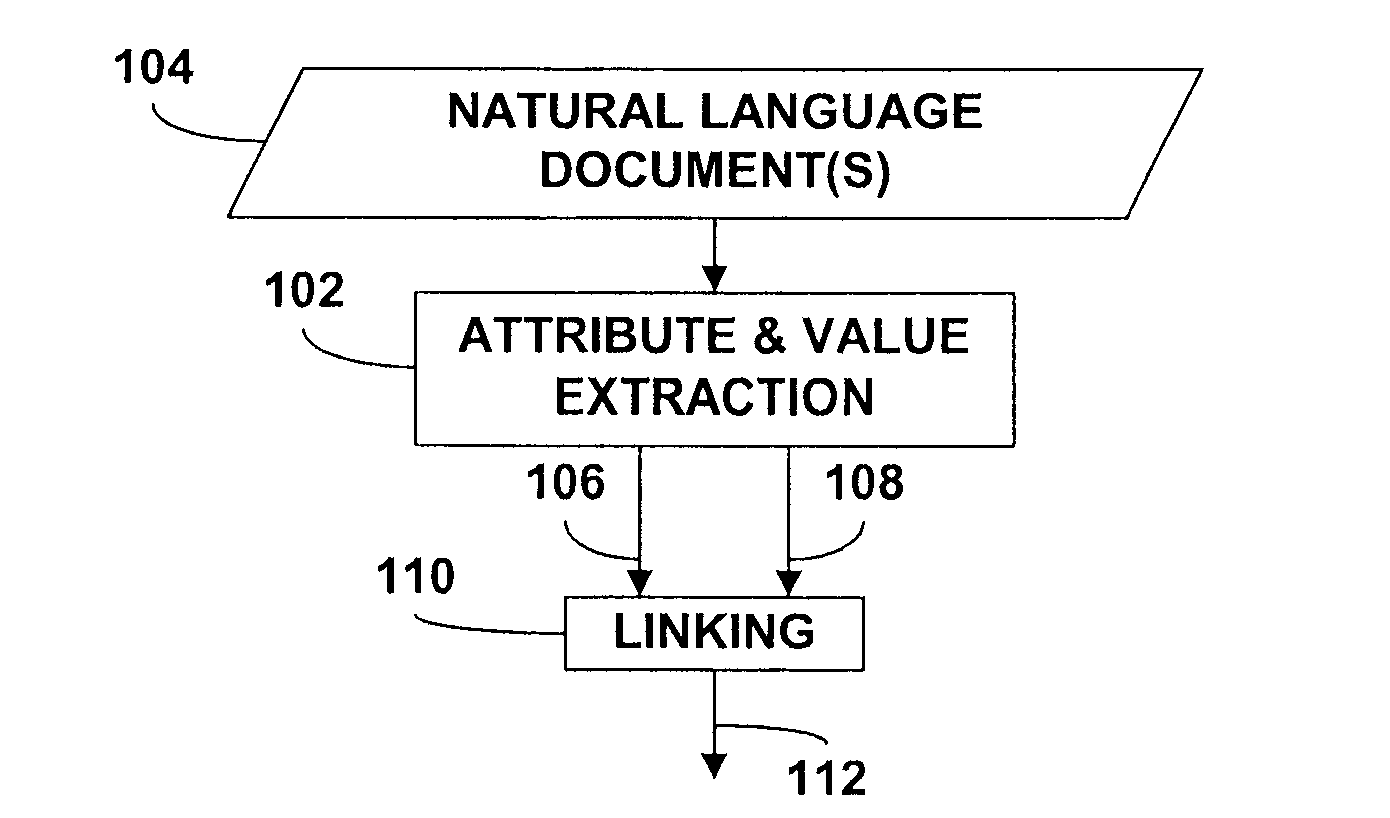
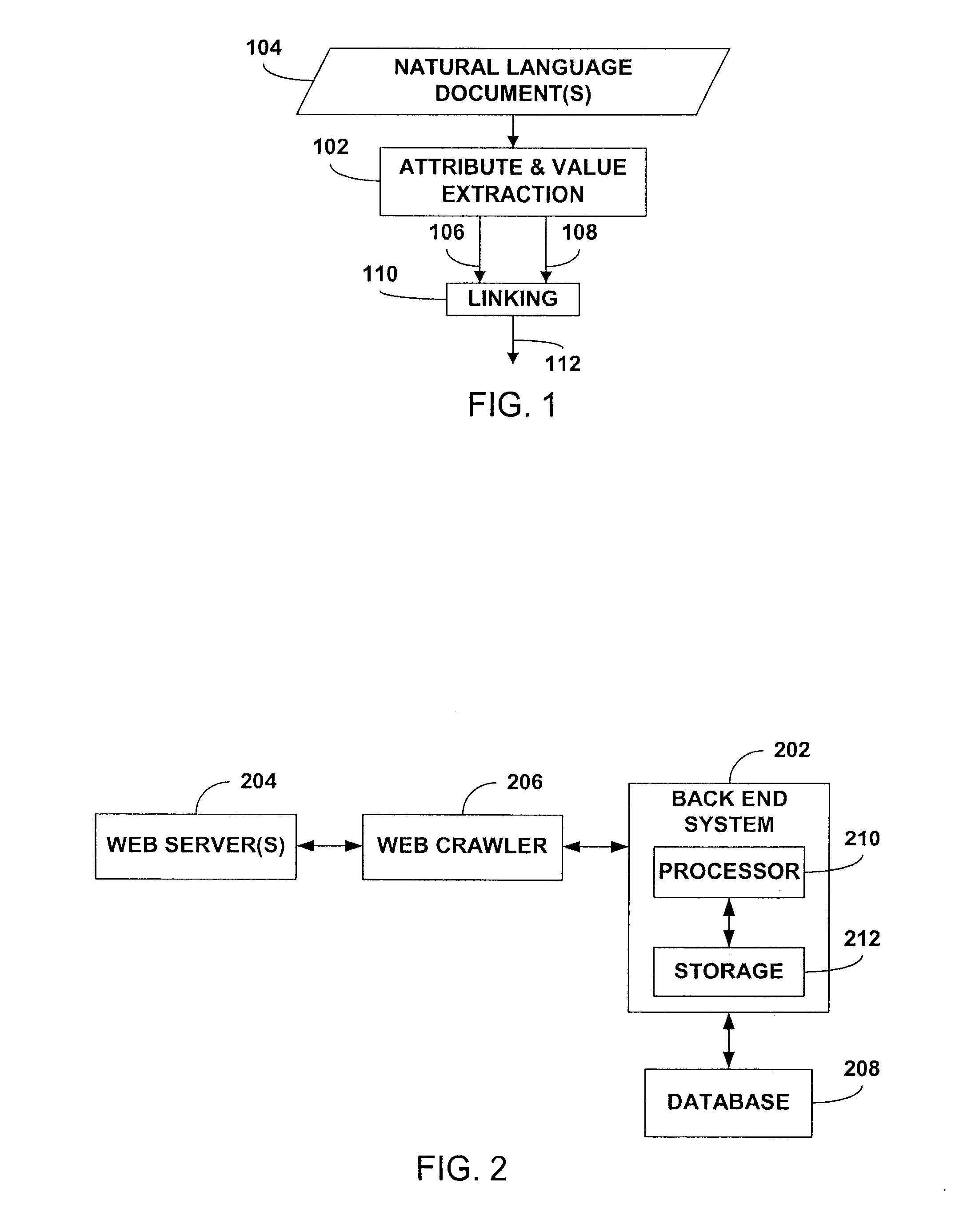
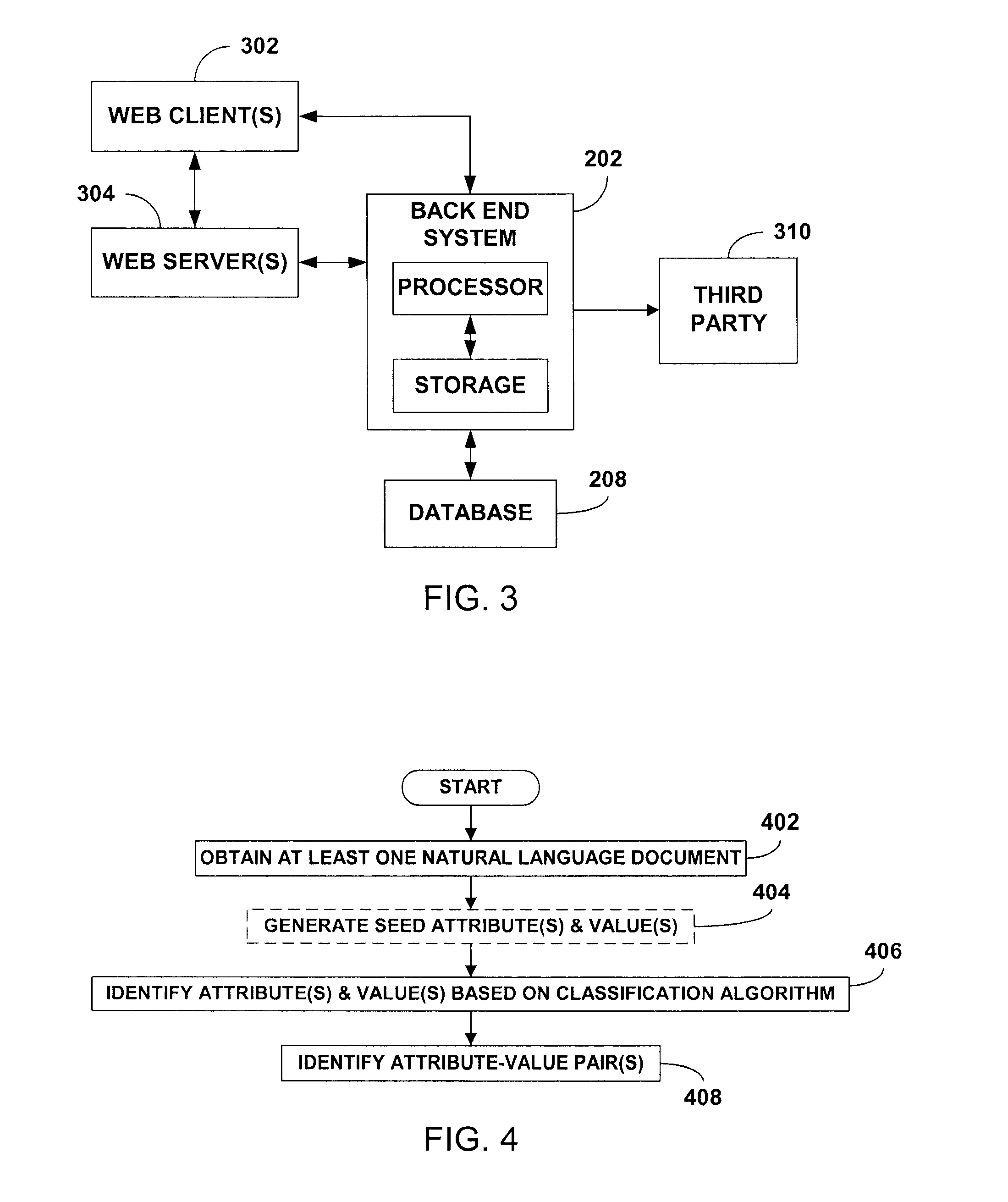
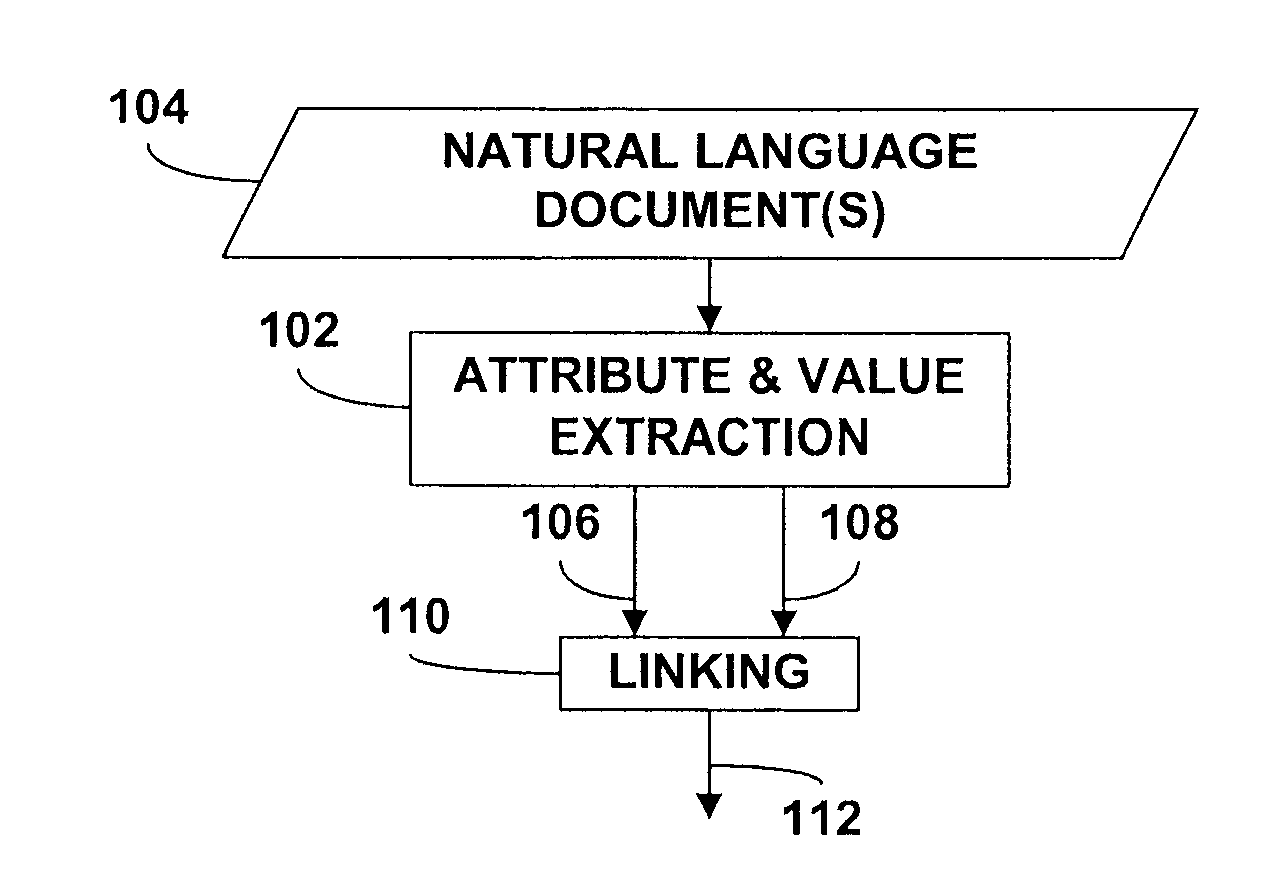
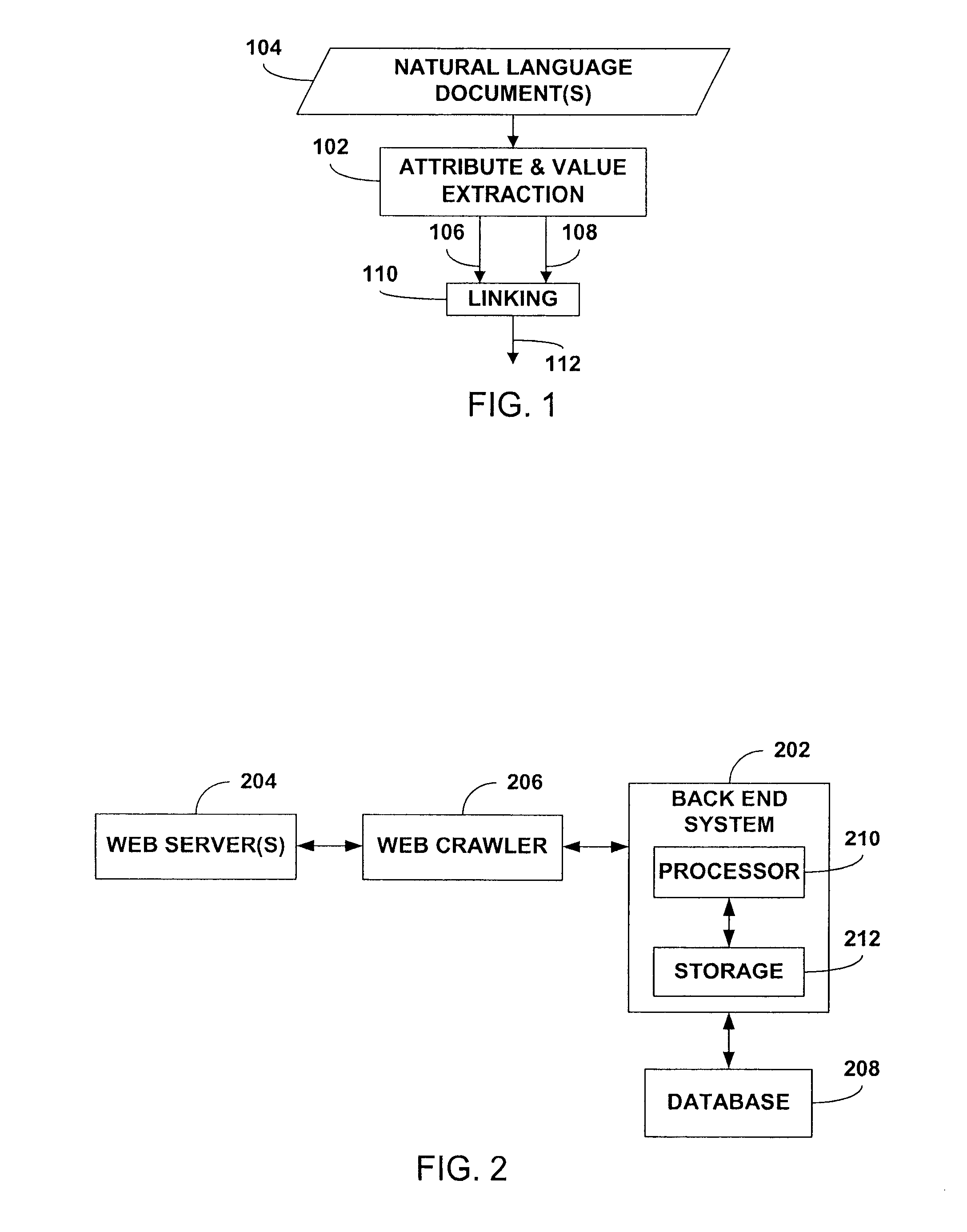
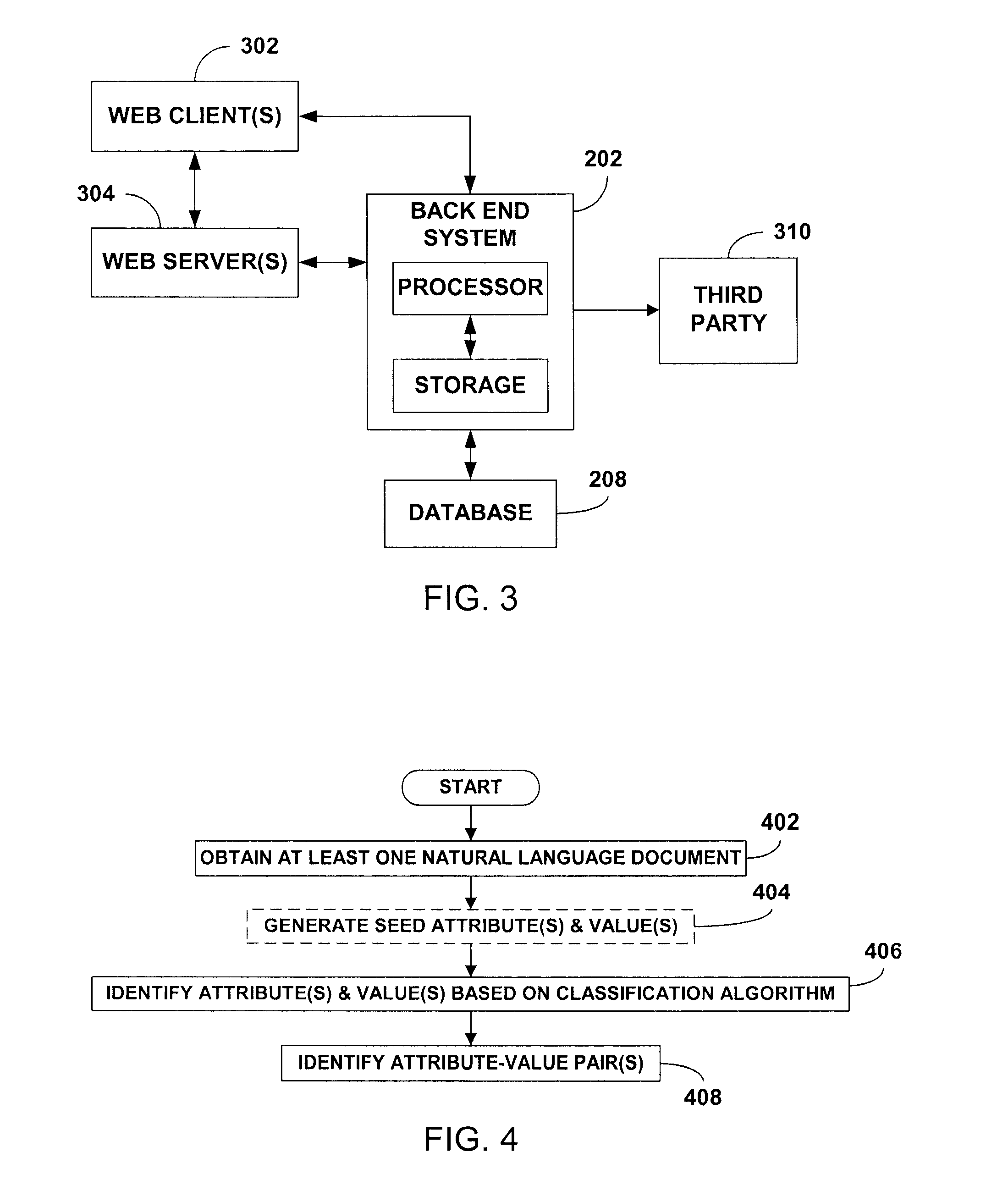
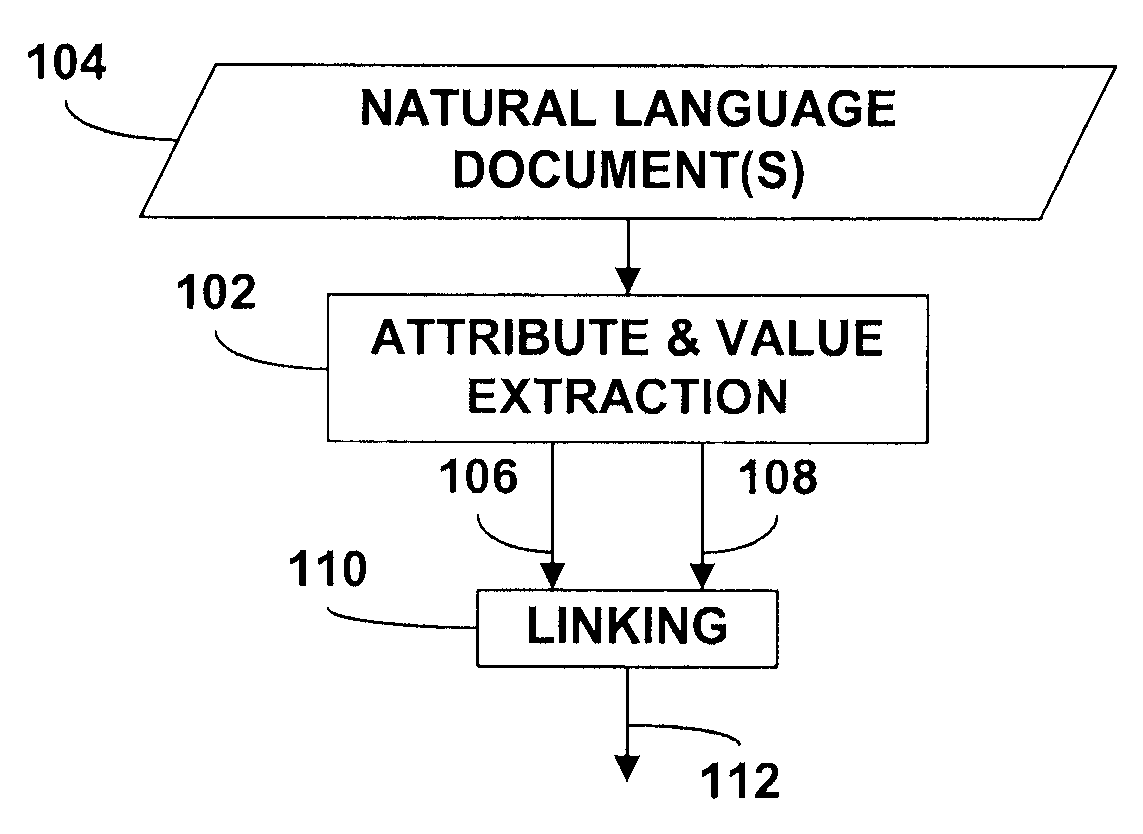
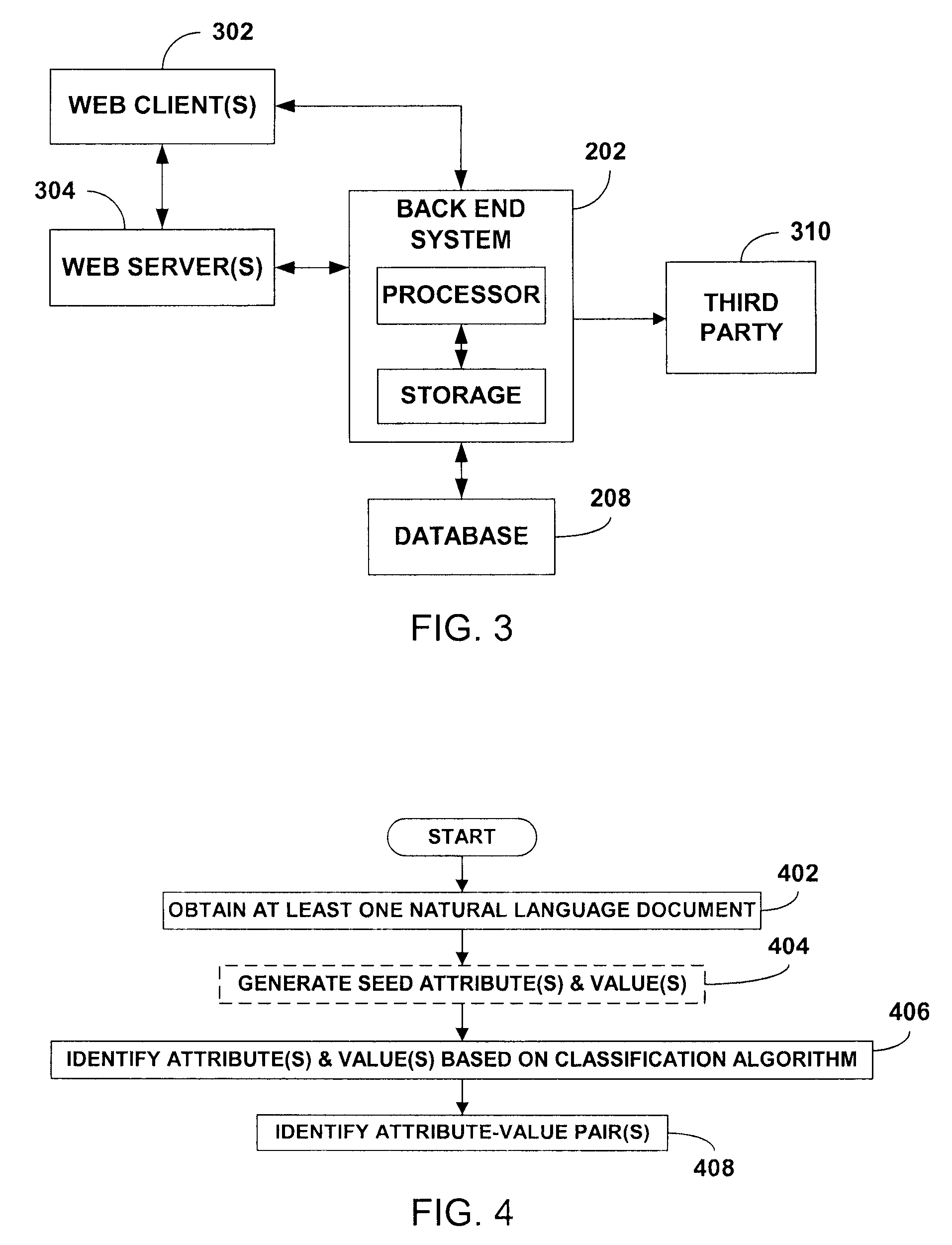
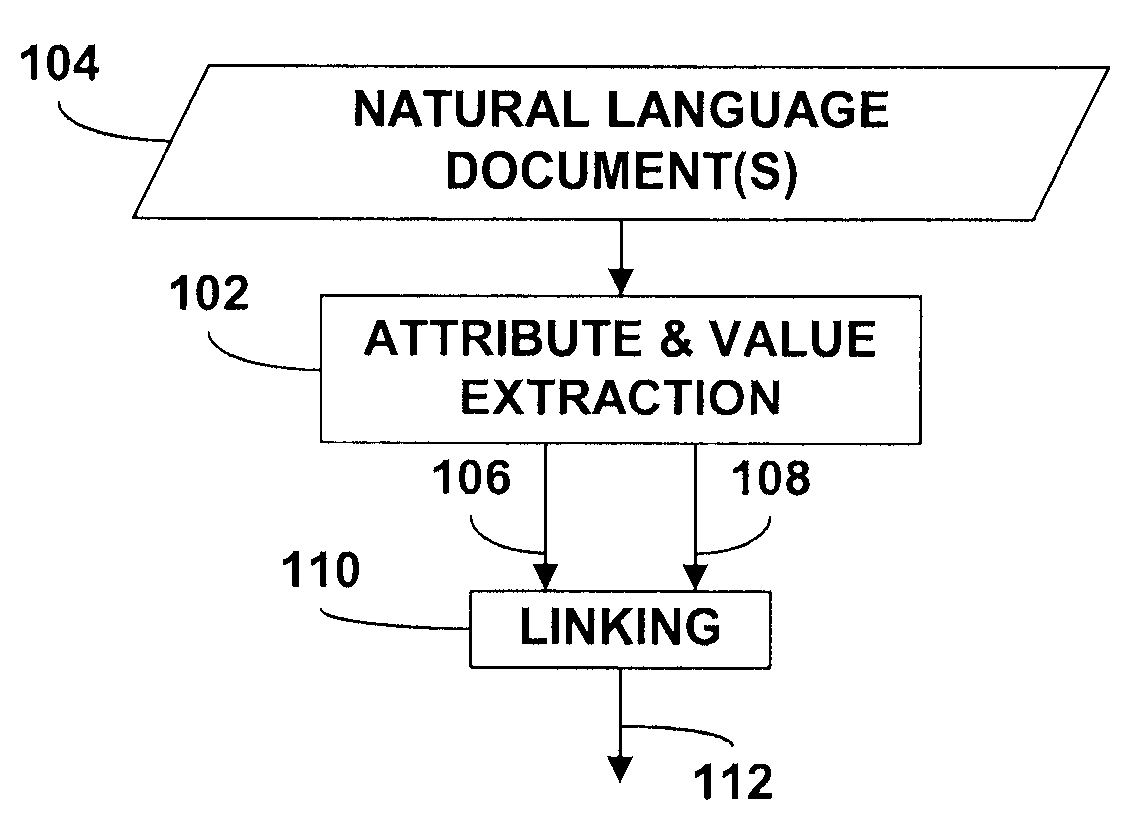
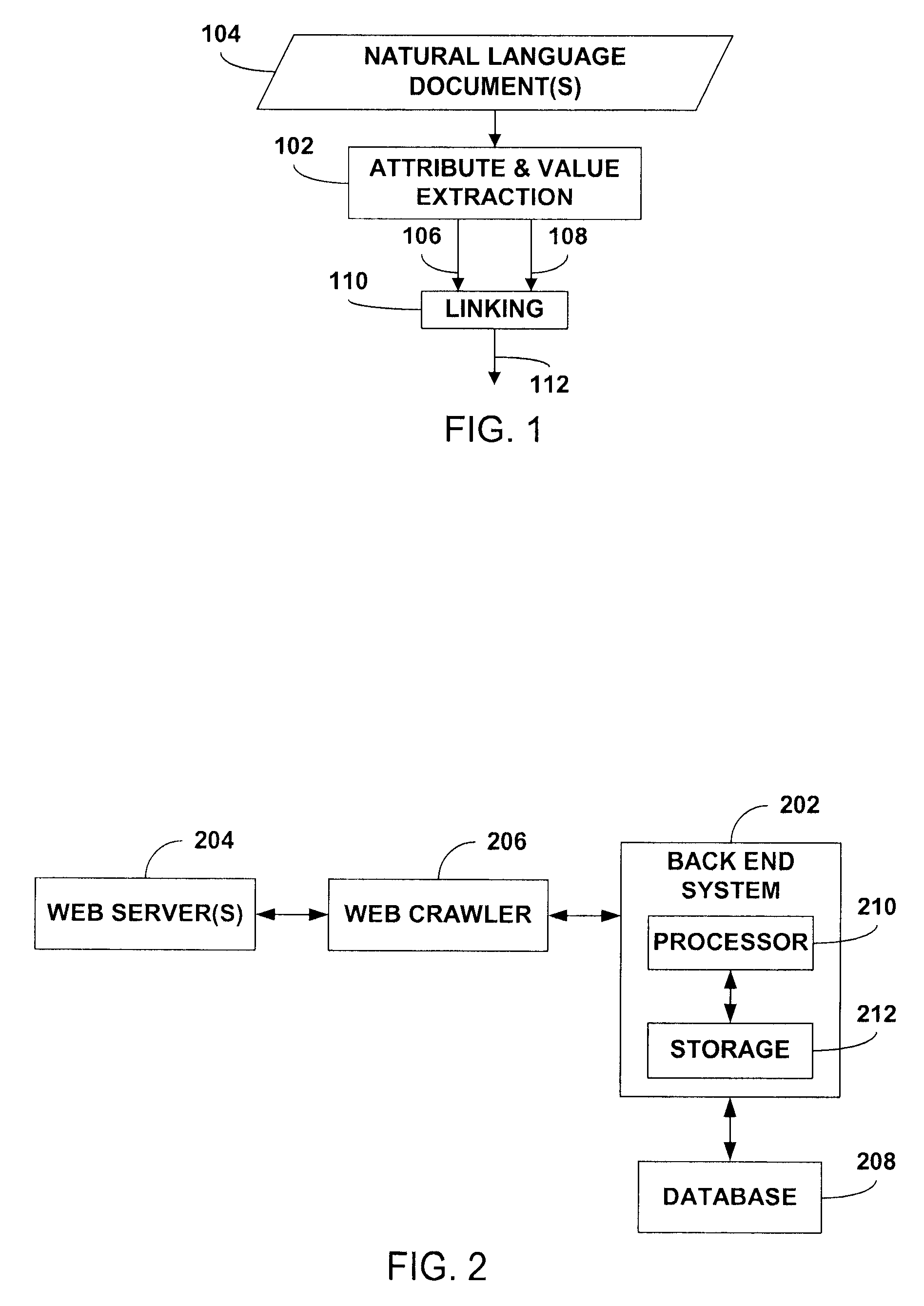
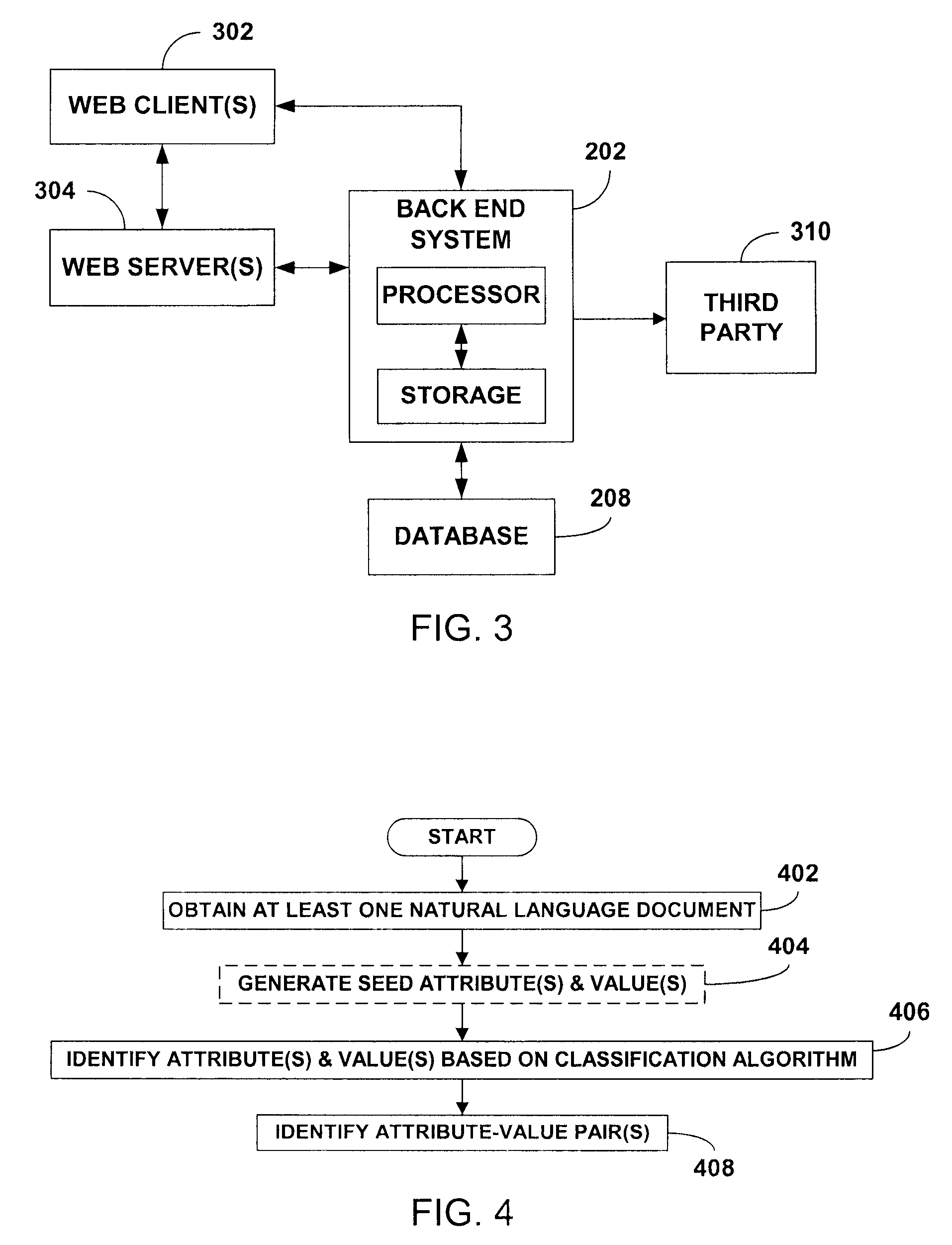
Extraction of attributes and values from natural language documents
ActiveUS20070282892A1Improve determinationEasy to implementNatural language analysisSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmDocument preparation
One or more classification algorithms are applied to at least one natural language document in order to extract both attributes and