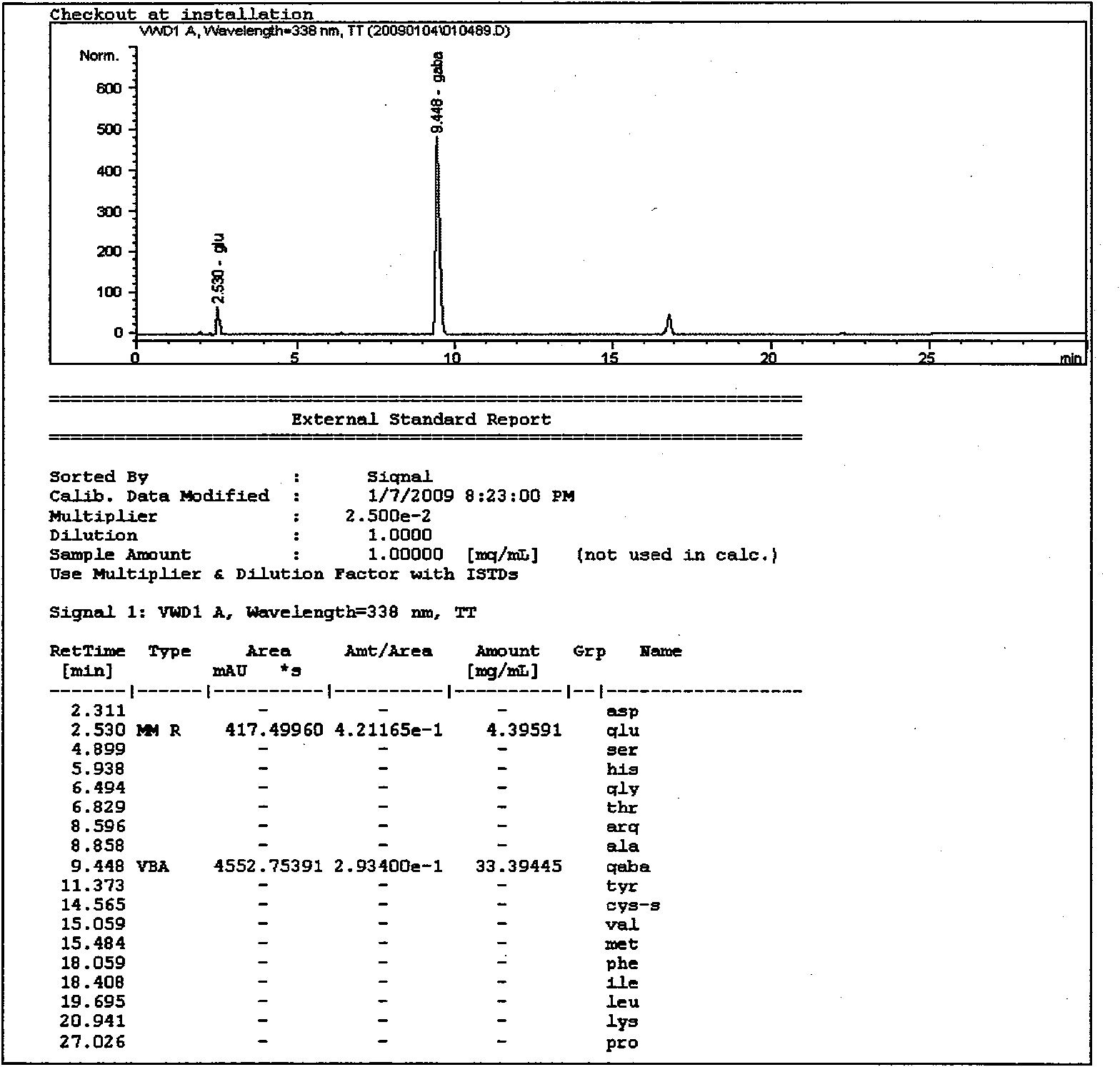
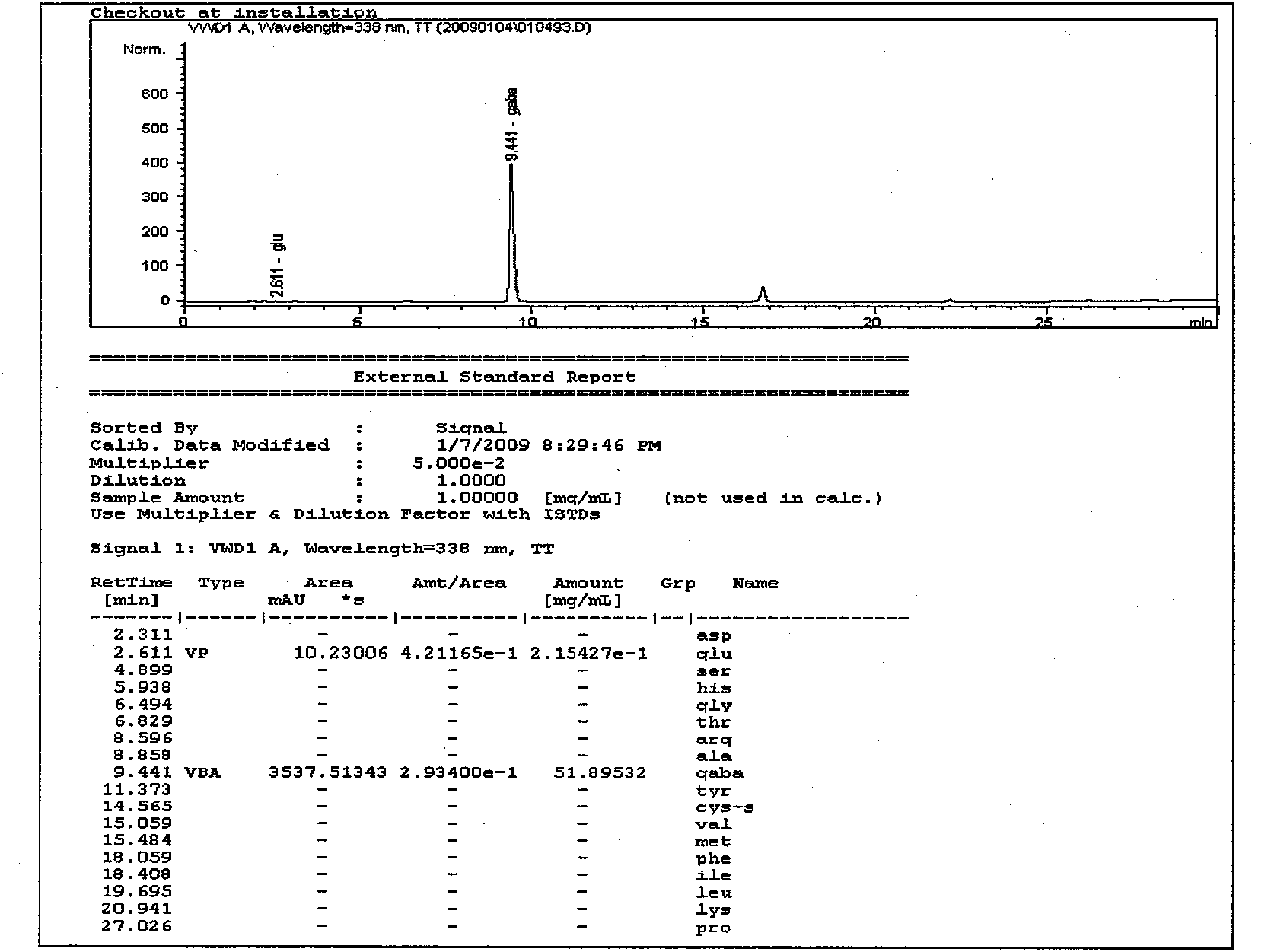
Breeding for efficiently converting L-glutamate into gamma-amino butyric acid lactobacillus
A technology of aminobutyric acid lactic acid bacteria and glutamic acid, which is applied in microorganism-based methods, bacteria, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of high GABA, unclear physiological significance, etc. high purity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Screening of strains that effectively transform L-glutamic acid into γ-aminobutyric acid
[0030] Strain screening and culture: Select soil, yogurt, homemade sauerkraut and other samples as materials, take 0.1mL of juice diluted to different concentrations, aseptically spread on the lactic acid bacteria selection medium plate, cultivate for 1-2 days at 30℃, A transparent circle is formed, and the medium around the colony becomes a single yellow colony, which is preliminarily identified as lactic acid bacteria. The plate streak method was used to repeatedly streak on the MRS plate to obtain pure strains. The separated and purified single colonies were connected to MRS solid slant medium and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C, and transferred once every 2 weeks.
[0031] Lactic acid bacteria isolation medium composition: beef extract 10g / L, yeast extract 10g / L, peptone 10g / L, glucose 5g / L, Tween 0.5g / L, tomato juice 200g / L, bromocresol green 0.1g / L, Calcium carbonate...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Ultraviolet mutagenesis screening of high-yield γ-aminobutyric acid strains
