Polymer hydrogel capable of in-situ crosslinking as substitute material of vitreous body
A hydrogel and polymer technology, applied in prosthetics, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of difficult removal of small molecules, harsh reaction conditions, and reduced mechanical strength, and achieve the effects of simple operation, easy preparation, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
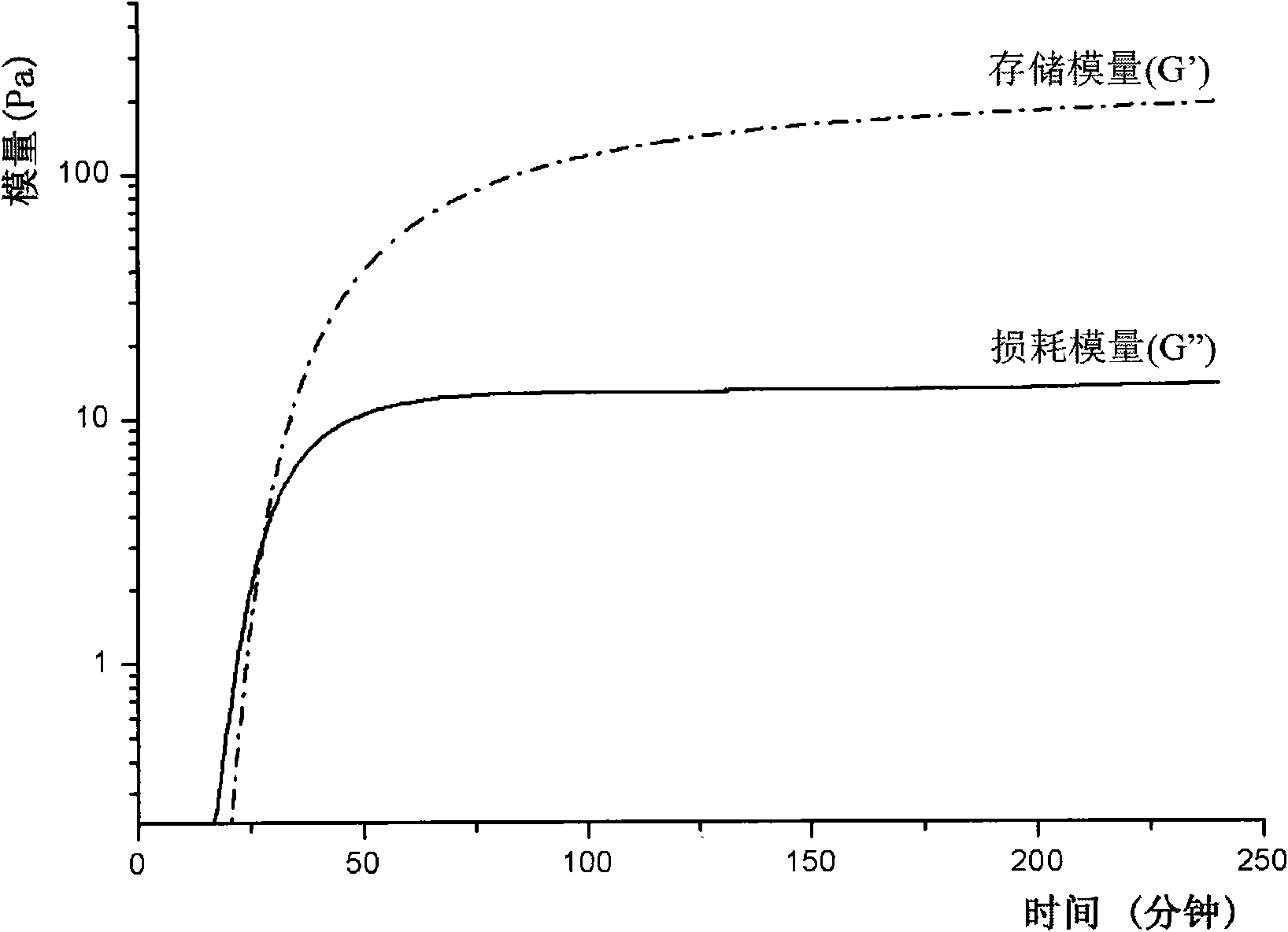
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1, Preparation of in situ hydrogel for vitreous cavity
