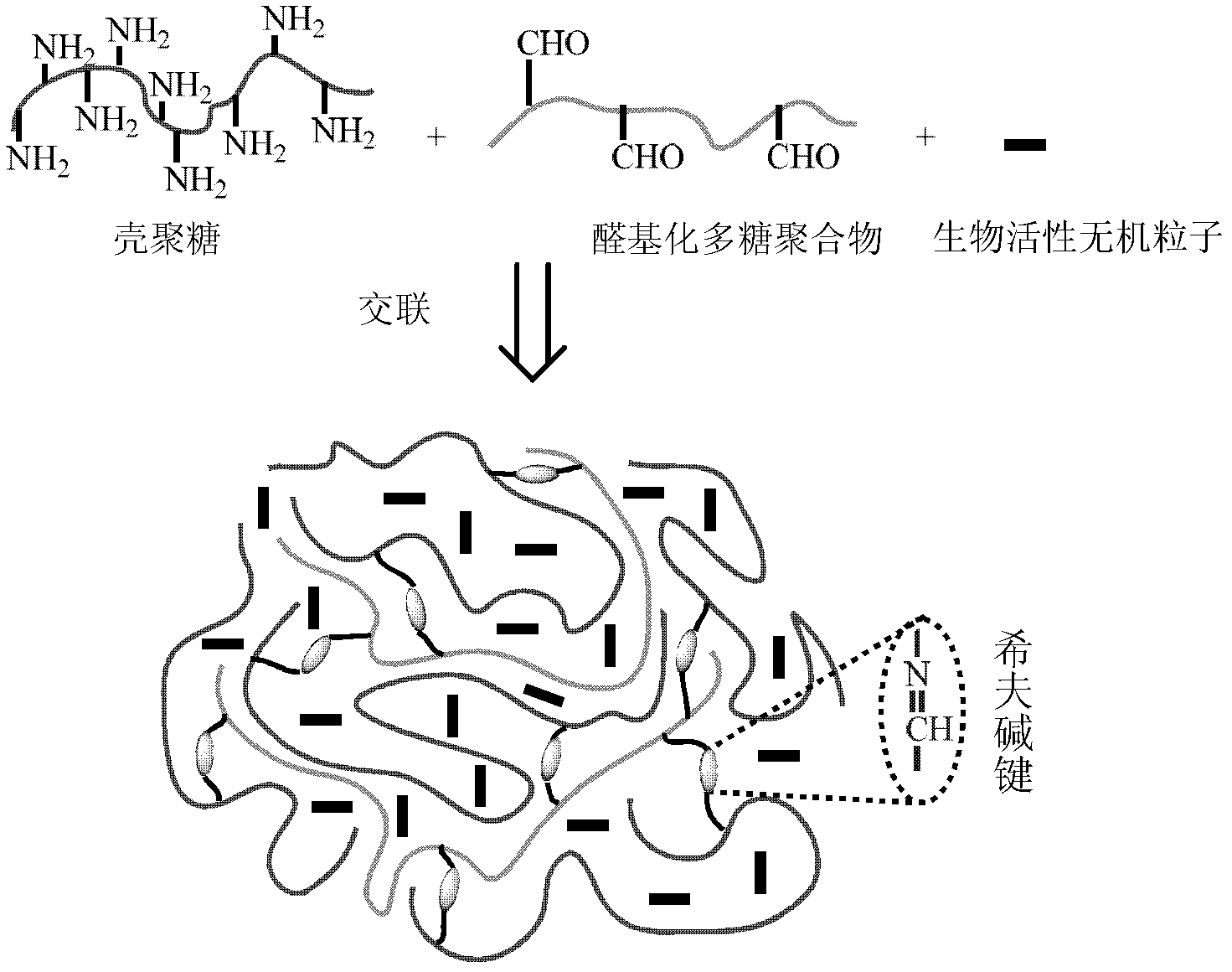
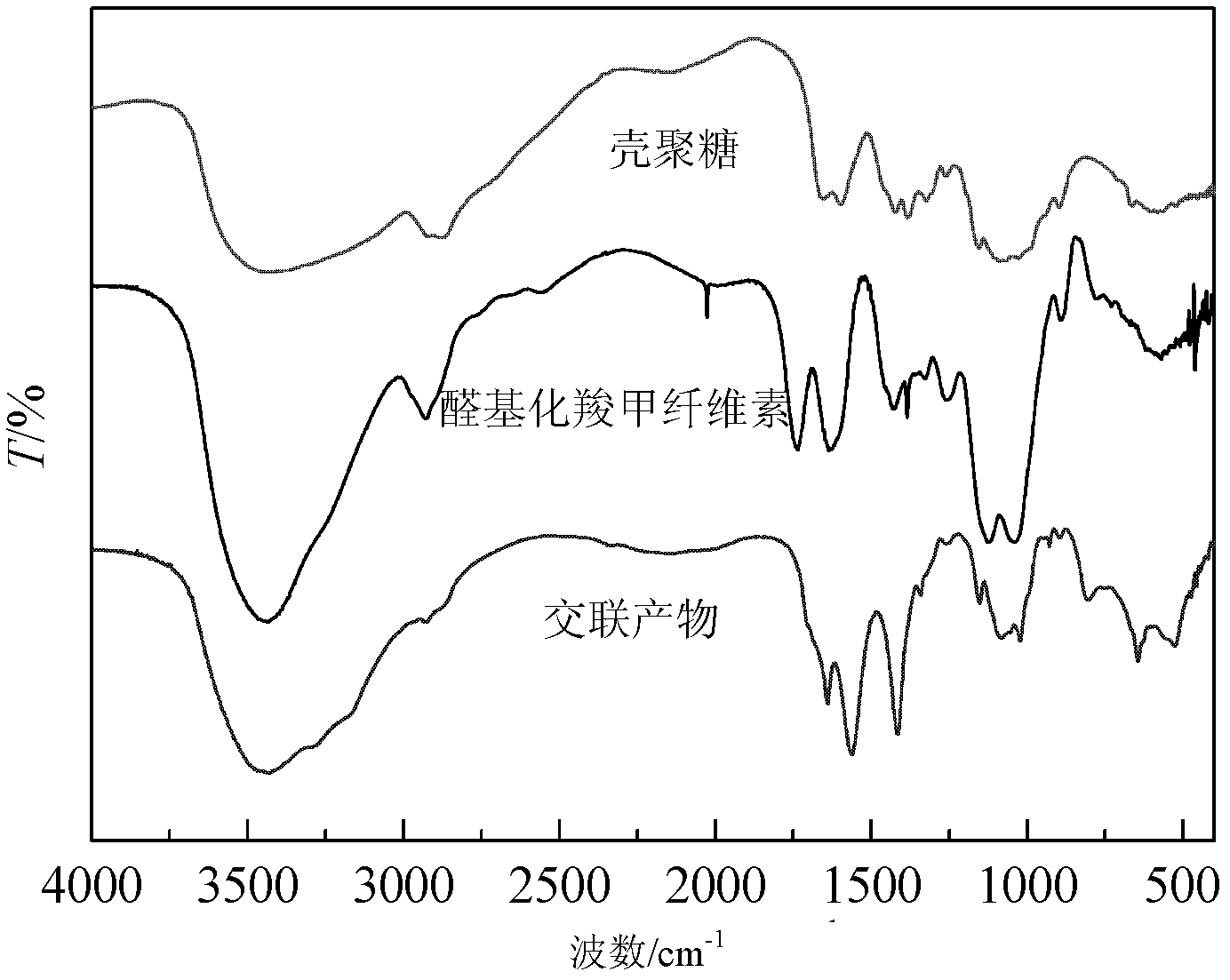
Preparation method for chitosan-based porous scaffolds with biological activity
A bioactive, porous scaffold technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of large influence on scaffold stability, reduce scaffold porosity, interfere with hydrogen bonding, etc., to improve biocompatibility, good pore size The effect of wall roughness and uncomplicated process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Preparation of chitosan / nano-hydroxyapatite composite porous scaffold
[0045] 1) Synthesis of water-soluble formylated carboxymethyl cellulose
[0046] First the water-soluble polysaccharide polymer sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is dissolved in water to form a mass percentage concentration of 5% polysaccharide polymer solution, and then the pH value of the polysaccharide polymer solution is adjusted to 3 with the sulfuric acid of 5mol / L in the dark Add sodium periodate 5 times the mass of the polysaccharide polymer in batches under the same conditions, react at 45°C for 6 hours under stirring, then add excess ethylene glycol to continue the reaction for 30 minutes; The ethanol mixture is fully washed until no iodine is detected; finally, water-soluble formylated carboxymethyl cellulose is obtained by vacuum drying at room temperature;
[0047] 2) Preparation of chitosan-hydroxyapatite slurry
[0048] Under stirring conditions, dissolve chitosan with a dea...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Preparation of chitosan / β-tricalcium phosphate composite porous scaffold
[0058] 1) Synthesis of water-soluble aldylated polysaccharide hyaluronic acid
