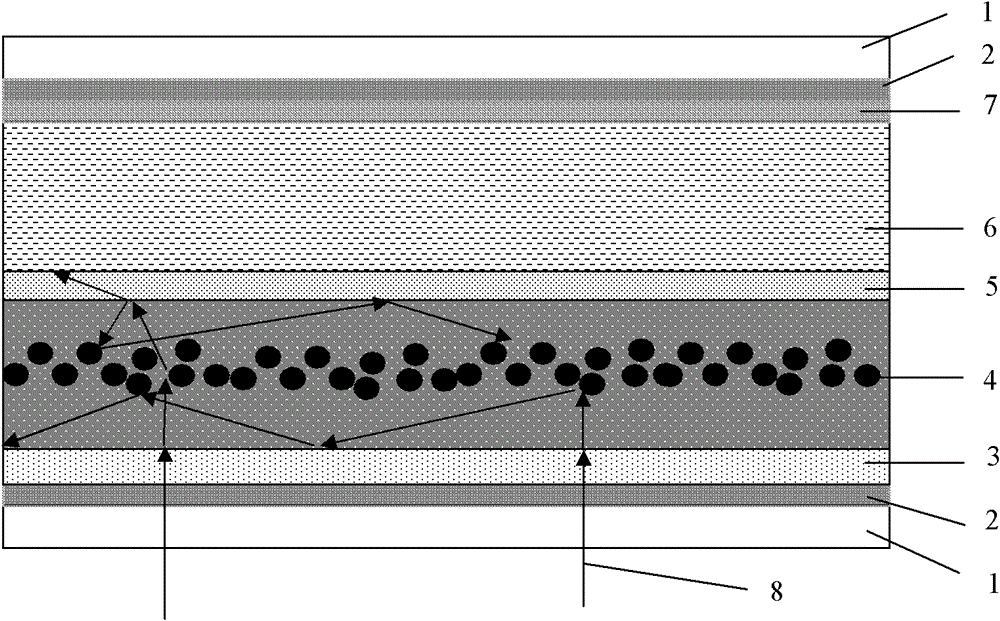
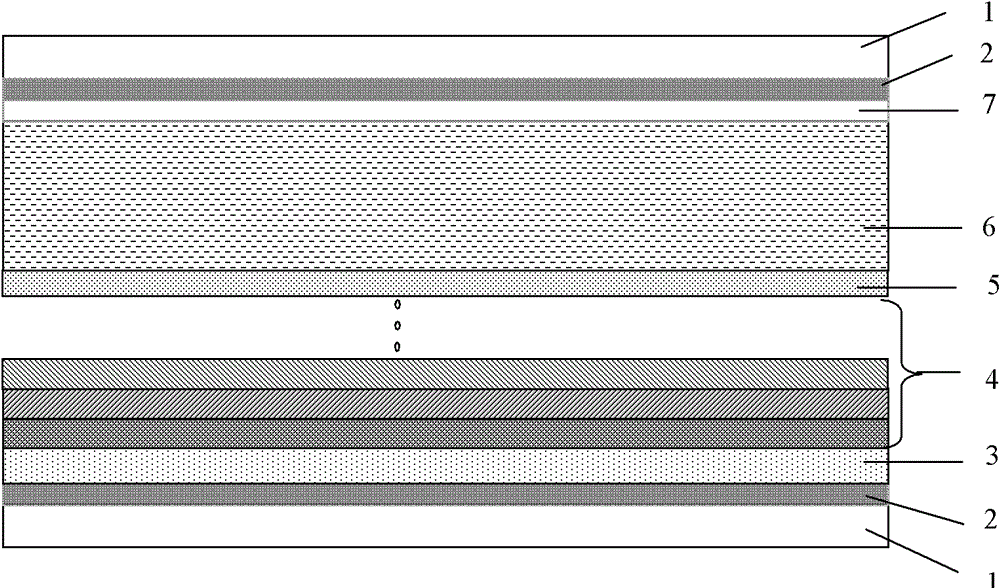
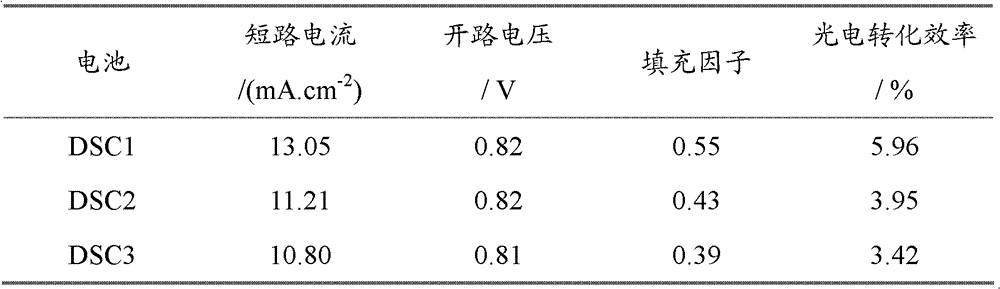
Dye-sensitized nanocrystalline thin film solar cell with light trapping structure
A solar cell and dye sensitization technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of affecting the number of photogenerated electrons, reducing the adsorption of dye molecules, limited light absorption and utilization, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] FTO conductive glass was used as a substrate, and anatase titanium dioxide (n=2.5) and rutile titanium dioxide (n=2.7) powders with different particle sizes were used to prepare photoanode films.
[0038] Pretreatment of the conductive substrate: Firstly, put the conductive glass into detergent, deionized water, and absolute ethanol for ultrasonic cleaning respectively. The ultrasonic time is 10-30min, and it is dried at 50-100°C.
[0039] The preparation methods of various powders are as follows:
[0040] Preparation of anatase and rutile powder: Dissolve an appropriate amount of tetrabutyl titanate in absolute ethanol, and add deionized water drop by drop under stirring until no white precipitate occurs. The white precipitate was washed, dried, divided into two parts, and calcined at 450° C. and 700° C. for 2 hours respectively to obtain anatase and rutile titanium dioxide powders with particle diameters in the range of 100-700 nm.
[0041] Rutile TiO 2 Preparation ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Using FTO conductive glass as the substrate, using anatase titanium dioxide (n=2.5) and rutile TiO 2 (n=2.7) microspheres assembled with nanorods to prepare photoanode films. The preparation methods of various powders are as follows:
