Method for extracting coenzyme Q10 from microorganism
An extraction method and microbial technology, applied in the field of extracting coenzyme Q10, can solve the problems of time-consuming, low extraction rate, and unsuitable for batch sample application, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost, high extraction rate, and rapid reagents and operation steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031]Embodiment 1, extract coenzyme Q from Rhodobacter sphaeroides 10
[0032] Coenzyme Q is extracted from Rhodobacter sphaeroides by ultrasonic crushing method of the present invention 10 , the specific method includes the following steps:
[0033] 1. Fermentation and cultivation of Rhodobacter sphaeroides
[0034] Rhodobacter sphaeroides ATCC 17023 (purchased from the American Type Microorganism Collection) was added to the medium shown in Table 1. The medium is mixed with the components in Table 1, the final volume is adjusted to 1 liter, the pH is adjusted to 7.0 (pH6-8 is acceptable), and then autoclaved at 121° C. for 20 minutes. For solid media, mix the above ingredients with 15 g of agar, then autoclave, cool the media to about 60°C, and pour into sterilized Petri dish plates. Stir under aerobic conditions, ferment and cultivate for 28 hours at a temperature of 25-35° C. (18-72 hours are all available). After the cultivation, 4 g of wet bacterial cells were obta...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: Alkaline alcohol saponification method extracts coenzyme Q 10 And HPLC content detection (control)
[0054] 1. Alkaline alcohol saponification to extract coenzyme Q 10
[0055] Take 4g of fermented product of Rhodobacter sphaeroides ATCC 17023, add 3g of pyrogallic acid, stir evenly, then add 5g of sodium hydroxide and 26mL of methanol aqueous solution, stir evenly, saponify at 90°C for 1 hour, after cooling rapidly, add 50mL of n-hexane, vigorously After oscillating, let stand to separate layers, extract twice, take the extract, wash with deionized water until neutral, then remove water with anhydrous sodium sulfate, 35°C rotary evaporation under reduced pressure, redissolve in absolute ethanol to obtain coenzyme Q 10 The crude extract was stored at -20°C until testing.
[0056] 2. HPLC content detection
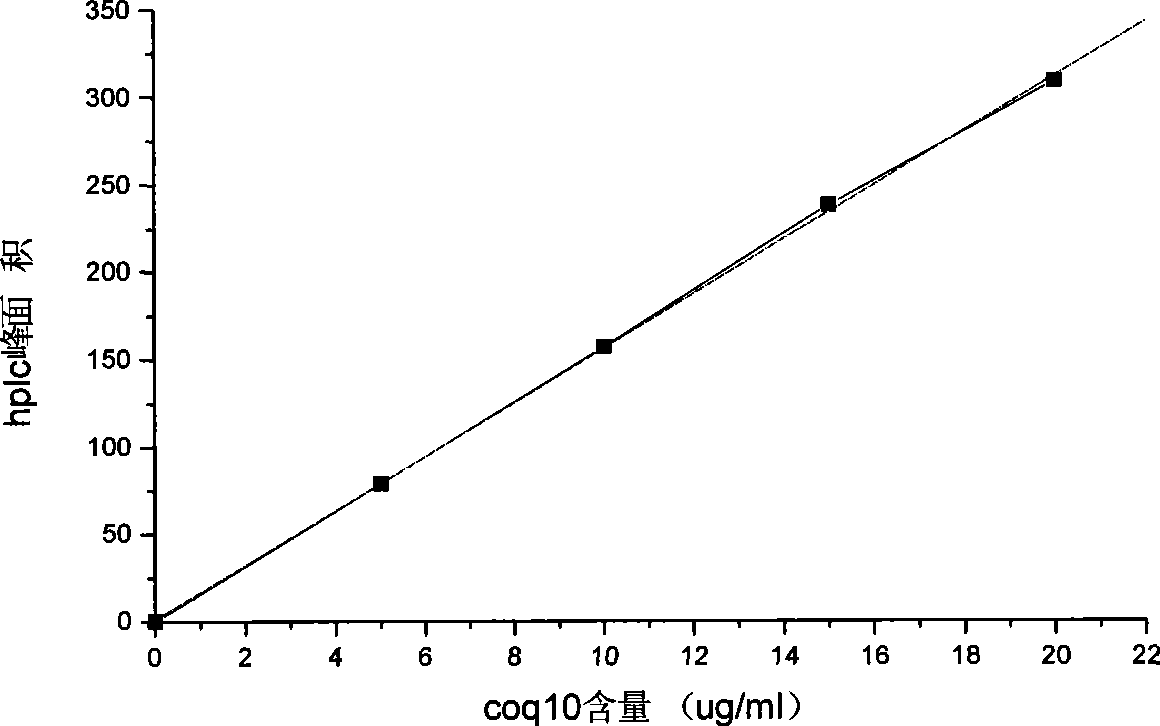
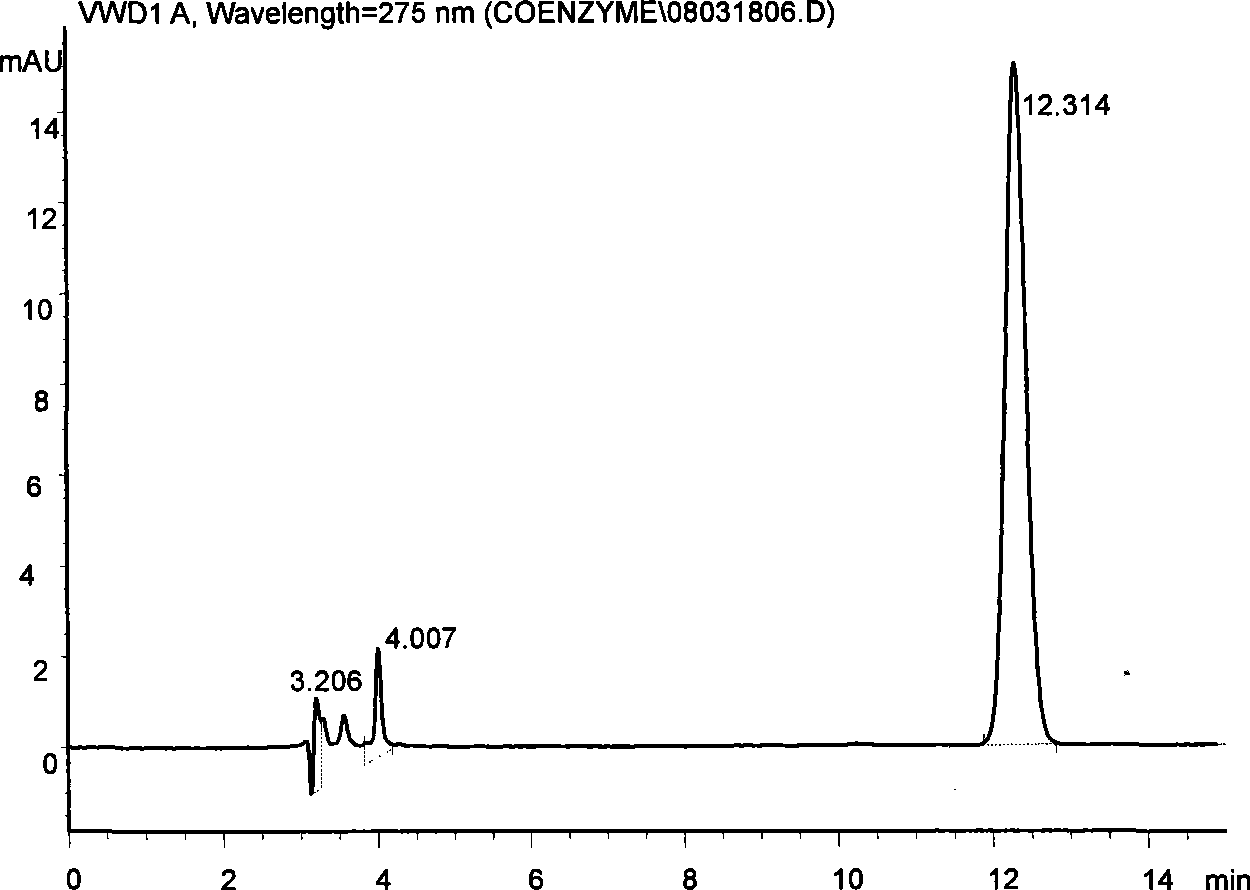
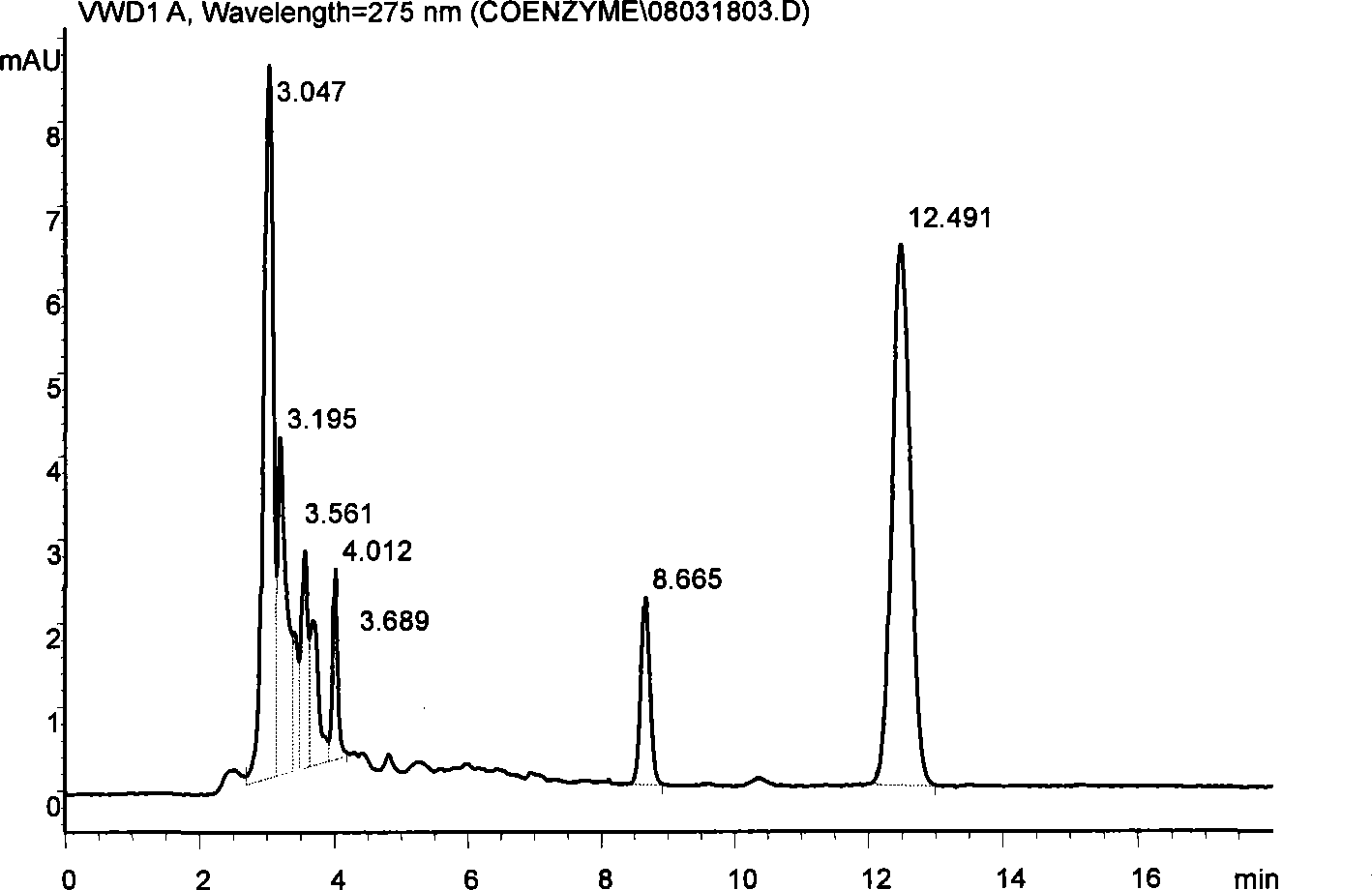
[0057] Carry out HPLC analysis with the method identical with step 2, the result is as follows Figure 4 As shown, coenzyme Q appears at the rete...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3: Coenzyme Q is extracted by alkaline lysis 10 And HPLC content detection
[0059] Coenzyme Q is extracted from Rhodobacter sphaeroides ATCC 17023 fermentation product by alkaline lysis method of the present invention 10 , the specific method includes the following steps:
[0060] Preparation of alkaline lysate:
[0061] Solution I: Accurately weigh 0.9908g glucose, 0.3028g Tris Cl, 0.3722g EDTA, dissolve them in distilled water, adjust the volume to 100mL, adjust the pH to 8.0, sterilize at 121°C for 20min, and put them into 10mL sterile EP tubes , stored at 4°C for later use.
[0062] Solution II: Accurately weigh 0.4000g NaOH and 0.5000g SDS, dissolve them in distilled water, dilute to 50mL, and set aside.
[0063] Solution III: Accurately weigh 14.7225g of potassium acetate, dissolve in distilled water, add 5.75mL of glacial acetic acid, make up to 50mL with distilled water, divide into 10mL sterile EP tubes, and store at 4°C for later use.
[0064]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com