values of a given product. Supervised classification algorithms, semi-supervised classification algorithms, unsupervised classification algorithms or combinations of such classification algorithms may be employed for this purpose. The at least one natural language document may be obtained via a public communication network. Two or more attributes (or two or more values) thus identified may be merged to form one or more attribute phrases or value phrases. Once attributes and values have been extracted in this manner, association or linking operations may be performed to establish attribute-value pairs that are descriptive of the product. In a presently preferred embodiment, an (unsupervised) algorithm is used to generate seed attributes and values which can then support a supervised or semi-supervised classification algorithm.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
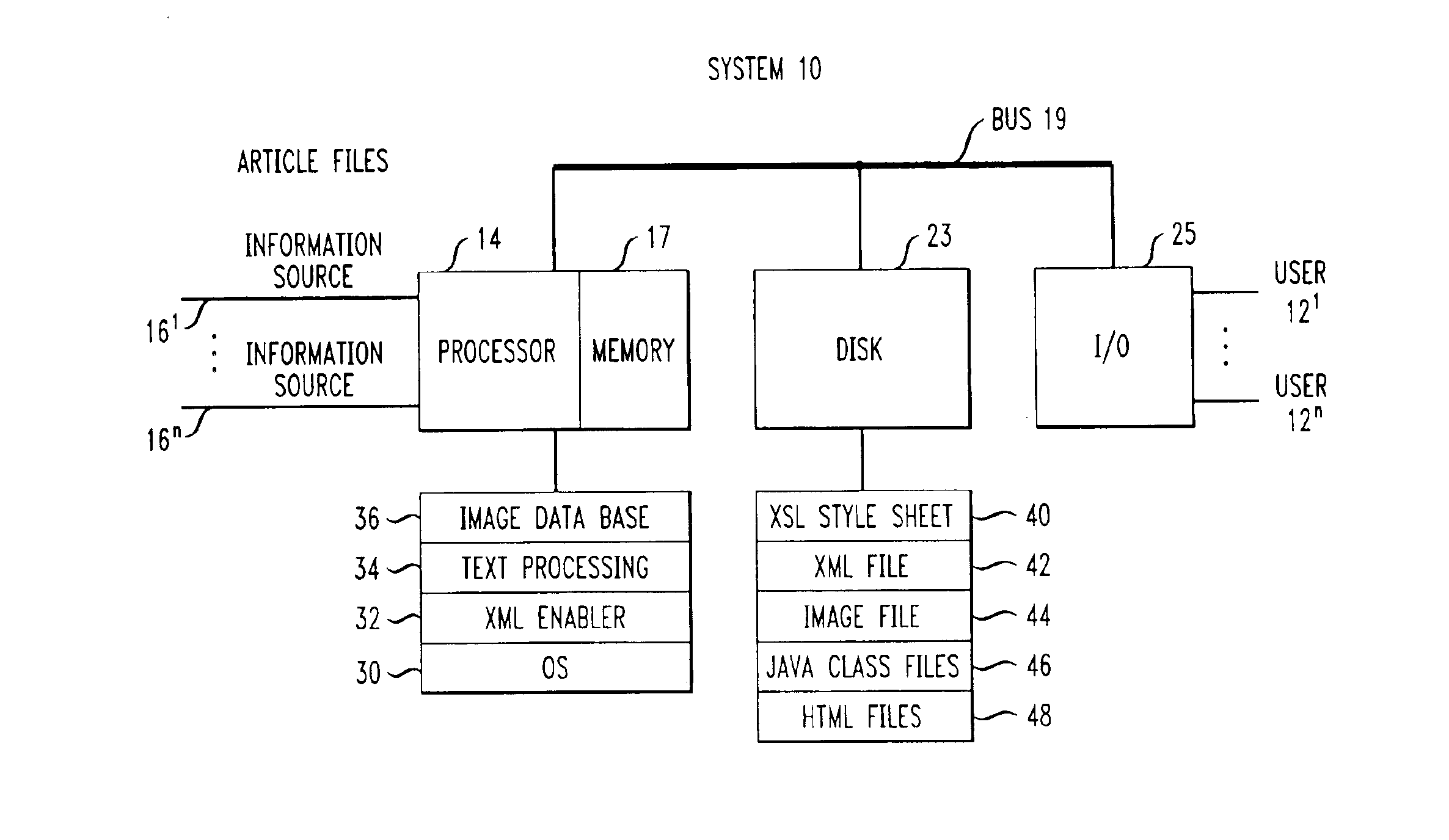
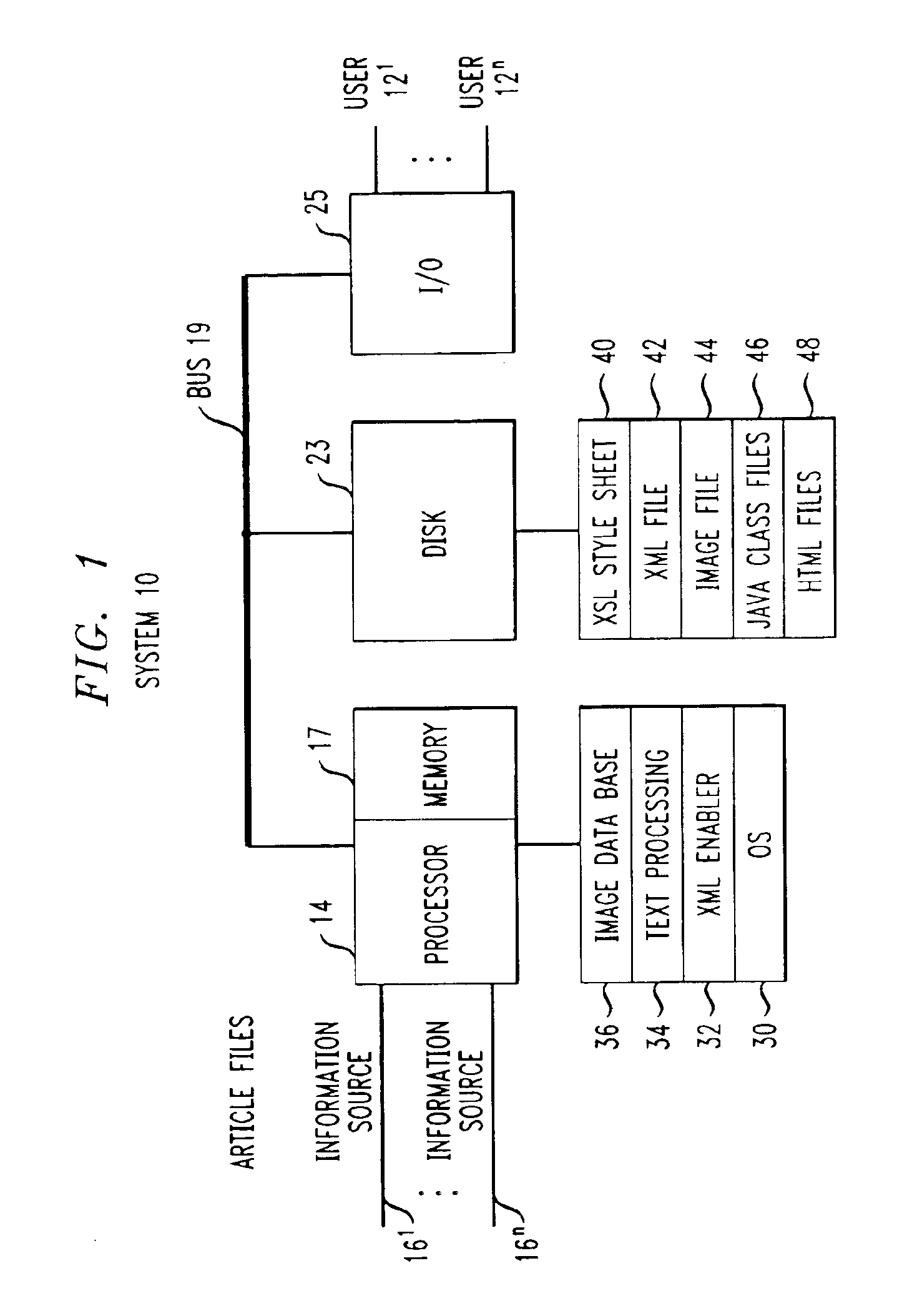
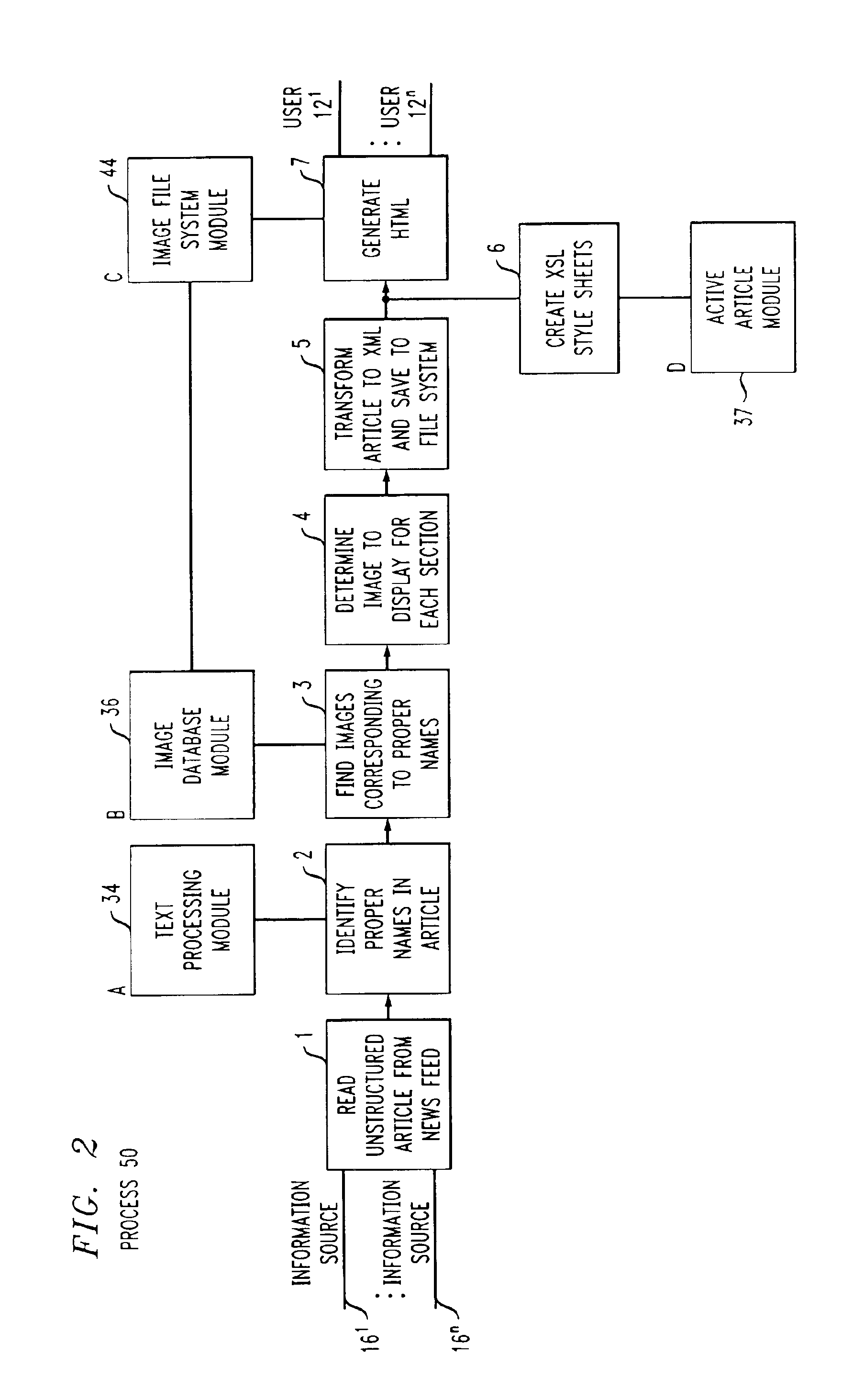
System and method for creating and editing, an on-line publication
InactiveUS7086002B2Digital computer detailsNatural language data processingQuery stringComputation process
A system and method automatically generate an on-line document from raw text into an engaging, interactive form for a plurality of viewers. Unstructured articles are read from an information feed. A computation process extracts and tags proper names of people, products, organizations, and places and categorizes them. An image database is used to link these proper names with image files. The image database consists of a series of attribute-value pairs for active searching of names. A URL query string is input to the database to extract the location of the image in the database file system. An Extensible Markup Language (XML) file is created from the raw text of the article, the list of proper names in the processed data and the image file references. The XML file is stored in a file system. An Extensible Stylesheet Language (XSL) file provides templates containing computational relationships between the text and images. The XML and XSL style sheets are combined to generate a Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) file containing an on-line story of the unstructured articles in a Java Applet which allows the system to provide a variety of interactive behaviors for a final presentation available by a viewer from a browser.