[0059] First, the water-soluble polysaccharide polymer hyaluronic acid is dissolved in water to form a polysaccharide polymer solution with a mass percent concentration of 2%, and then the pH value of the polysaccharide polymer solution is adjusted to 4 with 5mol / L sulfuric acid. Add sodium periodate 3 times the mass of the polysaccharide polymer in batches, react at 60°C for 4 hours with stirring, and then add excess ethylene glycol to continue the reaction for 30 minutes; Wash until no iodine is detected; finally, vacuum-dry at room temperature to obtain the water-soluble formylated polysaccharide hyaluronic acid;
[0060] 2) Preparation of chitosan-β-tricalcium phosphate slurry
[0061] Under stirring conditions, dissolve chitosan with a deacetylation degree of 90% and a molecular weight of 300,000 in ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3: Preparation of chitosan / α-tricalcium phosphate composite porous scaffold
[0071] 1) Synthesis of water-soluble aldylated polysaccharide alginic acid
[0072] First, the water-soluble polysaccharide polymer sodium alginate was dissolved in water to form a polysaccharide polymer solution with a mass percent concentration of 6%, and then the pH value of the polysaccharide polymer solution was adjusted to 1 with 5mol / L sulfuric acid, and then separated under light-proof conditions. Add sodium periodate 4 times the mass of the polysaccharide polymer in batches, react at 50°C for 5 hours with stirring, and then add excess ethylene glycol to continue the reaction for 30 minutes; Washing until no iodine is detected; finally, vacuum drying at room temperature to obtain the water-soluble aldylated polysaccharide alginic acid;
[0073] 2) Preparation of chitosan-α-tricalcium phosphate slurry
[0074] Under stirring conditions, dissolve chitosan with a deacetylation d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com