Method for detecting oxidative metal ion in water
A metal ion and oxidizing technology, applied in the direction of electrochemical variables of materials, can solve the problem of low lead, etc., and achieve the effect of low price, simple equipment and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
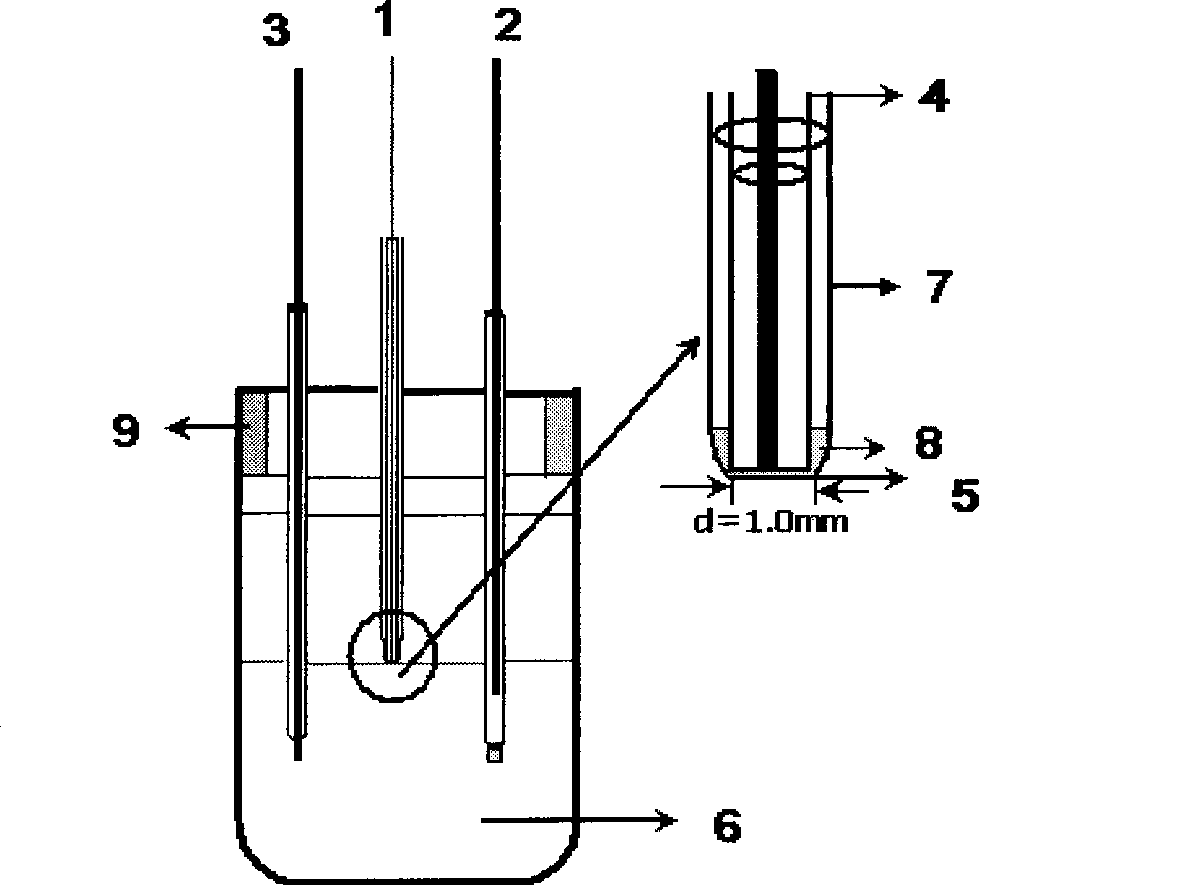
[0033] This example uses an electrochemical workstation (Autolab, PGSTAT30, Netherland Metrohm Co.Ltd) and an electrochemical three-electrode test system. The reference electrode is a calomel electrode, and the auxiliary electrode is a platinum electrode. The platinum wire is inserted into the capillary and sealed at the front to form Platinum electrode (working electrode).