[0048] Dissolve an appropriate amount of tetrabutyl titanate in absolute ethanol, and add deionized water drop by drop under stirring until no white precipitate occurs. The white precipitate was washed, dried, and calcined at 450° C. for 2 hours to obtain anatase titanium dioxide powder with a particle size in the range of 100-700 nm. TiCl 4 As titanium source, hydrochloric acid solution as solvent, rutile TiO was prepared by hydrothermal method 2 Microspheres assembled with nanorods, wherein the cross-sectional width of a single nanorod is 400-600 nm, and the diameter of the assembled microspheres is about 7 μm.
[0049] With terpineol and ethyl cellulose as additives, an anatase-type titanium dioxide slurry with a solid content of 2...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Using FTO conductive glass as a substrate, tin dioxide (n=2.0), anatase titanium dioxide (n=2.5) and rutile titanium dioxide (n=2.7) powders were used to prepare photoanode films. The preparation methods of various powders are as follows:
[0052] Dissolve an appropriate amount of tetrabutyl titanate in absolute ethanol, and add deionized water drop by drop under stirring until no white precipitate occurs. The white precipitate was washed, dried, divided into two parts, and calcined at 450° C. and 700° C. for 2 hours respectively to obtain anatase and rutile titanium dioxide powders with particle diameters in the range of 100-700 nm. Take appropriate amount of SnCl 4 ·5H 2 O is dissolved in PEG200, and after calcining, tin dioxide powder with a particle size of about 500nm is obtained. With terpineol and ethyl cellulose as additives, the above powders were respectively configured into a slurry with a solid content of 20%, wherein the tin dioxide slurry was expressed ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com