Owner:IBM CORP
Extraction of attributes and values from natural language documents
ActiveUS7996440B2Improve determinationEasy to implementNatural language analysisDigital data processing detailsDocumentation procedureAlgorithm
One or more classification algorithms are applied to at least one natural language document in order to extract both attributes and values of a given product. Supervised classification algorithms, semi-supervised classification algorithms, unsupervised classification algorithms or combinations of such classification algorithms may be employed for this purpose. The at least one natural language document may be obtained via a public communication network. Two or more attributes (or two or more values) thus identified may be merged to form one or more attribute phrases or value phrases. Once attributes and values have been extracted in this manner, association or linking operations may be performed to establish attribute-value pairs that are descriptive of the product. In a presently preferred embodiment, an (unsupervised) algorithm is used to generate seed attributes and values which can then support a supervised or semi-supervised classification algorithm.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Efficient merging and filtering of high-volume metrics
ActiveUS20170364563A1Relational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsInformation retrievalAttribute–value pair
The disclosed embodiments provide a system for processing data. During operation, the system obtains a set of records from a set of inputs, with each record containing an entity key, a partition key, and one or more attribute-value pairs. Next, the system sorts and indexes the records by the entity key for each partitioned input. The system then processes a query of the records by matching entity key values to the sorted and indexed records for each input partition in the query. Next, the system merges the subset of records with the same entity key values into records, with each merged record containing an entity key field and a single field that includes a list of attribute-value pairs from the subset. Finally, the system outputs the merged records in response to the query.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of data retrieval, and search engine using such a method
InactiveUS20110022600A1Many possibilityEasy to operateDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData retrievalReverse index
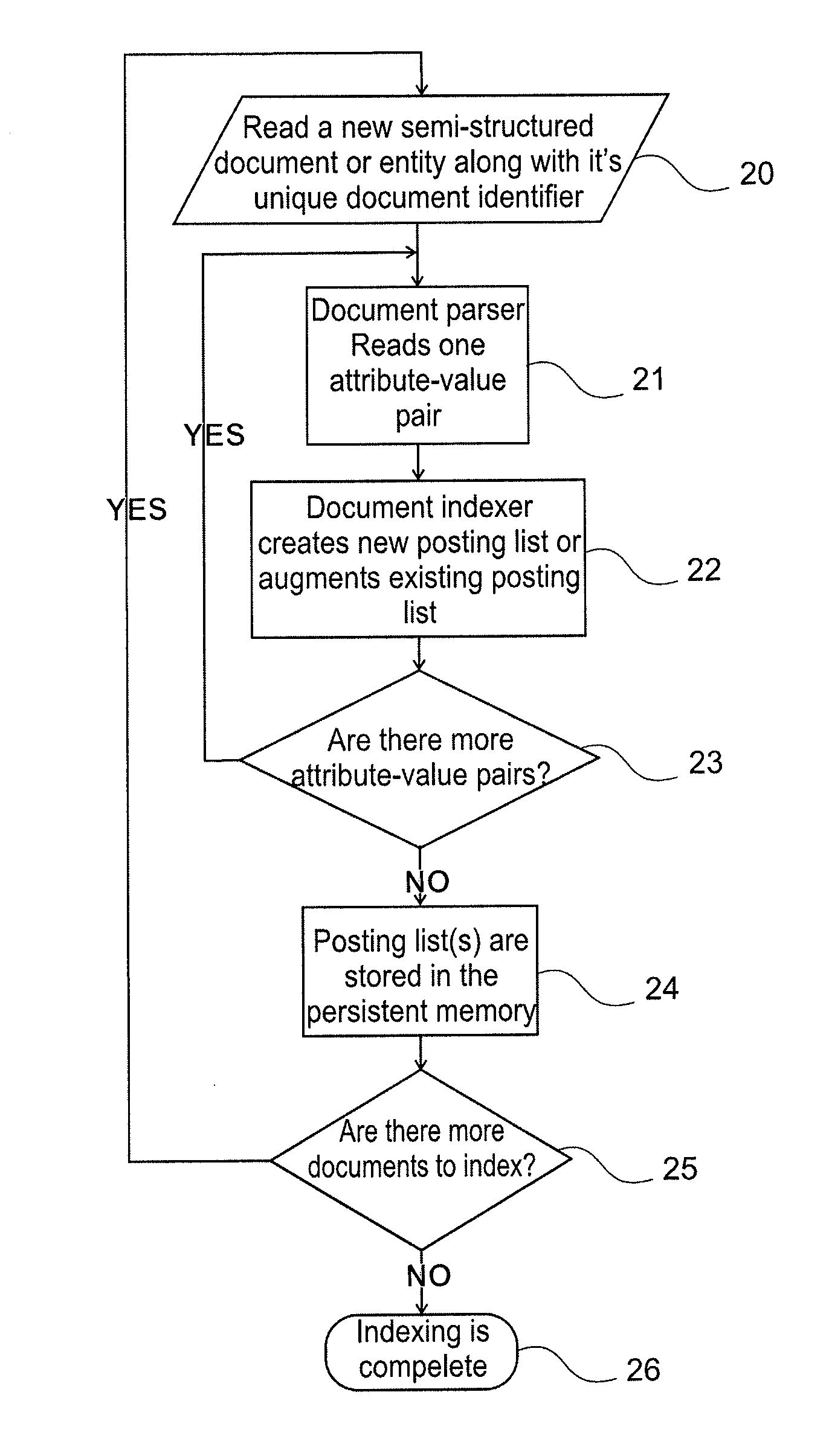
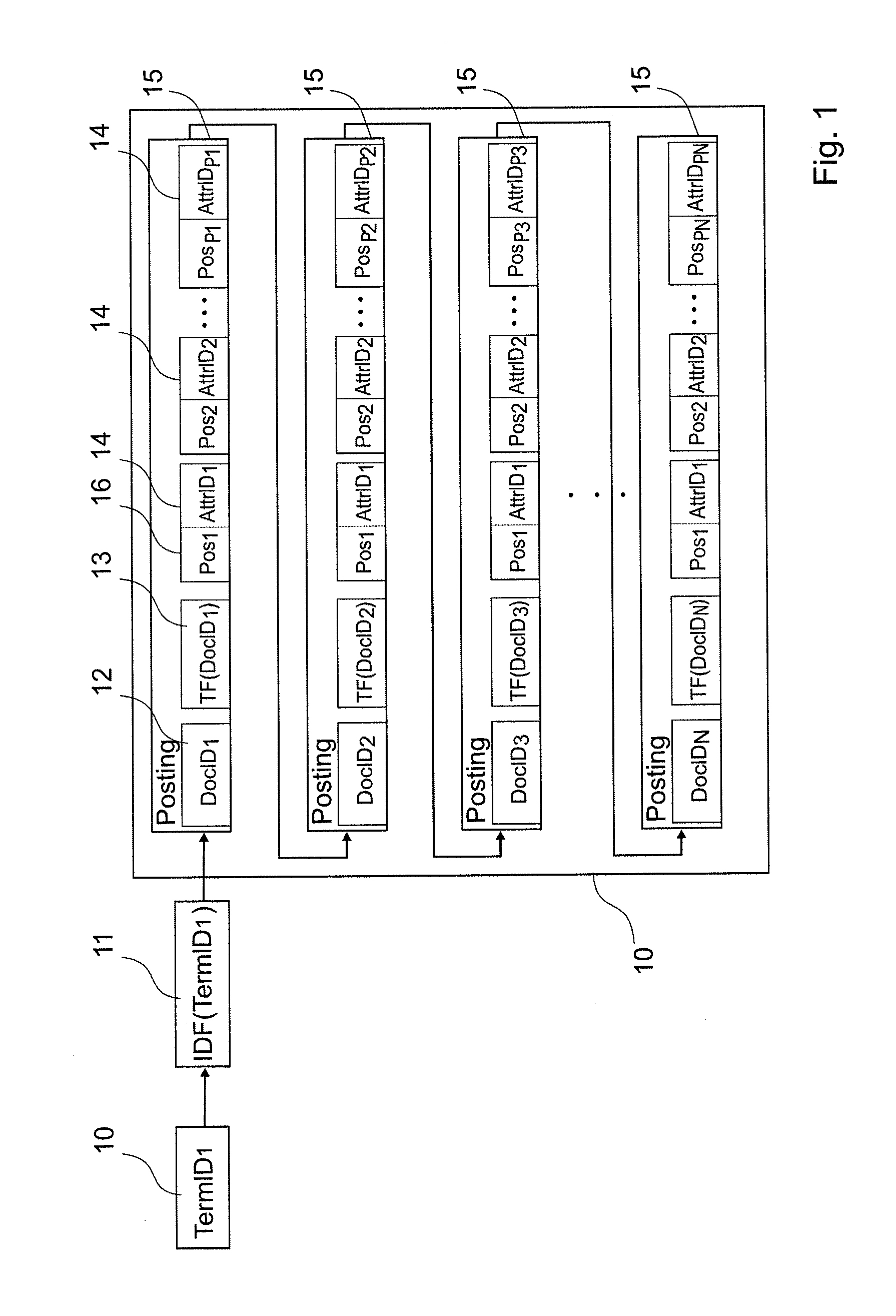
