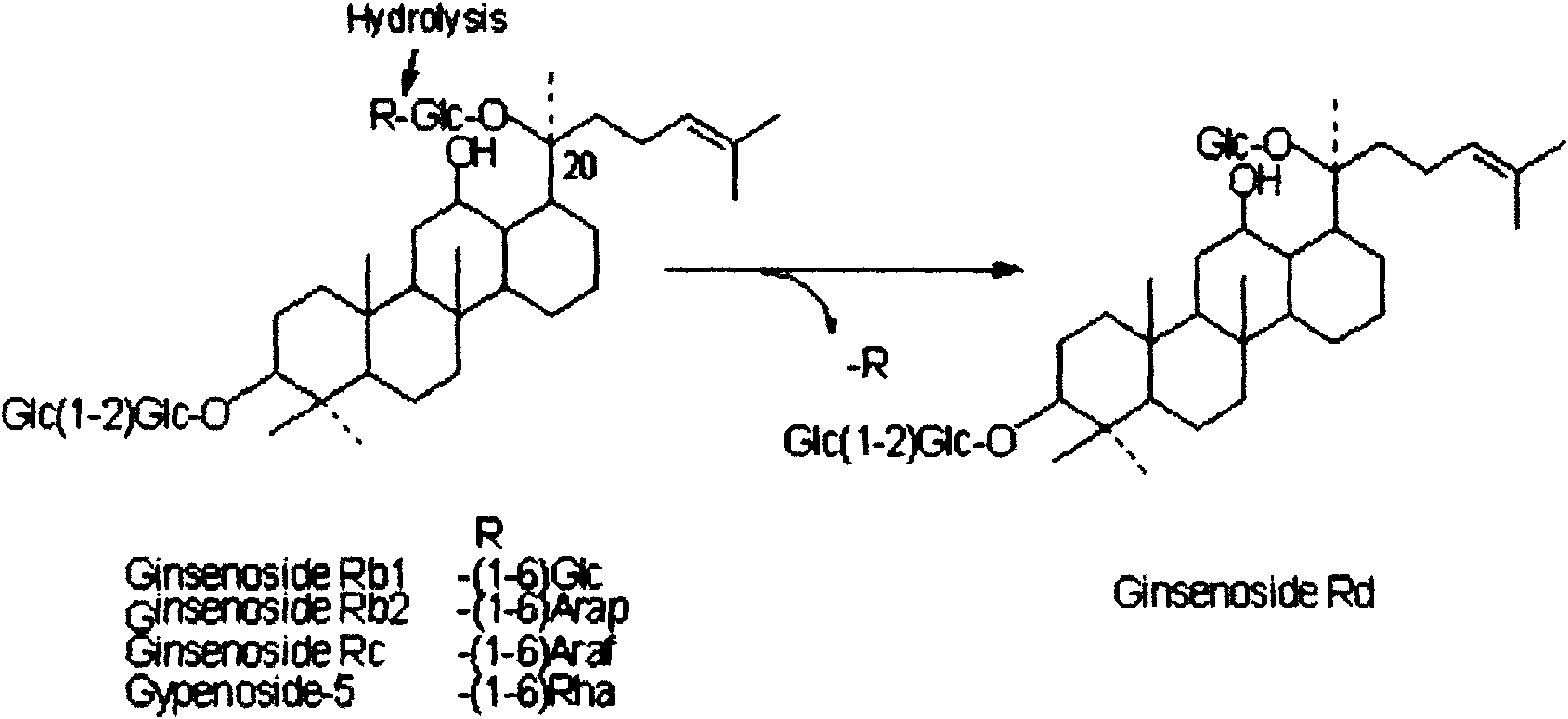
Method for preparing ginsenoside Rd by using microbial transformation
A technology of microbial transformation and ginsenoside, applied in the field of fermentation, can solve the problems of large amount of enzyme, high cost of substrate, non-specific and obvious inhibition of transformation products, etc., and achieves the effect of high transformation rate and expansion of drug resource sources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0031] To the tolerance test of notoginseng stem and leaf saponins of the original bacteria of example 1
[0032] Strain: Paecilomyces sp.4685, the screened strain grows well and is used as the starting strain.
[0033] Culture medium: potato culture medium (20% of potato, 2% of glucose is mixed with soup liquid), sub-package in 10 * 150cm test tube, every tube 4ml, add Panax notoginseng stem and leaf saponin according to Table 1, plug the test tube mouth with silica gel stopper, Sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes.
[0034] Inoculation: the rejuvenated fresh slant was washed with 0.9% saline to prepare 10 7 spores / ml of the spore suspension, add 0.1ml of the spore suspension to each test tube equipped with medium, cultivate for 6 days at 28°C, and observe the growth of the bacteria (Table 1).