[0034] The iodine stock solution was obtained by direct preparation to study the reaction mechanism of iodine at the interface of MIBK / aqueous solution. The preparation method is prepared by the reaction of hydrogen peroxide and KI, and then the exact concentration is calibrated by the iodometric method, and the corresponding dilution is carried out according to the concentration required for the experiment. Pipette the calibrated iodine solution and MIBK in a separatory funnel to carry out an equal-volume extraction, and after standing to separate layers, take the extracted I 2 The MIBK was placed in a ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This example uses an electrochemical workstation (Autolab, PGSTAT30, Netherland Metrohm Co.Ltd) and an electrochemical three-electrode test system. The reference electrode is a calomel electrode, and the auxiliary electrode is a platinum electrode. The platinum wire is inserted into the capillary and sealed at the front to form Platinum electrode (working electrode).
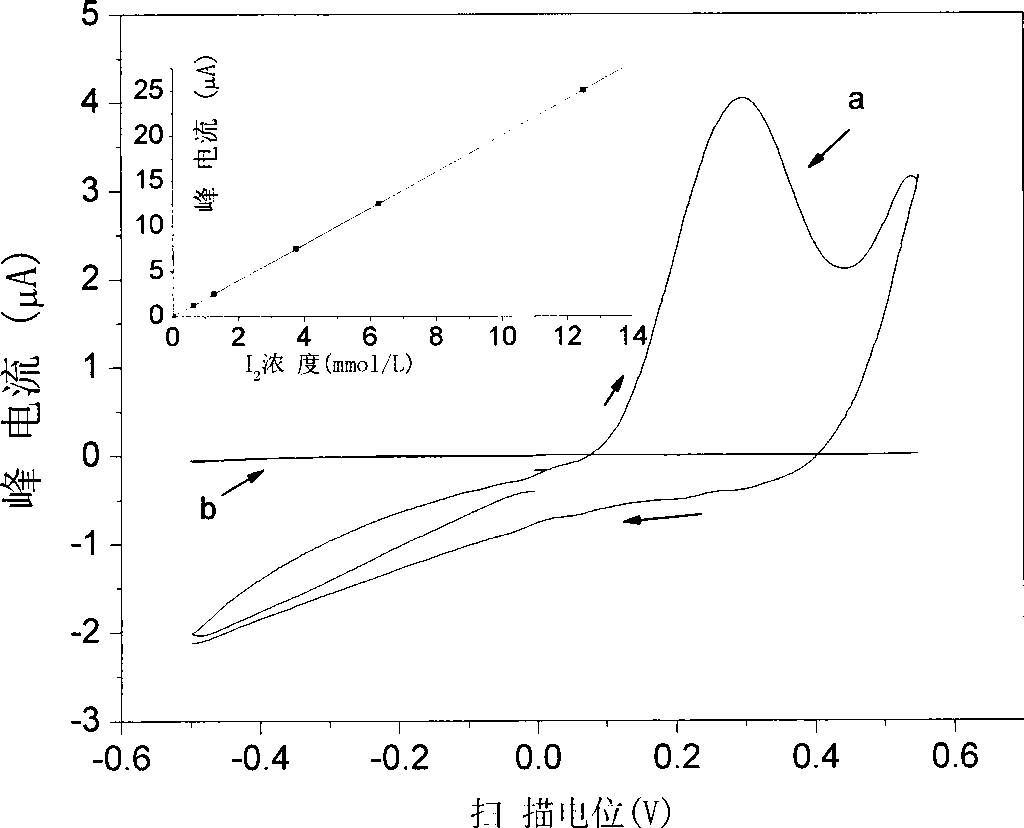
[0041] Pipette the copper ion solution into a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, transfer excess KI solution, add water to dilute to 10ml, add an equal volume of MIBK solvent, and extract in the Erlenmeyer flask. During the measurement, use a micro-injector to draw a small amount (generally 20-40 μL) of the extracted sample and inject it into a glass microtube. The aqueous phase is a 1mol / L KCl solution, which is circulated on the liquid / liquid interface with a three-electrode system. Voltammetric analysis (eg figure 1 shown).