A method of data retrieval from a data repository in response to a query having either list of keywords and / or list of attribute-value pairs, the method comprising the steps of:providing an inverted index generated from the data repository, the inverted index indicating the attribute with which each term is encountered in each entity when such an attribute is available;retrieving data from the inverted index by searching said inverted index based on said attribute-value pairs or keywords;providing scores to entities.A method of forming an inverted index from a data repository and a search engine for retrieval of data from a data repository is also provided.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
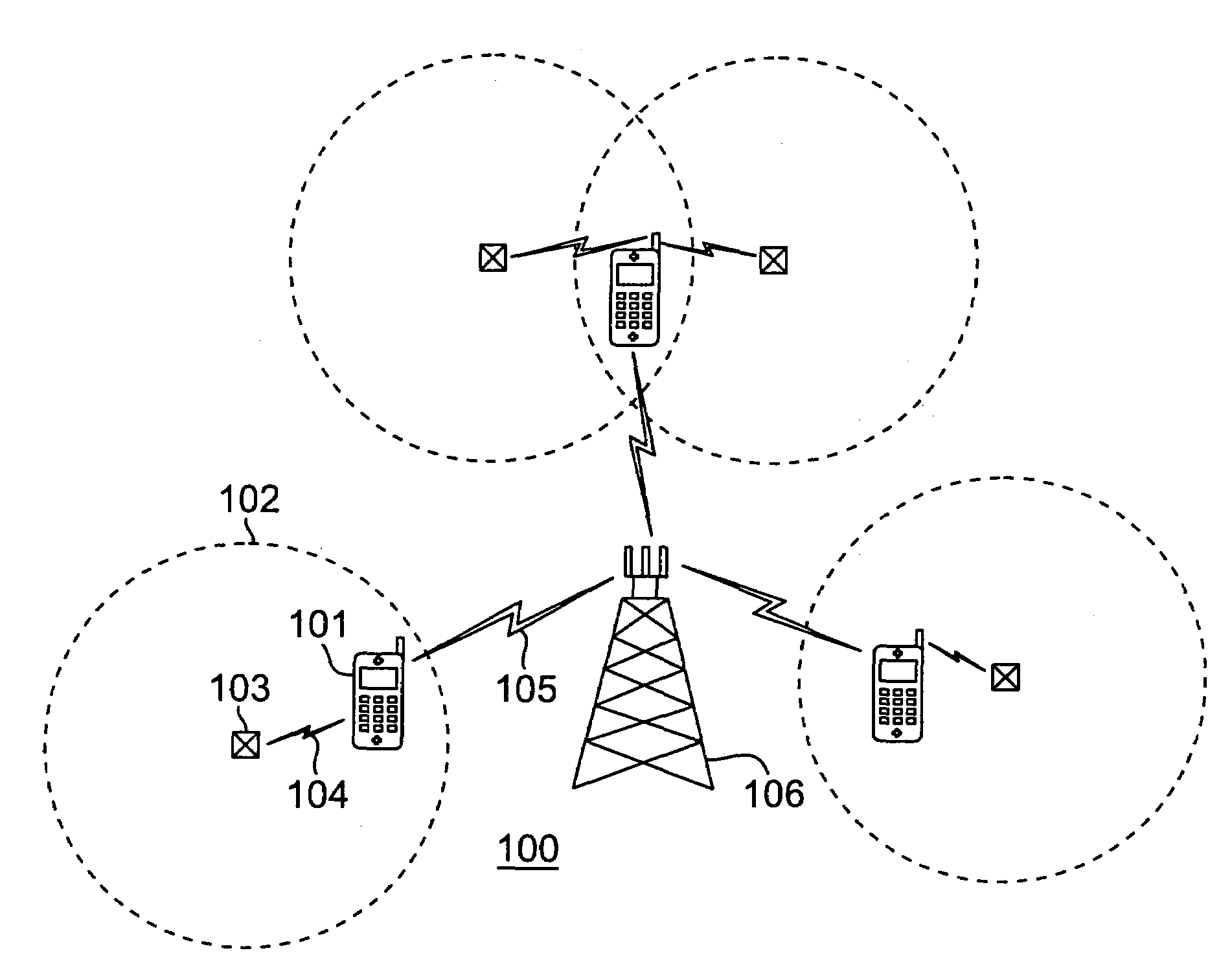
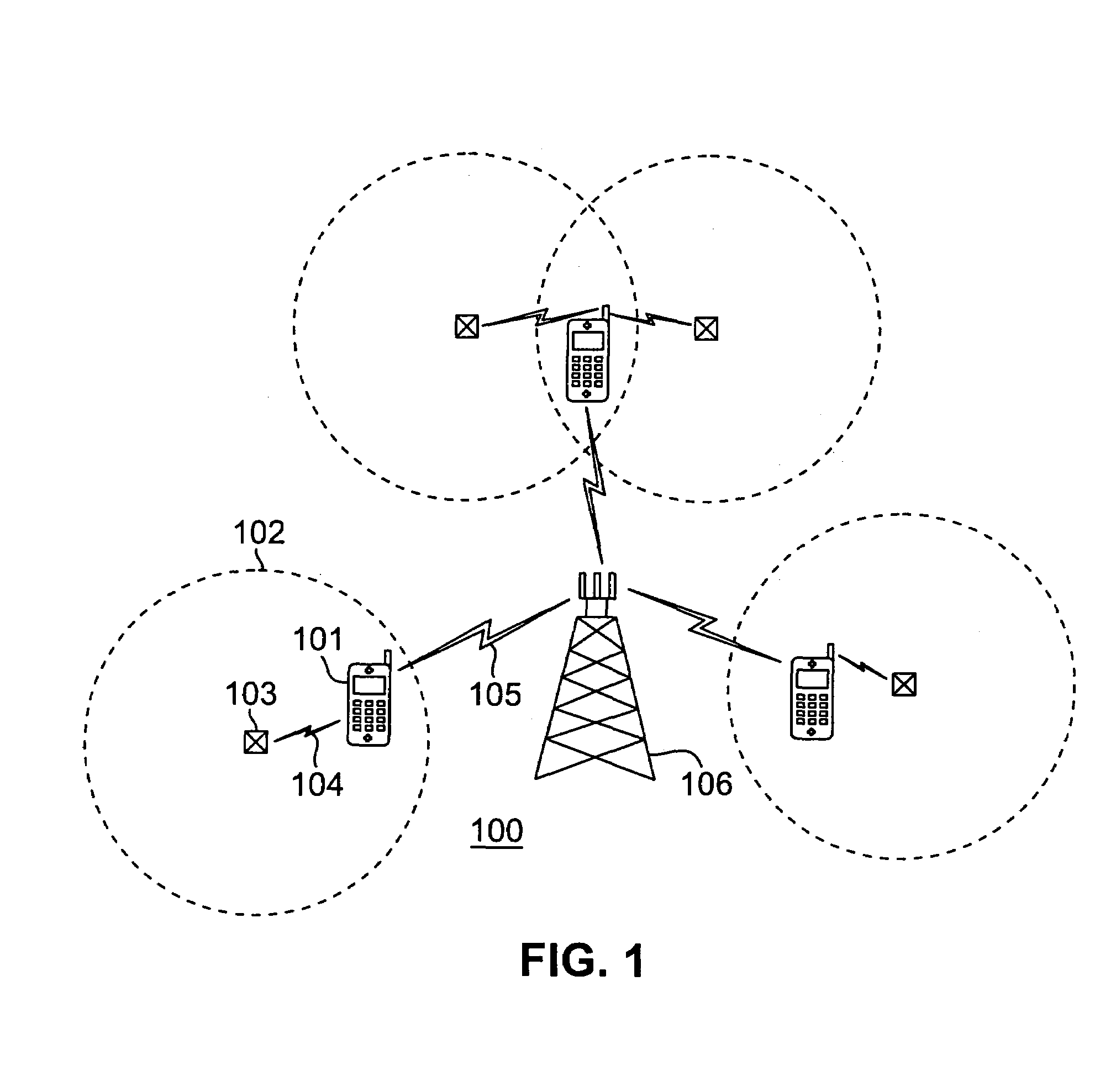
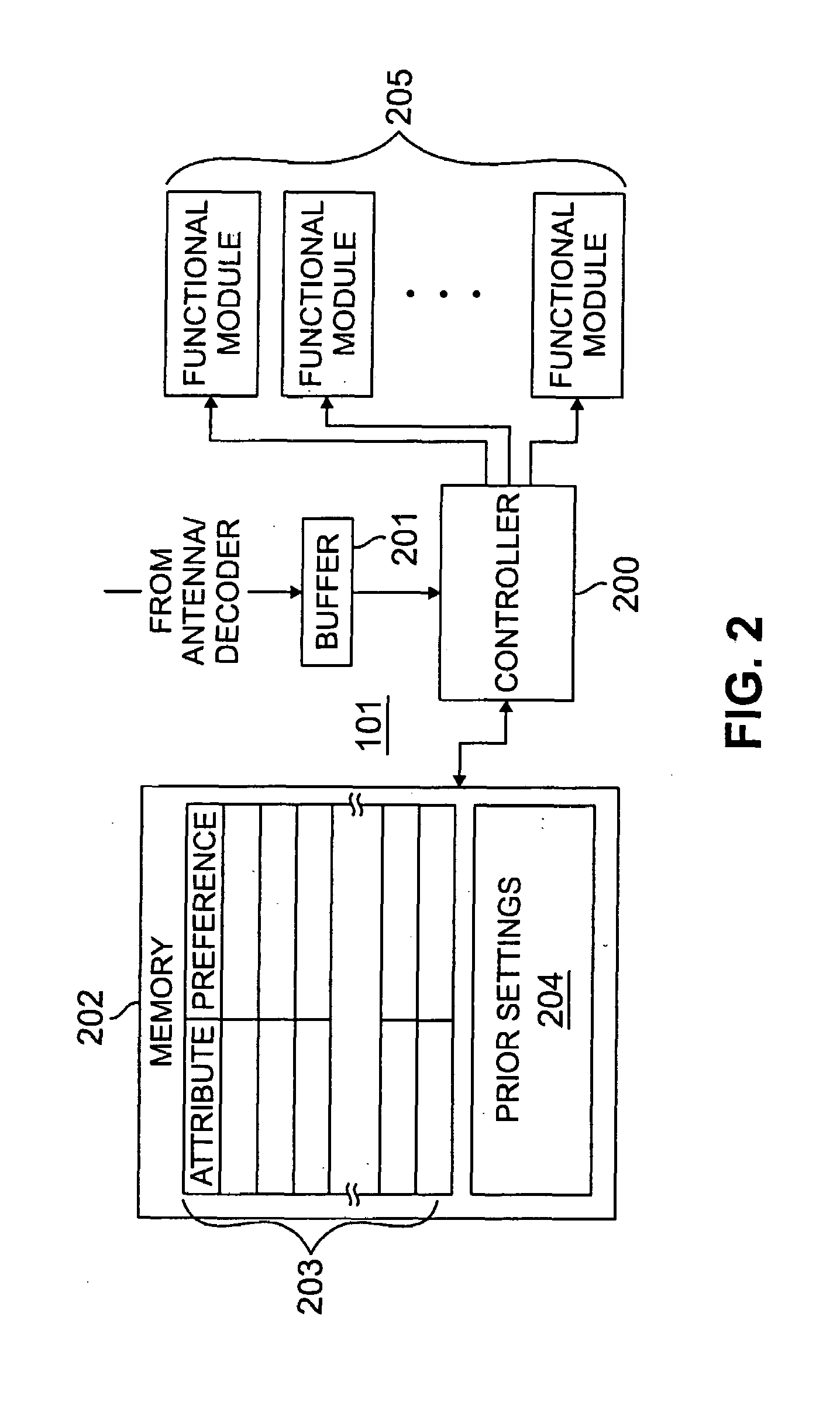
Method and apparatus for optional automatic configuration of wireless communications device behavior within small area transmitter service regions
InactiveUS7209705B2Guaranteed automatic operationNear-field transmissionRadio transmissionAuto-configurationCommunication device
A zone-based behavior service is supported by a small area wireless transmitter to communicate behaviors, encoded as attribute-value pairs, to wireless devices within the service area of the small area transmitter. In response to entering the service area and discovering the zone-based behavior service, operation of a wireless communications device is automatically customized to conform to the specified behaviors according to corresponding user preferences. For example, audible ring tones are automatically disabled when proscribed by the zone-based behavior service and such proscription is accepted by the user in previously defined attribute options, but automatic re-routing of incoming calls suggested by the behavior service may be rejected by the user or require manual acceptance from the user. Upon leaving the service area of the small area transmitter, the wireless communications device automatically restores prior operational parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Developing diameter applications using diameter interface servlets
ActiveUS8042118B2Facilitate communicationCreates delayMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication serverBase class
Mechanisms for developing Diameter applications are provided. The mechanisms extend the application server servlet model to support Diameter applications. A “base protocol” servlet is provided that handles the basic Diameter protocol functionality. Base application servlets are provided for each Diameter interface (for example, an “Sh” base servlet for the IMS “Sh” interface). These servlets are base classes for application code. The base application servlets implement additional semantics on top of the base protocol servlet to support additional attribute-value pair semantics. With the system and method, Diameter servlets share the same ServletContext as HTTP and SIP servlets. This mechanism facilitates communication between the various application entities and facilitates generation of converged applications.
