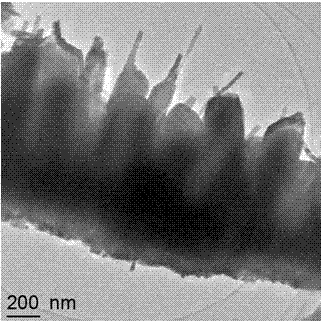
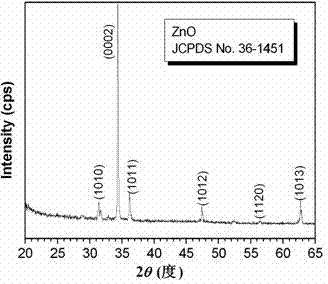
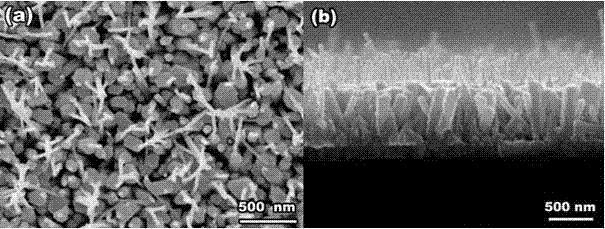
Preparation method of injector-shaped ZnO nanostructural array for field emission
A nanostructure and injector technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, single crystal growth, liquid phase epitaxial layer growth, etc., can solve the difficulty of effective control of the aspect ratio of the tip part of the one-dimensional ZnO nanostructure, high reaction temperature , Difficult to large-scale industrial production and other issues, to achieve the effect of easy industrial scale implementation, simple and easy operation process, and improved electrical conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] (1) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate into distilled water, and keep stirring to prepare Zn 2+ A clear solution with a concentration of 0.005mol / L, and the pH of the solution is controlled at 5.0±0.1 with NaOH or HCl, and the resulting solution is recorded as A;
[0020] (2) Use the A solution prepared above as the electrolyte, and use a three-electrode electrochemical deposition system (conductive glass as the working electrode, a platinum electrode as the counter electrode, and a saturated calomel electrode as the reference electrode) to directly grow ZnO on the conductive glass substrate. Nanopillar array; the deposition potential used is -0.5V, the electrolyte temperature is 50°C, and the deposition time is 30min;
[0021] (3) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate, hexamethylenetetramine and sodium fluoride in a beaker containing distilled water in sequence, and keep stirring, the molar concentration ratio of the three is 1:1:1, where...
Embodiment 2
[0025] (1) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate into distilled water, and keep stirring to prepare Zn 2+ A clear solution with a concentration of 0.005mol / L, and the pH of the solution is controlled at 5.0±0.1 with NaOH or HCl, and the resulting solution is recorded as A;
[0026] (2) Use the A solution prepared above as the electrolyte, and use a three-electrode electrochemical deposition system (conductive glass as the working electrode, a platinum electrode as the counter electrode, and a saturated calomel electrode as the reference electrode) to directly grow ZnO on the conductive glass substrate. Nanopillar array; the deposition potential used is -1.1V, the electrolyte temperature is 50°C, and the deposition time is 30min;
[0027] (3) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate, hexamethylenetetramine and sodium fluoride in a beaker containing distilled water successively, and keep stirring, the molar concentration ratio of the three is 1:1:2, wher...
Embodiment 3
[0031] (1) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate into distilled water, and keep stirring to prepare Zn 2+ A clear solution with a concentration of 0.005mol / L, and the pH of the solution is controlled at 5.0±0.1 with NaOH or HCl, and the resulting solution is recorded as A;
[0032] (2) Use the A solution prepared above as the electrolyte, and use a three-electrode electrochemical deposition system (conductive glass as the working electrode, a platinum electrode as the counter electrode, and a saturated calomel electrode as the reference electrode) to directly grow ZnO on the conductive glass substrate. Nanopillar array; the deposition potential used is -1.5V, the electrolyte temperature is 50°C, and the deposition time is 30min;
[0033](3) Dissolve analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate, hexamethylenetetramine and sodium fluoride in a beaker containing distilled water successively, and keep stirring, the molar concentration ratio of the three is 1:1:2, where...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com