[0029] Polymer preparation of component A:
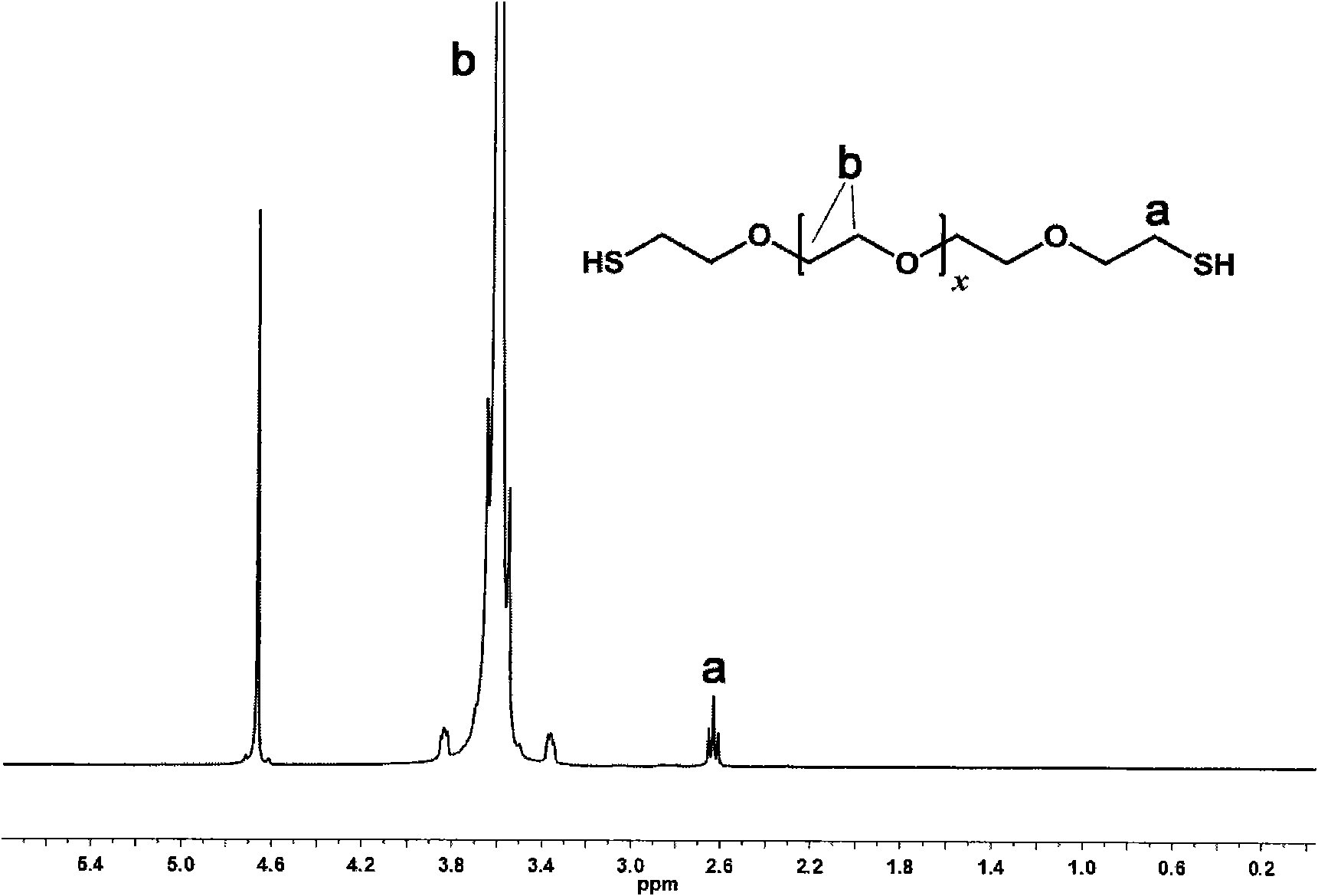
[0030] Use hydroxyl-terminated PEG (number-average molecular weight of 6000, provided by Sigma-Aldrich, item number 81260) (please provide the company name and catalog number that sells the product) as raw material, refer to literature (Lee, Y., etc., Biomacromolecules, 2005, 6:24) to prepare the compound represented by formula I, wherein x is an integer greater than 100 and less than 200.