[0042] The cyclic voltammetry conditions are: the scanning potential range is -0.5...
Embodiment 3
[0045] This example uses an electrochemical workstation (Autolab, PGSTAT30, Netherland Metrohm Co.Ltd) and an electrochemical three-electrode test system. The reference electrode is a calomel electrode, and the auxiliary electrode is a platinum electrode. The platinum wire is inserted into the capillary and sealed at the front to form Platinum electrode (working electrode).
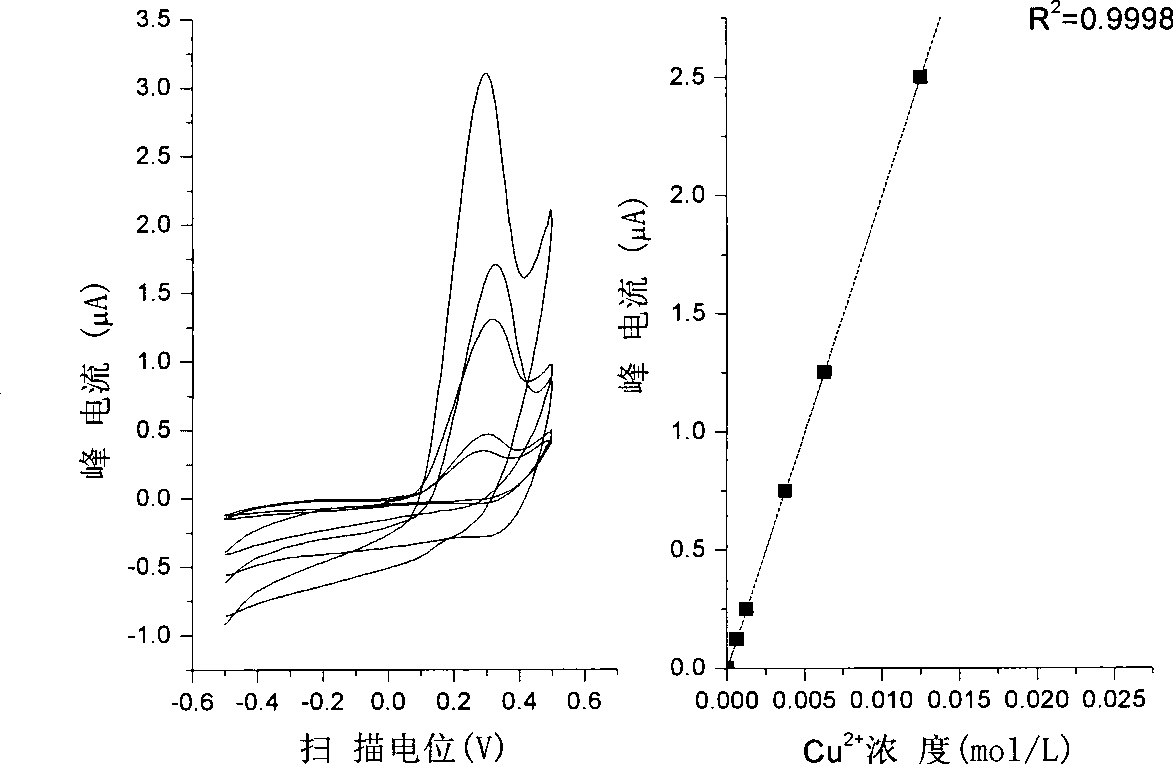
[0046] Pipette the Cr(VI) solution into a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, transfer excess KI solution, add water to dilute to 10ml, add an equal volume of MIBK solvent, and extract in the Erlenmeyer flask. During the measurement, use a micro-injector to draw a small amount (generally 20-40 μL) of the extracted sample and inject it into a glass microtube. The aqueous phase is a 1mol / L KCl solution, which is circulated on the liquid / liquid interface with a three-electrode system. Voltammetric analysis (eg figure 1 shown).
[0047] The cyclic voltammetry conditions are: the scanning potential range is -0.5~+0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com