Owner:SNAPCHAT
System and method for retrieving and normalizing product information
InactiveUS8768937B2Shorten the timeWeb data retrievalDigital data processing detailsWorld Wide WebAttribute–value pair
A method and system for retrieving and normalizing product information are described. The system retrieves product information from sources that are accessed over a network. Next, the system creates markup language based on the product information. The markup language includes a first attribute-value pair that includes a first attribute and a first value. Next, the system normalizes the markup language by translating the first attribute to a second attribute responsive to an identification of the first attribute in a list that includes a plurality of attributes that are associated with a first product and the second attribute. The second attribute is a canonical representation of the plurality of attributes respectively.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
Charging for an IP based communication system
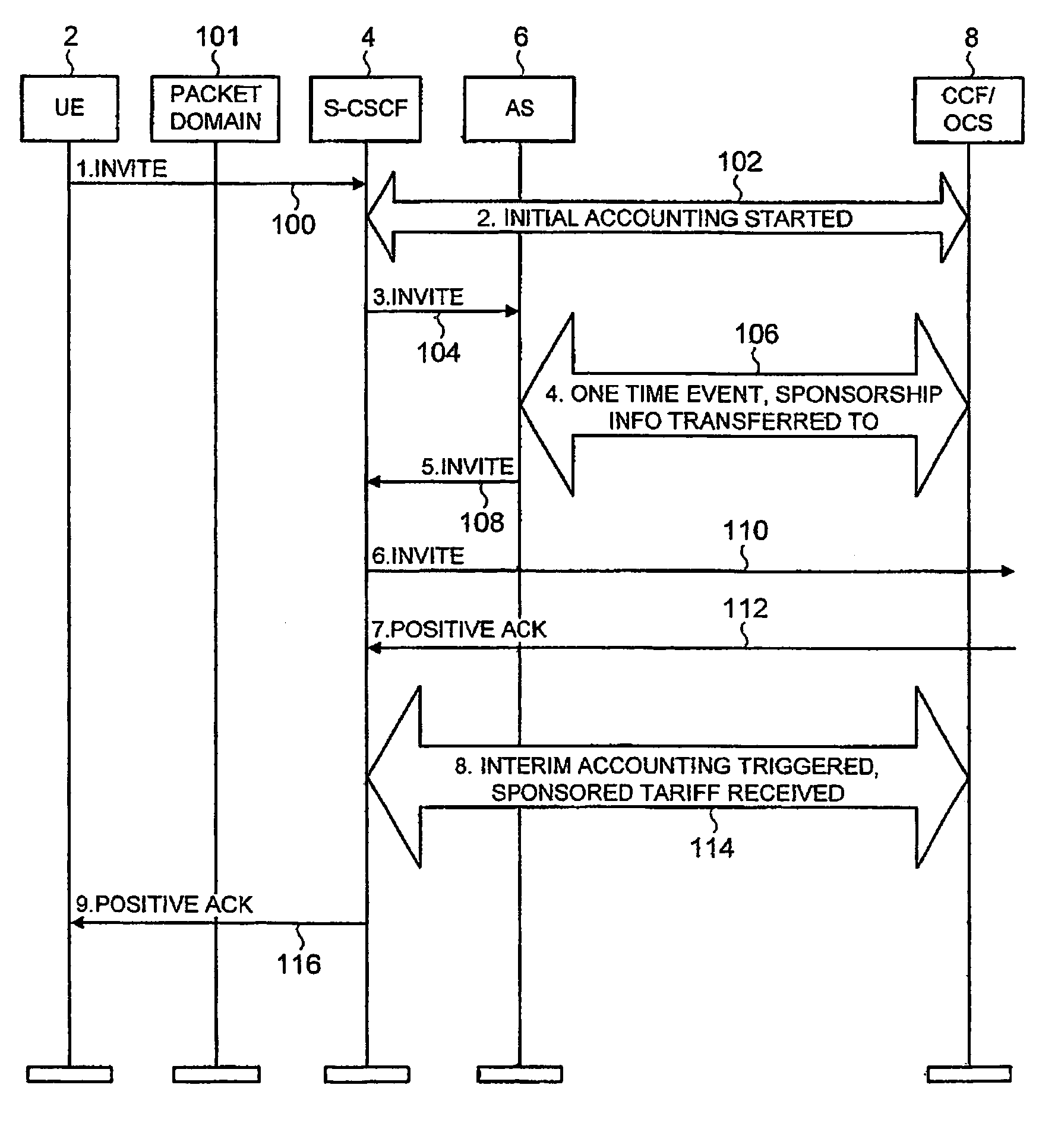
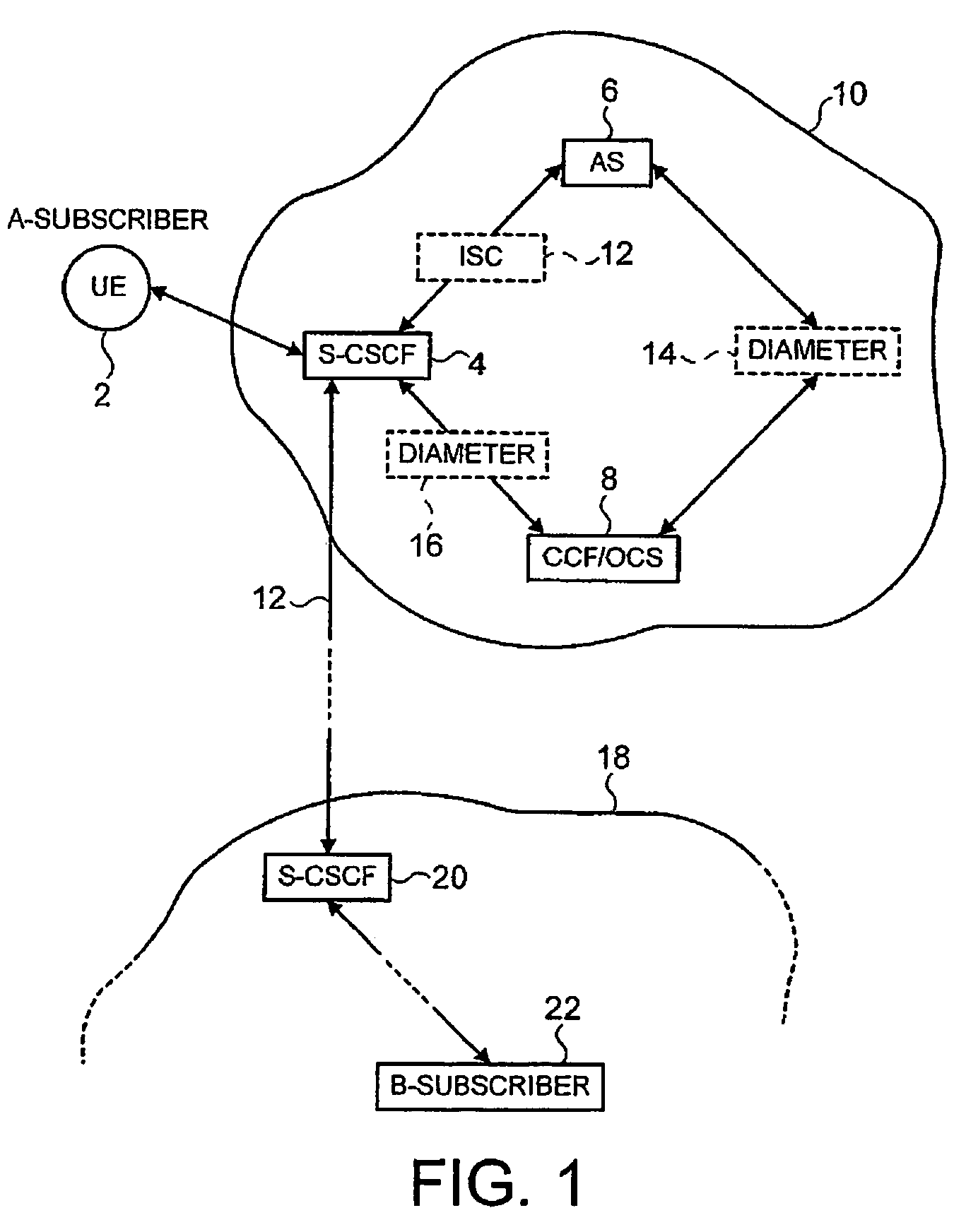
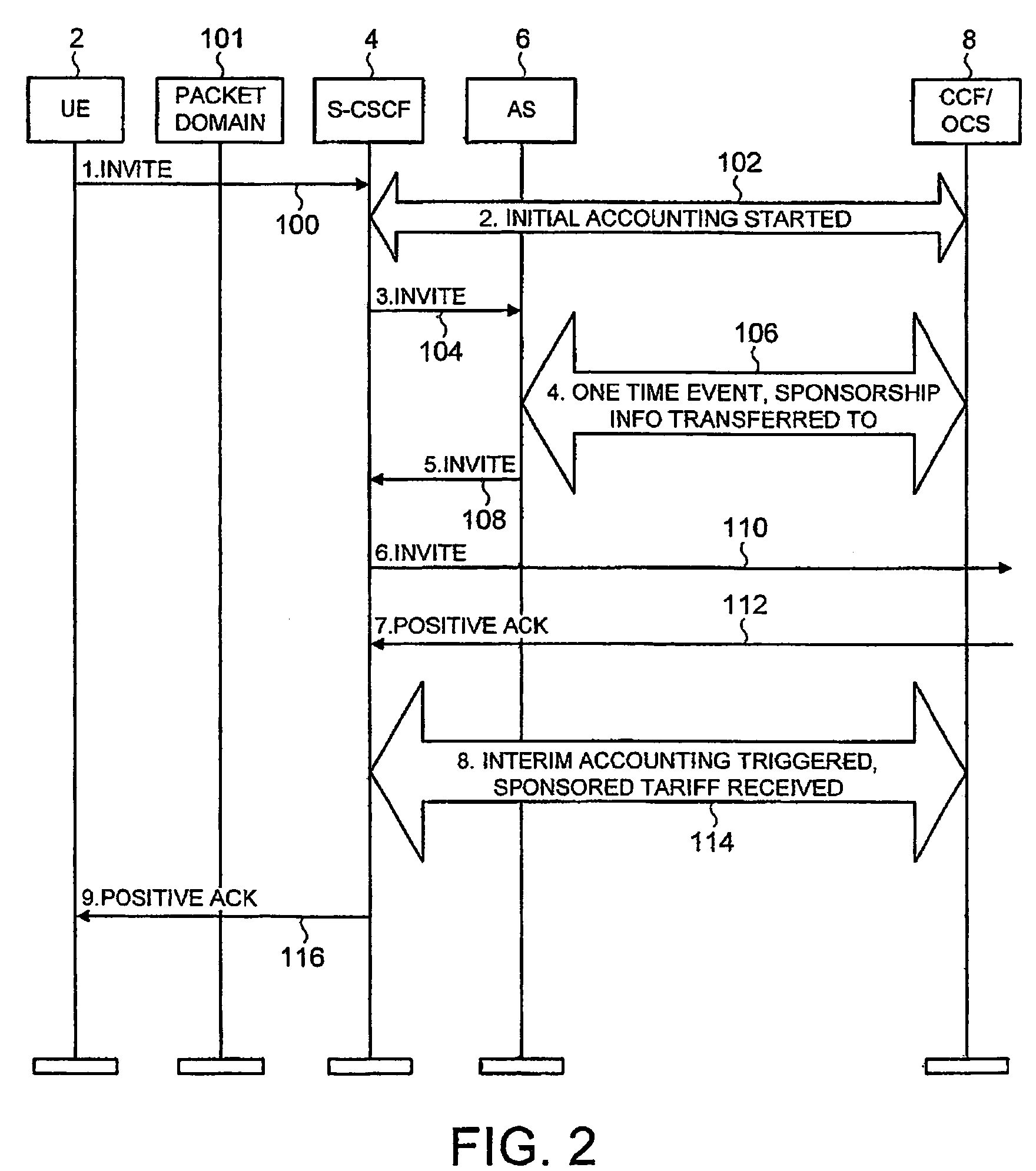
ActiveUS7424102B2Effective sponsorshipIncrease the diameterSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsCommunications systemAttribute–value pair
There is disclosed a method for charging for services in a communication system supporting a Diameter IP protocol, comprising defining at least one attribute value pair to define sponsorship information.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Notification method of user equipment access protocol and system thereof
InactiveCN101447918AFacilitate the execution of subsequent processingAccounting/billing servicesTelephonic communicationUser equipmentNotification system
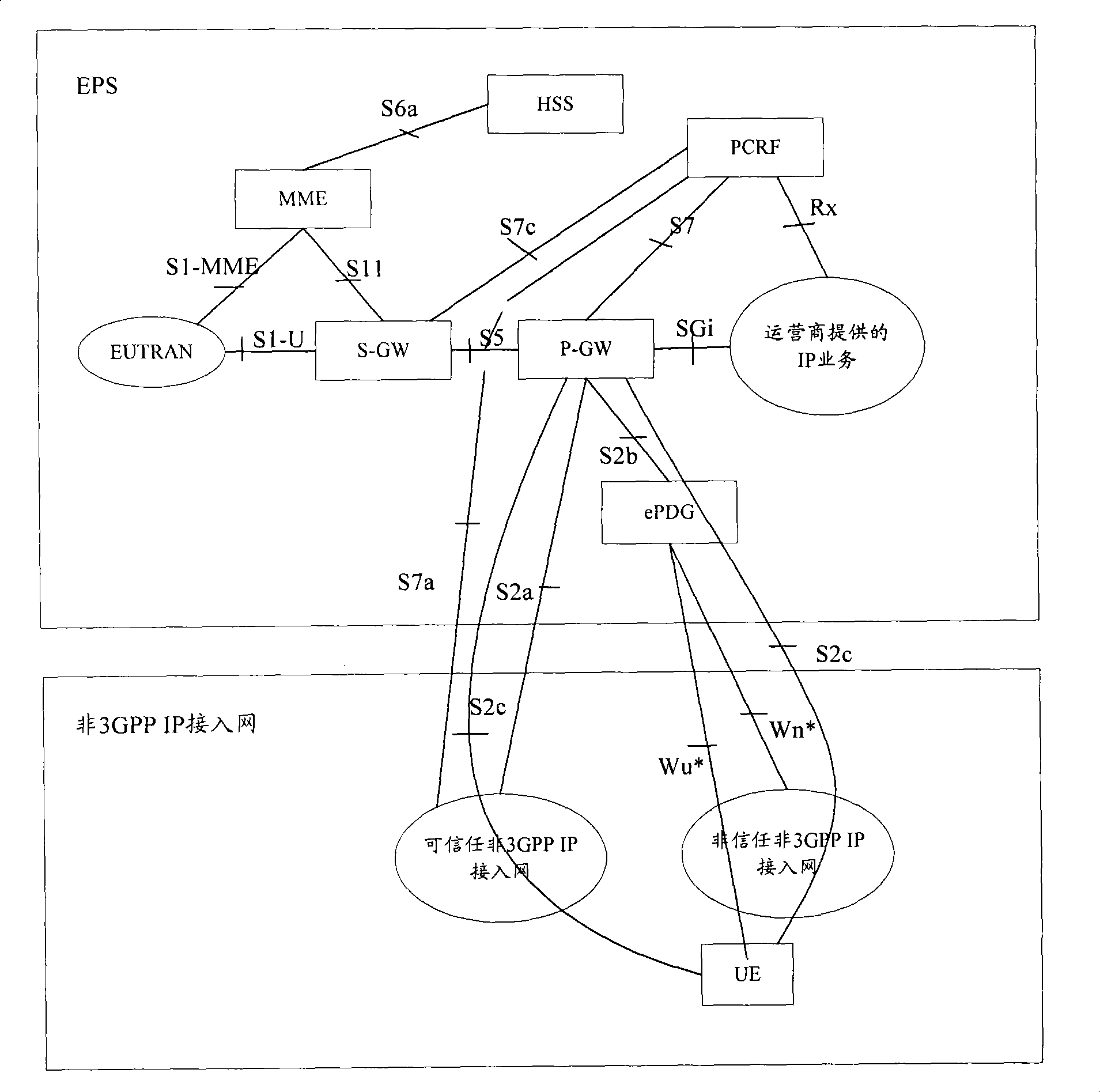
The invention discloses a notification method of a user equipment access protocol. The method comprises the following steps: step S402: when user equipment accesses to a network by a specific protocol, an access gateway assigns a care-of address to the user equipment, a specific attribute value pair is set in a first session request message to represent the care-of address, and the first session request message is sent to a policy and charging rule function entity; step S404: a packet data network gateway assigns a home address to the user equipment, and the user equipment sends the care-of address and the home address to the packet data network gateway; and S406: the packet data network gateway sets a specific attribute value pair in the second session request message to represent the care-of address, and a preset attribute value pair represents the home address, and the session request message is sent to the policy and charging rule function entity. Additionally, the invention further discloses a notification system of the user equipment access protocol.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method, apparatus and computer program product for making semantic annotations for easy file organization and search
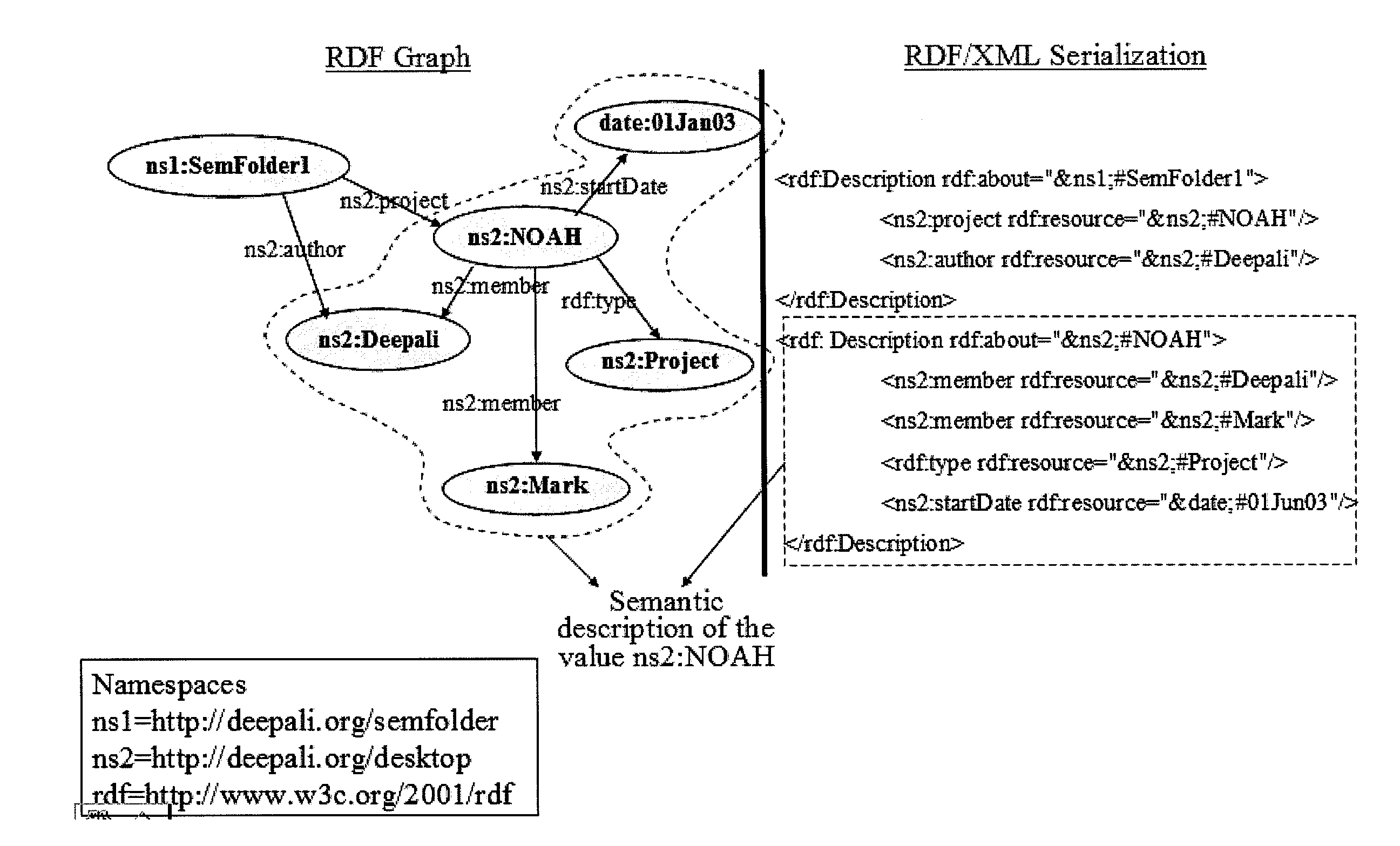
InactiveUS7702645B2Easy to createEase organizationData processing applicationsObject oriented databasesComputer scienceSemantic annotation
