Method for purifying and separating oligosaccharides
A technology for purification and separation of oligosaccharides, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of solvents, cumbersome operations, and increased experimental steps, so as to achieve simple and controllable experimental operations and a wide range of applications Broad and repeatable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
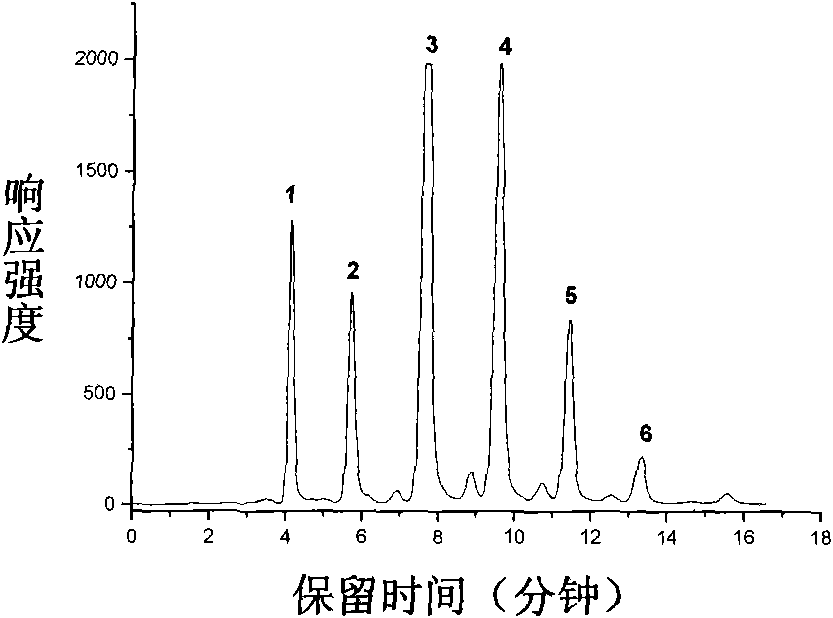
[0028] 50 mg of galactooligosaccharides was dissolved in 1 mL of pure water, and the injection volume was 30 μL.
[0029] A maltose chromatographic column (Click Maltose, 10×100mm, see invention patent 200710010808.8) was used with a column temperature of 30°C and a flow rate of 3.0mL / min. Phase A is water, phase B is acetonitrile, 0-10min, A / B (V / V): 70 / 30→60 / 40, 10-25min, A / B: 60 / 40.
[0030] Post-column split, split volume ratio 5:1, about 1 / 6 of which enters the detector, the detector is evaporative light scattering (ELSD), instrument parameter settings: gas pressure 35psi, drift tube temperature 85°C, gain value 1. A total of 6 different sample peaks were detected; they were galactooligosaccharides with degrees of polymerization of 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7;
[0031] Samples were injected 10 times continuously, and the fractions were collected according to the retention time of the 6 sample peaks. A total of 6 fractions were obtained. The fractions were concentrated to about ...
Embodiment 2
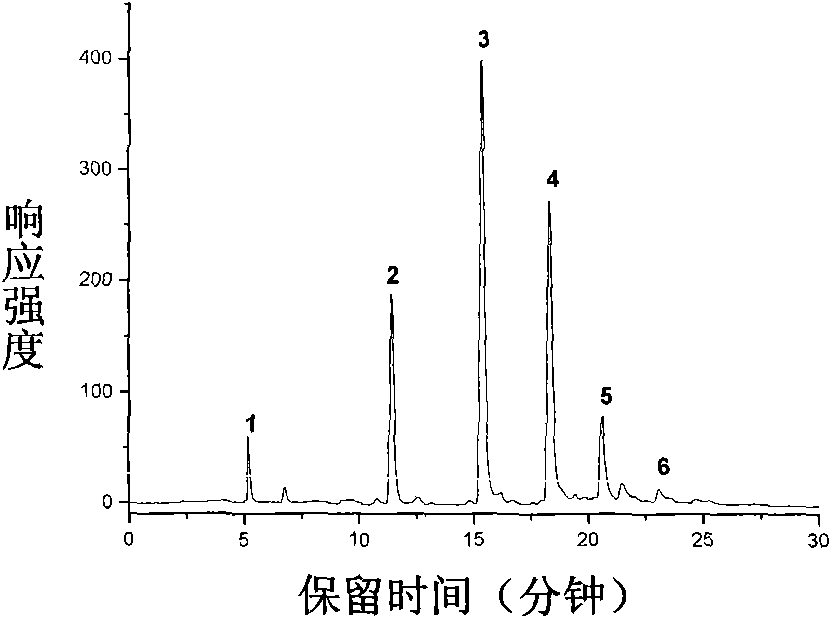
[0033] 50 mg of galactooligosaccharides was dissolved in 1 mL of pure water, and the injection volume was 5 μL.
[0034]A diol-based chromatographic column (Diol, 4.6×150 mm) was used with a column temperature of 30° C. and a flow rate of 1.0 mL / min. Phase A is water, phase B is acetonitrile, 0-10min, A / B (V / V): 80 / 20→70 / 30, 10-25min, A / B: 70 / 30-60 / 40. The detector is evaporative light scattering (ELSD), and the instrument parameter settings are: gas pressure 35psi, drift tube temperature 85°C, gain value 10. A total of 6 different sample peaks were detected; they were galactooligosaccharides with degrees of polymerization of 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Fructose oligosaccharide 30mg, dissolved in 1mL pure water, injection volume 10μL.
[0037] A maltose chromatographic column (Click Maltose 4.6×100mm, see invention patent 200710010808.8) was used with a column temperature of 30°C and a flow rate of 1.0mL / min. Phase A is water, phase B is acetonitrile, 0-60min, A / B (V / V): 70 / 30→50 / 50, 60-70min, A / B: 50 / 50-40 / 60. The detector is evaporative light scattering (ELSD), and the instrument parameter settings are: gas pressure 35psi, drift tube temperature 85°C, gain value 10. A total of 46 different sample peaks were detected; they were fructooligosaccharides with a degree of polymerization of 5-50.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com