[0035] Table 1 Bacterial growth in different concentrations of notoginseng stem and leaf saponins liquid medium
[0036]
[0037] +++When no saponin is added, the bacteria grow ver...
example 2
[0039] Example 2 Substrate-induced screening of high substrate tolerance, high specificity of the production strain Paecilomyces --Paecilomyces sp.4685
[0040] Strain: Paecilomyces Bainier sp.4685 strain with good growth condition was selected as the starting strain.
[0041] Culture medium: potato culture medium (20% of potato, 2% of glucose is mixed with soup liquid), sub-package in 10 * 150cm test tube, every tube 4ml, add different amounts of Panax notoginseng stem and leaf saponin respectively, make final concentration be 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60mg / ml, etc., plug the mouth of the test tube with a silica gel stopper, and sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes.
[0042] Induction: It can be seen from the tolerance experiment of strains that high concentration of saponins can inhibit the growth of bacteria, therefore, the concentration of saponins in stems and leaves of notoginseng should be continuously increased to select resistant strains.
[0043] Take 0.1ml of the bacter...
example 3
[0044] The optimization of example 3 transformation medium
[0045] Seed medium: 3% sucrose, 3% soybean flour, 0.1% ammonium sulfate, 0.1% magnesium sulfate, 0.1% calcium chloride, 0.5% bran.
[0046] Fermentation medium: 3% starch, 3% cottonseed flour, 0.1% sodium nitrate, 0.1% magnesium sulfate, 0.1% calcium chloride, 0.5% bran.
[0047] All media were packed in 250ml Erlenmeyer flasks with a volume of 30ml, and sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0048] After the seed bottles were inoculated, they were cultured on a shaker at 28° C. and 220 r / min for 36 hours to obtain a seed bacterial liquid. Insert 6% of the inoculum into the fermentation bottle at 28°C and cultivate on a shaker at 220r / min for 36h, add 2% notoginseng saponin and 0.6% Tween 80 solution, and continue to cultivate at 28°C on a shaker at 220r / min 72h.
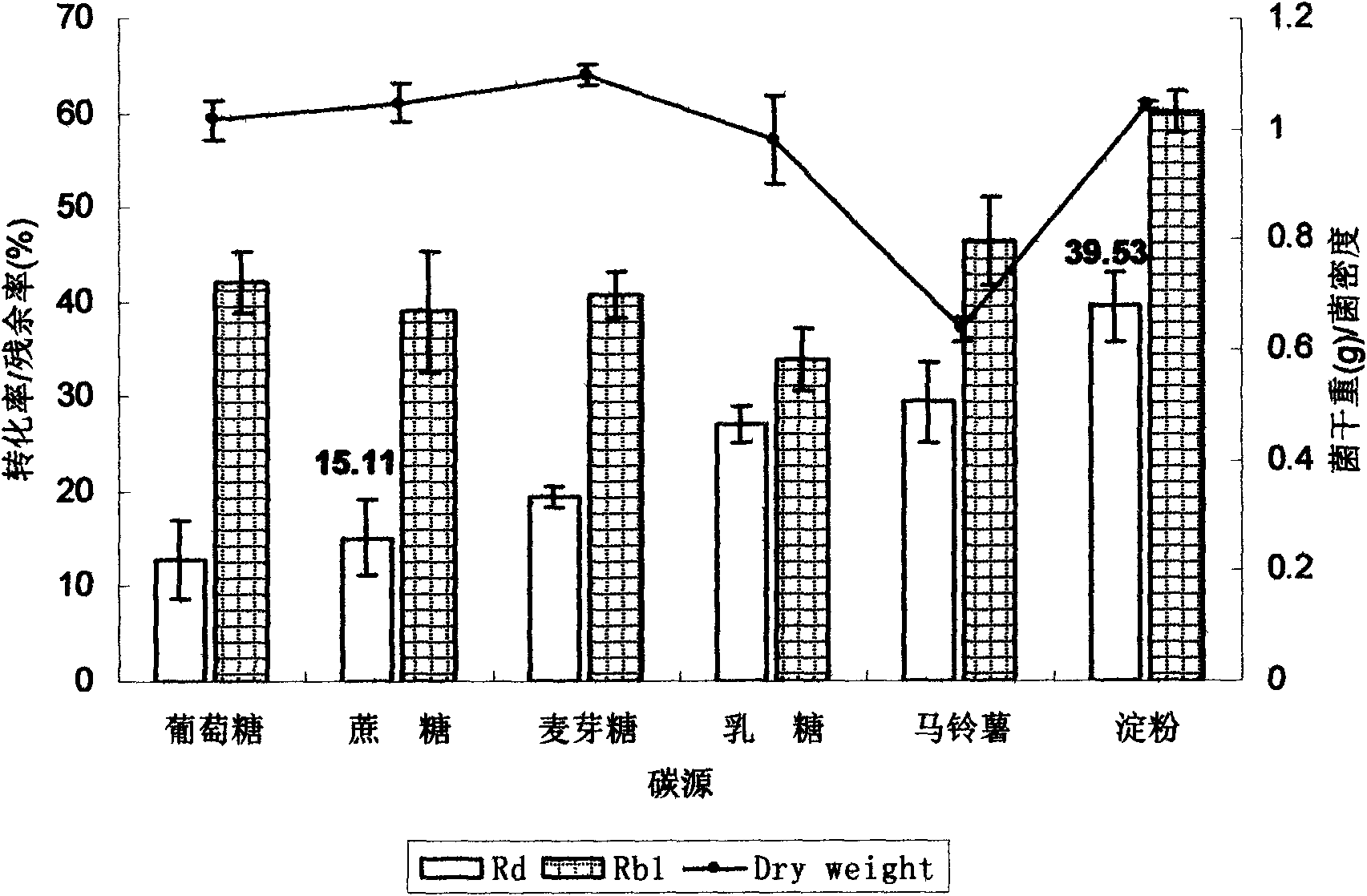
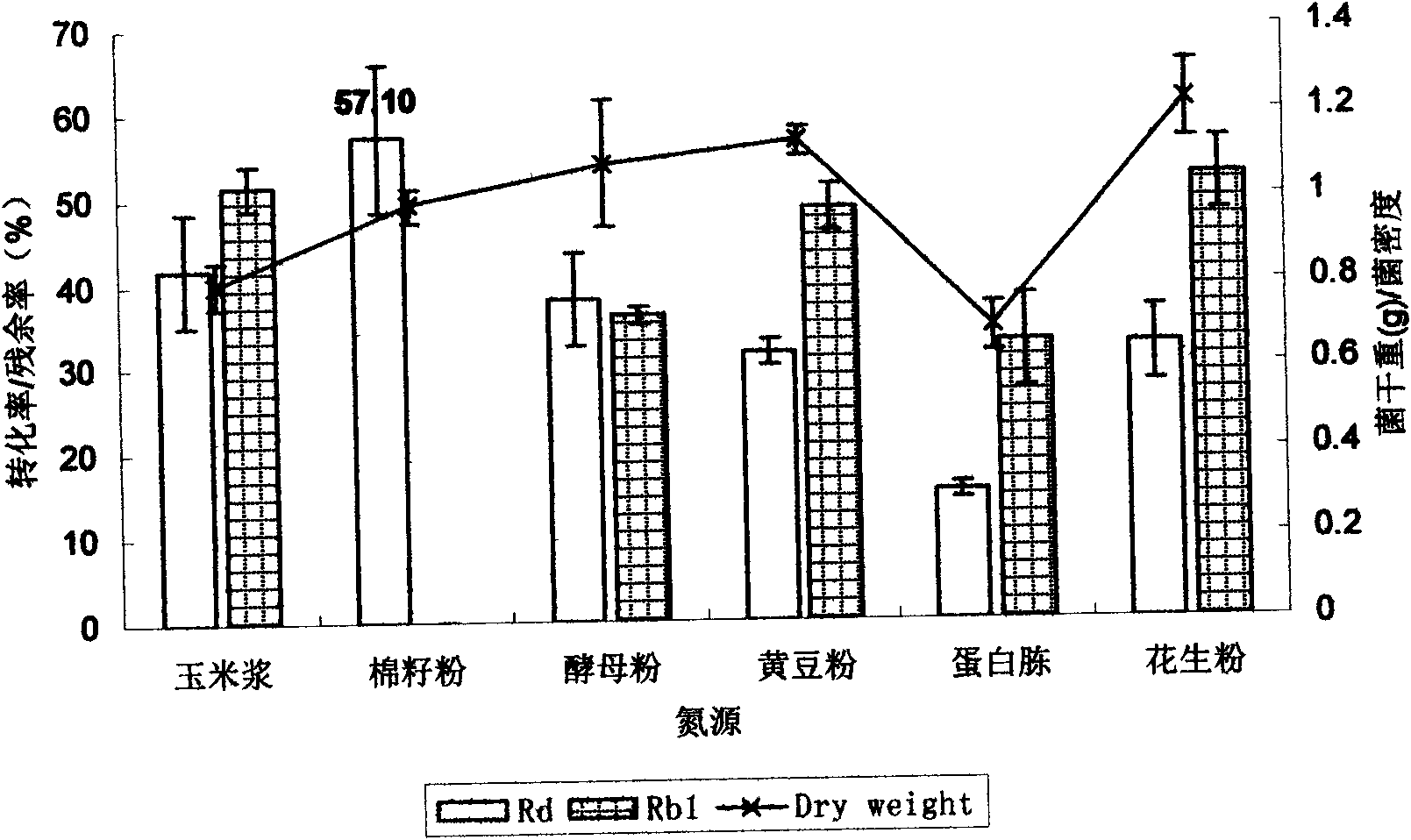
[0049] Carbon source optimization: The effects of glucose, sucrose, maltose, lactose, potato, and starch on the conversion rate of Rd were investigated respe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com