A device for generating semantic folder annotations is provided. The device includes a semantic folder editor which enables a user to create attribute-value pairs corresponding to a semantic folder(s). The device is capable of downloading ontolog(ies) and associated data from an ontology server which may be utilized to determine relationships between the attribute-value pairs created by the user. The device includes an annotations generator which specifies the semantic folder descriptions of the semantic folders based on attribute-value relationships determined by the ontolog(ies). The device is capable of allowing a user to insert an object(s) into a semantic folder(s) and the annotations generator assigns all attribute-value pairs corresponding to the semantic folder to the object(s). The annotations assigned to object(s) may be stored in a semantic triple store. The device further includes a search engine which may be employed by a user to search semantic folders to locate an object(s).
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Extraction of attributes and values from natural language documents
InactiveUS20070282872A1Improve determinationEasy to implementDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmDocument preparation
One or more classification algorithms are applied to at least one natural language document in order to extract both attributes and values of a given product. Supervised classification algorithms, semi-supervised classification algorithms, unsupervised classification algorithms or combinations of such classification algorithms may be employed for this purpose. The at least one natural language document may be obtained via a public communication network. Two or more attributes (or two or more values) thus identified may be merged to form one or more attribute phrases or value phrases. Once attributes and values have been extracted in this manner, association or linking operations may be performed to establish attribute-value pairs that are descriptive of the product. In a presently preferred embodiment, an (unsupervised) algorithm is used to generate seed attributes and values which can then support a supervised or semi-supervised classification algorithm.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Extraction of attributes and values from natural language documents
InactiveUS7970767B2Improved determinationEasy to implementDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDocumentation procedureAlgorithm
One or more classification algorithms are applied to at least one natural language document in order to extract both attributes and values of a given product. Supervised classification algorithms, semi-supervised classification algorithms, unsupervised classification algorithms or combinations of such classification algorithms may be employed for this purpose. The at least one natural language document may be obtained via a public communication network. Two or more attributes (or two or more values) thus identified may be merged to form one or more attribute phrases or value phrases. Once attributes and values have been extracted in this manner, association or linking operations may be performed to establish attribute-value pairs that are descriptive of the product. In a presently preferred embodiment, an (unsupervised) algorithm is used to generate seed attributes and values which can then support a supervised or semi-supervised classification algorithm.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com