Titanium dioxide photonic crystal film for photocatalytic degradation of organic matters
A titanium dioxide and photonic crystal technology, applied in the field of photocatalysis, can solve the problems of difficult control of film structure and thickness, complicated preparation process, poor process controllability, etc., to improve catalytic activity and energy utilization efficiency, simple preparation method, and production cost. low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
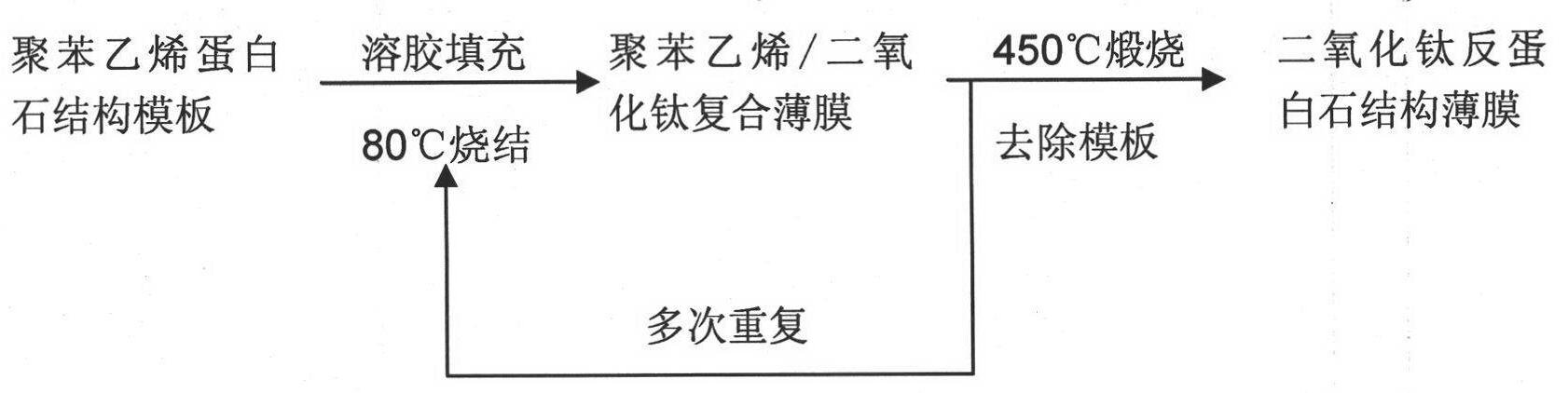
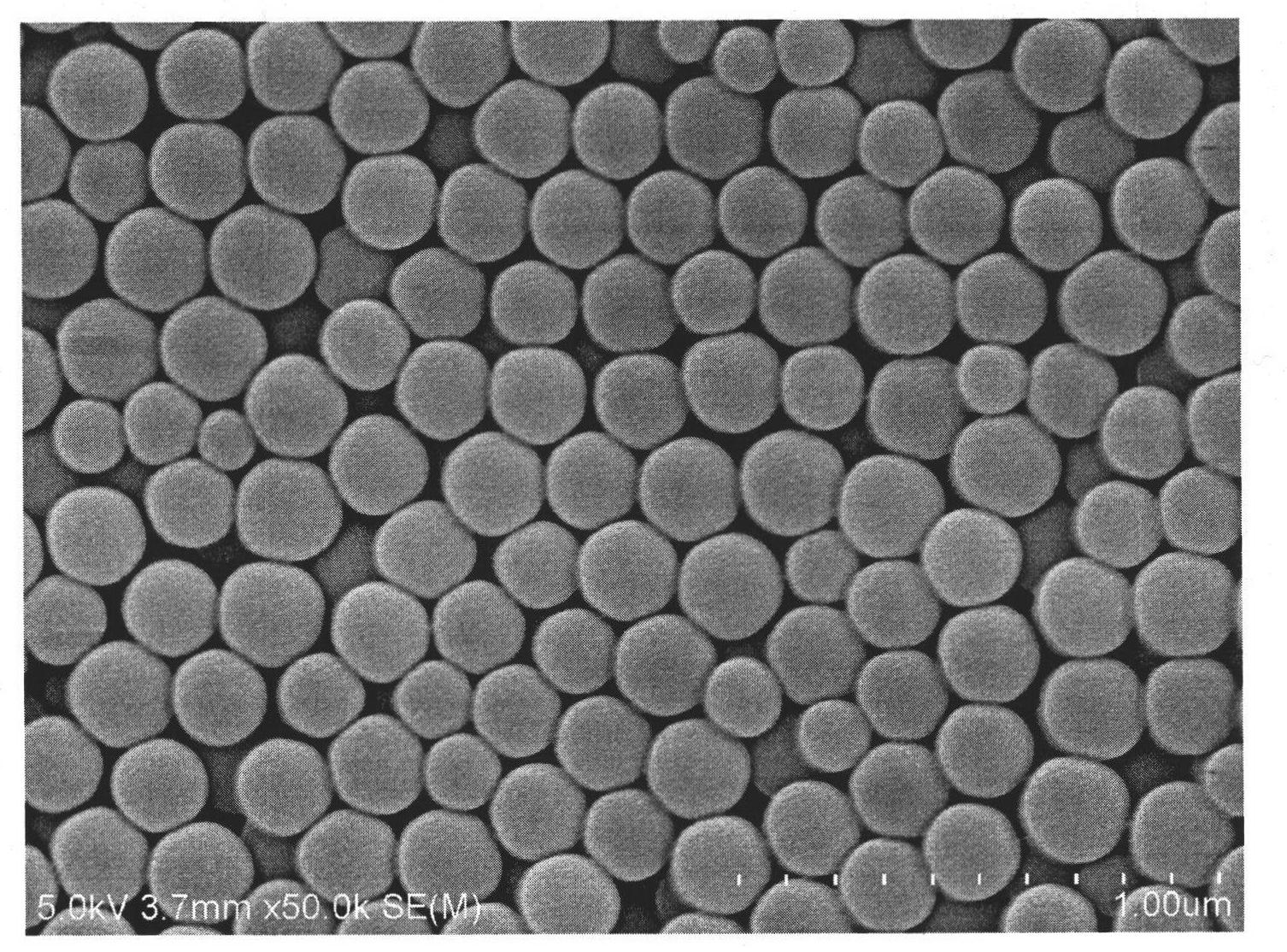
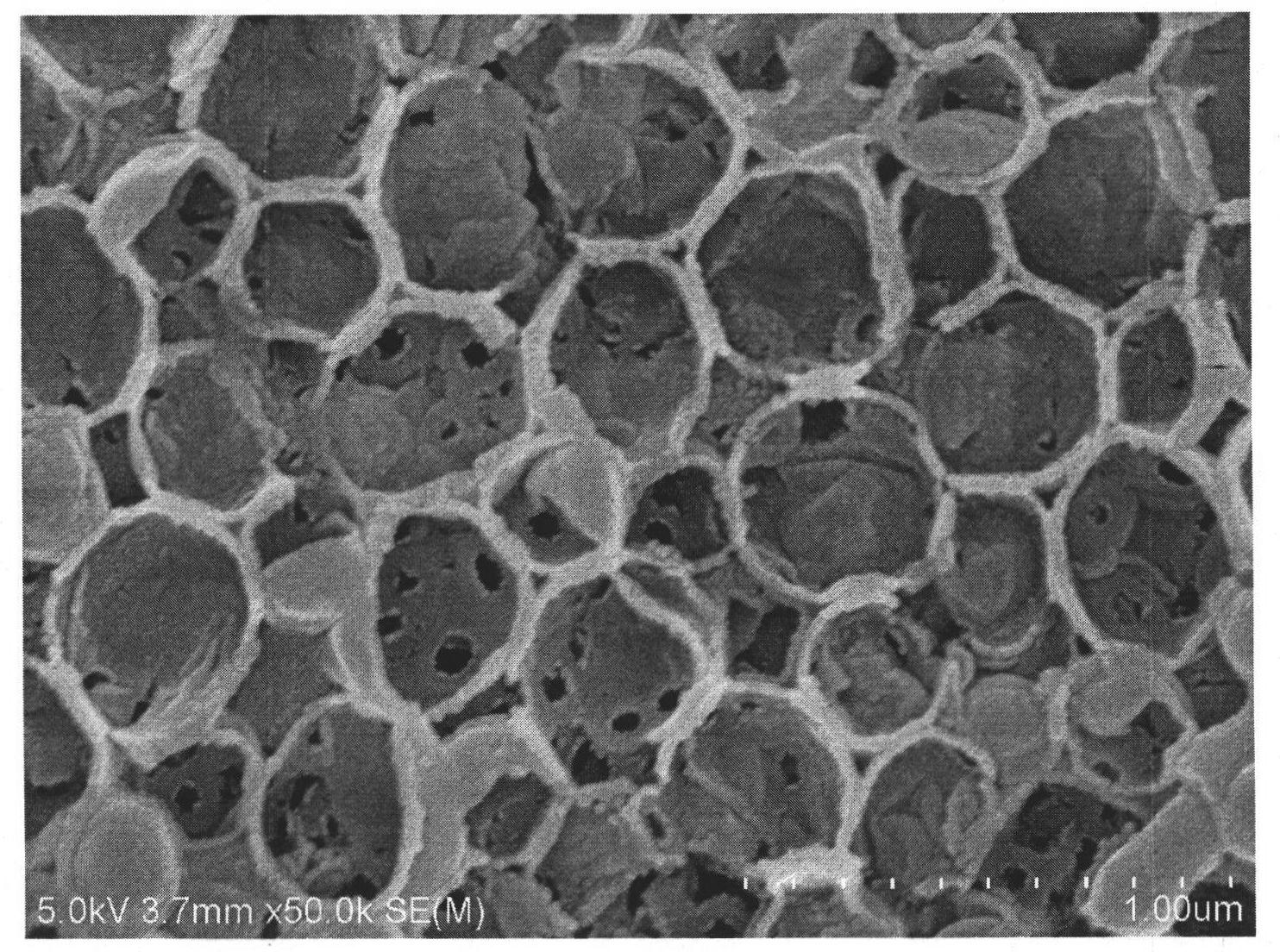
[0019] Using a suspension of monodisperse polystyrene microspheres with a diameter of 100 nm and ethanol as a dispersant, polystyrene microspheres with an ordered structure were deposited on the surface of quartz glass hydrophilically treated with sodium hydroxide solution through a vertical deposition assembly process at room temperature. Layers of spheres are deposited, forming opal-structured film templates. After the template is formed, place it in