[0036] Take the strain obtained in Example 1 as the starting strain. After the strain is activated, the bacteria are diluted with sterile normal saline (0.85% NaCl solution), and the cell density is 10 8 Pcs / mL of bacterial suspension; under 15W UV lamp, 30cm away from the irradiated bacterial suspension, by changing the irradiation time to obtain different mutagenic doses; formulate its growth curve, ultraviolet lethality curve, the bacterial suspension is induced After the transformation treatment, it was diluted and spread on a gradient plate containing the metabolite GABA, and cultured at 30°C for 1 day. By visual observation, pick out the colonies growing on the relatively thicker part of the upper layer of the gradient plate and store them on the slope.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Study on the transformation ability of mutant strains
[0038] The strains screened in Example 2 were placed on a solid medium (casein peptone 10g / L, beef extract 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, glucose 5g / L, sodium acetate 5g / L, citrate diamine 0.2 g / L, Tween 0.1g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.2g / L, manganese sulfate 0.05g / L, calcium carbonate 20g / L, agar 20g / L, pH 6.5) 18h, pick a single colony and inoculate it in liquid activation medium (casein peptone 10g / L, beef extract 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, glucose 5g / L, sodium acetate 5g / L, citrate diamine 0.2g / L, Tween 0.1g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.2g / L, manganese sulfate 0.05g / L, calcium carbonate 20g / L, pH 6.5), and then transferred to the seed medium (Peptone 5g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, glucose 10g / L, sodium succinate 5g / L, pH 6.5), culture for 1d; collect the bacteria by centrifugation, wash the bacteria with sterilized water, and put them in a 100...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com