Ion exchange chromatography fixed phase, preparing method and application of the same
An ion-exchange chromatography and stationary phase technology, applied in the field of ion-exchange chromatography stationary phase and its preparation and application, can solve the problem of low protein recovery rate and achieve improved separation selectivity, good biocompatibility and biological affinity, high The effect of mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
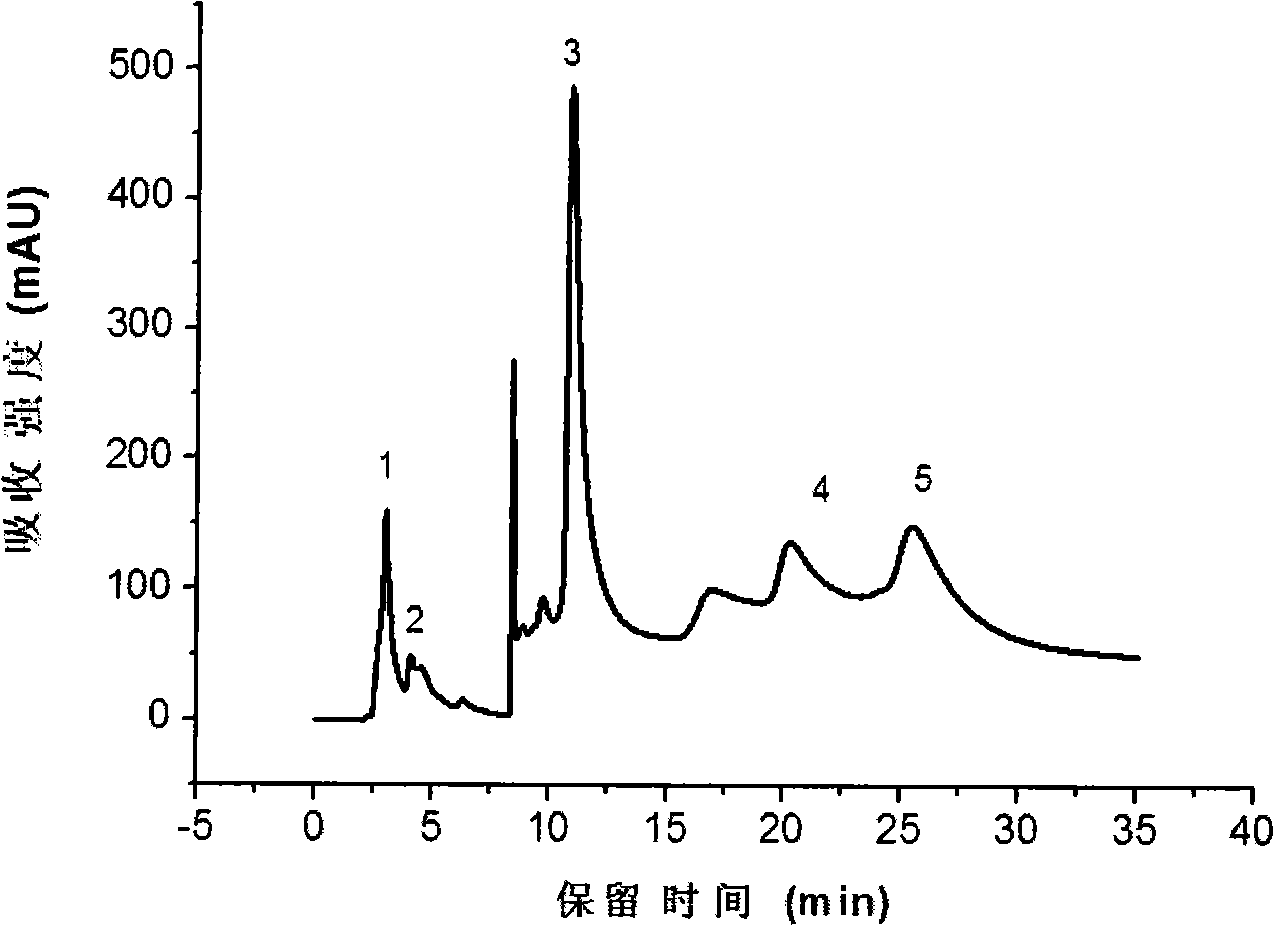
[0017] Example 1: Preparation of hydroxyapatite-coated zirconium-magnesium composite oxide ion-exchange chromatography stationary phase and separation of proteins
[0018] (1) Preparation of supersaturated calcium-phosphorus solution: Dissolve analytically pure sodium chloride, potassium chloride, disodium hydrogen phosphate, hydrochloric acid, and calcium chloride in water successively, and its ion concentrations are respectively [Na + ]=136.8mM, [K + ]=3.71mM, [Cl - ]=144.5mM, [Ca 2+ ] = 3.10 mM, [HPO 4 2- ] = 1.86 mM. The prepared solution was adjusted to pH 7.4 with trishydroxymethylaminomethane and stored at 5°C.