an oven at 80°C and sinter for 1 hour to improve the strength of the template during post-processing. Add ethanol first, then butyl titanate, stir evenly, then add deionized water to mix butyl titanate, absolute ethanol and deionized water in a certain molecular ratio (1:100:5), and stir at room temperature until a transparent sol is formed. The obtained opal structure film template was vertically immersed in the sol, and the sol was fully penetrated into the template by the action of capillary force. After standing for 5 minut...
Embodiment 2
[0022] The preparation method of the titanium dioxide inverse opal photonic crystal film is the same as in Example 1, except that the monodisperse polystyrene microsphere suspension with a diameter of 200 nm is vertically deposited to prepare the opal structure film template.
[0023] Using the obtained inverse opal structure porous titanium dioxide photonic crystal film with a pore diameter of 200 nm as a photocatalyst, the method of Example 1 was used to photocatalytically degrade phenanthrene, and the 8-hour degradation rate of phenanthrene was measured to be 90.0%. Photocatalytic experiments prove that the photocatalytic degradation rate constant of this film (taking phenanthrene as an example) is 2.1 times that of the amorphous nano-TiO2 film.
Embodiment 3
[0025] The preparation method of the titanium dioxide inverse opal photonic crystal film is the same as in Example 1, except that the monodisperse polystyrene microsphere suspension with a diameter of 300 nm is vertically deposited to prepare the opal structure film template.
[0026] Using the obtained inverse opal structured porous titanium dioxide photonic crystal film with a pore size of 300 nm as a photocatalyst, the photocatalytic degradation of phenanthrene was carried out according to the method in Example 1, and the 8-hour degradation rate of phenanthrene was measured to be 84.6%. The photocatalytic experiment proves that the photocatalytic degradation rate constant of this film (taking phenanthrene as an example) is 1.8 times that of the amorphous nano-TiO2 film.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com