[0031]
[0032] Formula I
[0033] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0034] Dissolve 30.0 g of hydroxy-terminated PEG (number-average molecular weight: 6000) in 500 mL of dry THF, add 4.5 mL of triethylamine and 5.7 g of p-toluenesulfonic acid chloride, react at room temperature for 24 hours, and mix the resulting product with thioacetic acid 3.5 g of potassium was refluxed at 85° C. for 4 hours, and finally the resulting product was stirred with 2M methan...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2, Preparation of in situ hydrogel for vitreous cavity
[0046] Polymer preparation of component A:
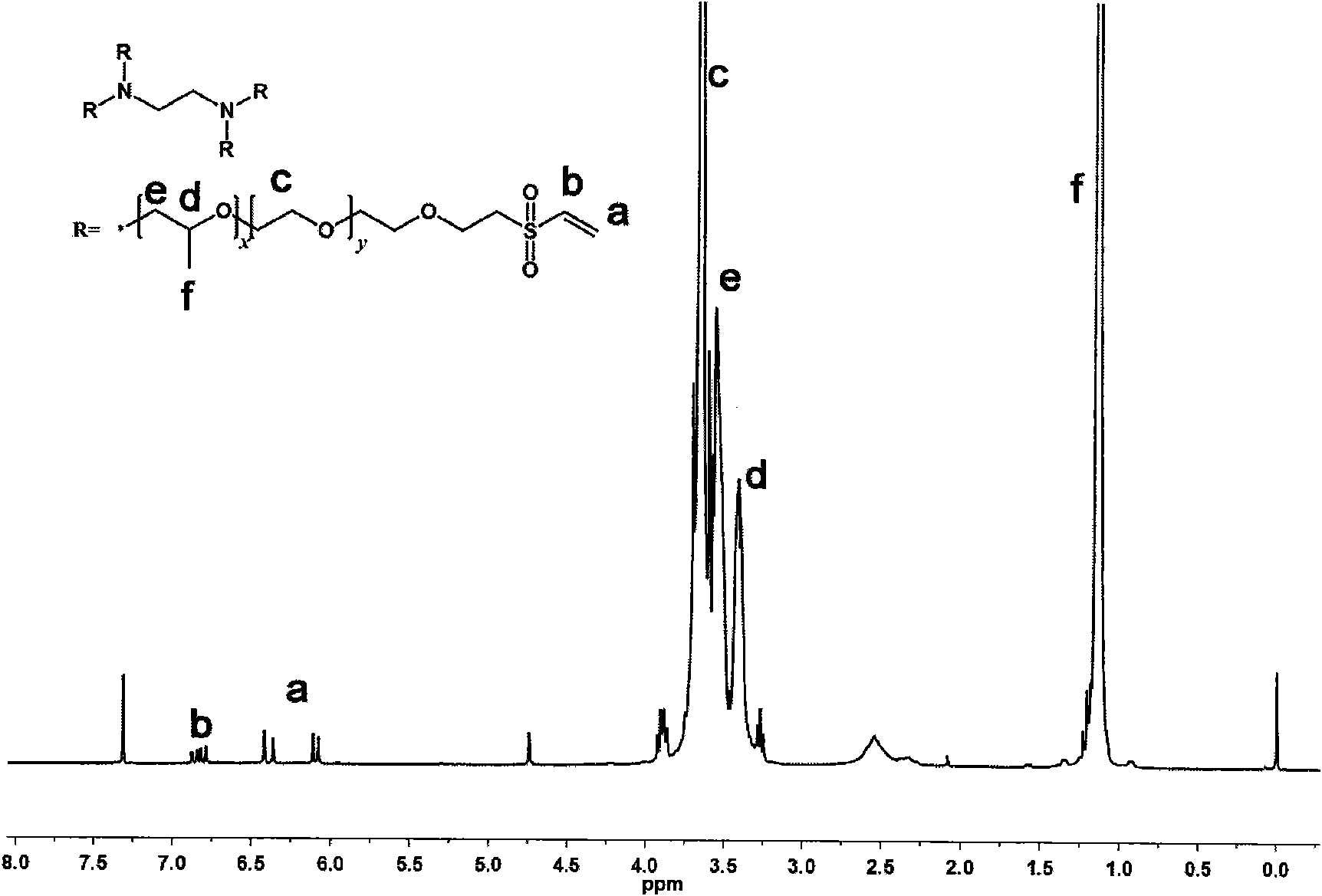
[0047] Using PVA (the number average molecular weight is 31000-50000, provided by Sigma-Aldrich, product number 363138) as raw material, the compound shown in formula III is prepared according to the method of reference (Tortora, M., etc., Biomacromolecules, 2007, 8: 209), wherein , x is an integer of 700-1200.
[0048]
[0049] Formula III
[0050] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0051] Dissolve 30.0g of PVA (number average molecular weight: 37,000) in 500mL of distilled water, heat to 80°C to dissolve completely, add 3.0g of sodium metaperiodate, and reflux the solution for 30 minutes. After cooling to room temperature, add 3.5g barium chloride, filter out insoluble matter, add 45.0g cysteine dissolved in 100mL pH=4.5 buffer solution to the solution, heat to reflux for 1 hour, cool to room temperature, and continue stirring After 30 m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com