[0019] (2) Deposition and growth of hydroxyapatite coating: the zirconium-magnesium composite oxide was treated with 1M sodium hydroxide, washed until neutral, and dried at 160° C. for 8 hours. Next, immerse in 0.5M disodium hydrogen phosphate solution and saturated calcium hydroxide solution in turn, wash and dry at 120°C. Then soak it in 500mL supersat...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: Preparation of hydroxyapatite-coated silica gel microspheres ion-exchange chromatography stationary phase and separation of proteins
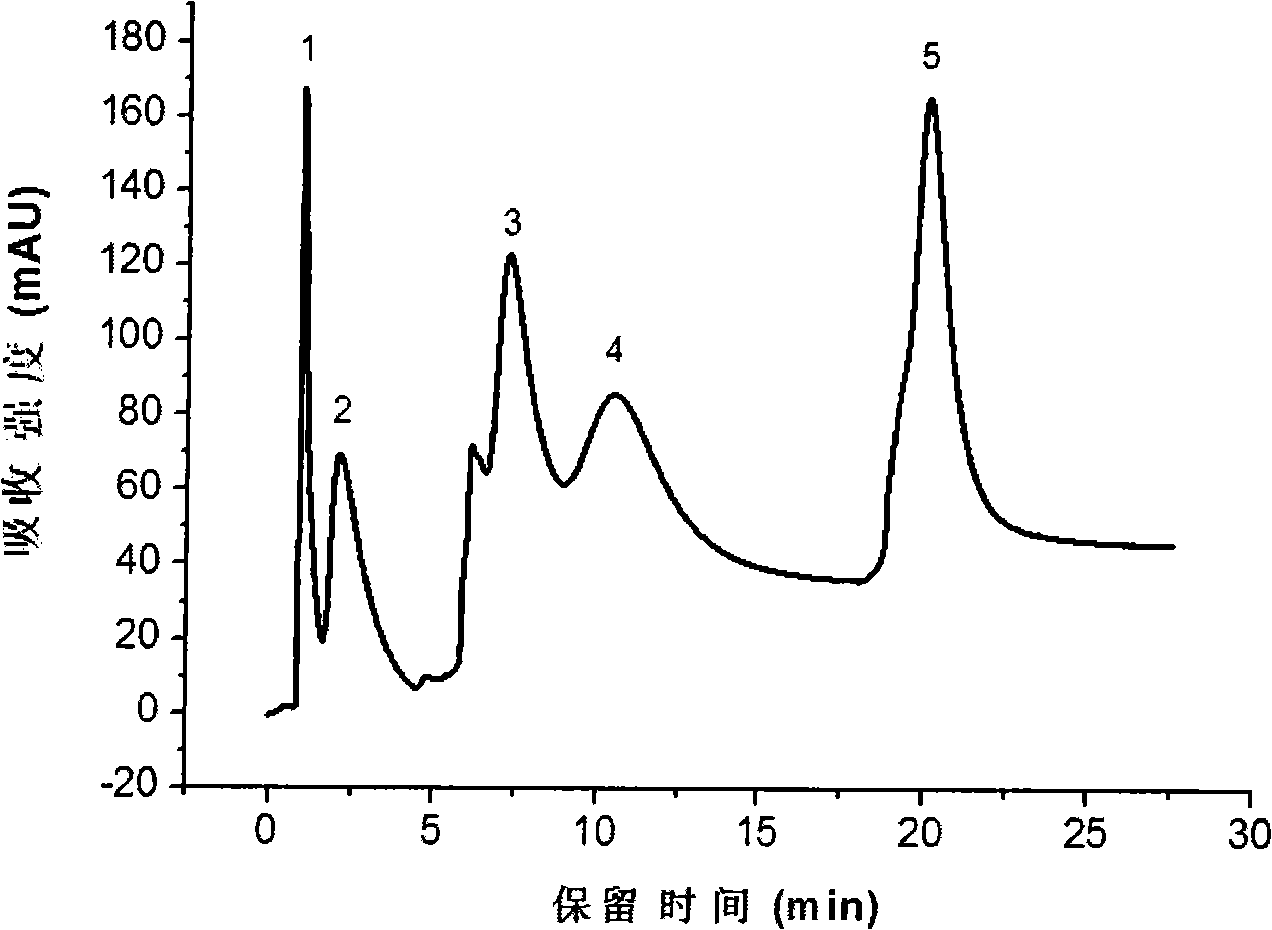
[0022] The 5 μm silica gel microspheres were treated with 1M hydrochloric acid, washed until neutral, and dried at 160°C for 8 hours. Soak it in 500mL of supersaturated calcium-phosphorus solution, keep the temperature at 36.5±0.5°C, take it out after soaking for a period of time, rinse it with secondary water, and dry it at 120°C. The above-mentioned materials were packed into a 150mm × 4.6mmi.d. chromatographic column, and with phosphate buffer solution as mobile phase, five kinds of proteins were separated in gradient mode (such as figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
[0023] Example 3: Preparation of hydroxyapatite-coated capillary
[0024] Take the capillary, rinse with 1M sodium hydroxide solution, secondary water, 1M hydrochloric acid, and secondary water for 1 hour in sequence, and then dry at 120° C. for 4 hours under nitrogen. Under the action of gravity, the supersaturated calcium-phosphorus solution was continuously injected into the capillary, and the temperature was kept at 36.5±0.5° C., and deposited for 14 days to prepare the capillary coated with hydroxyapatite.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com