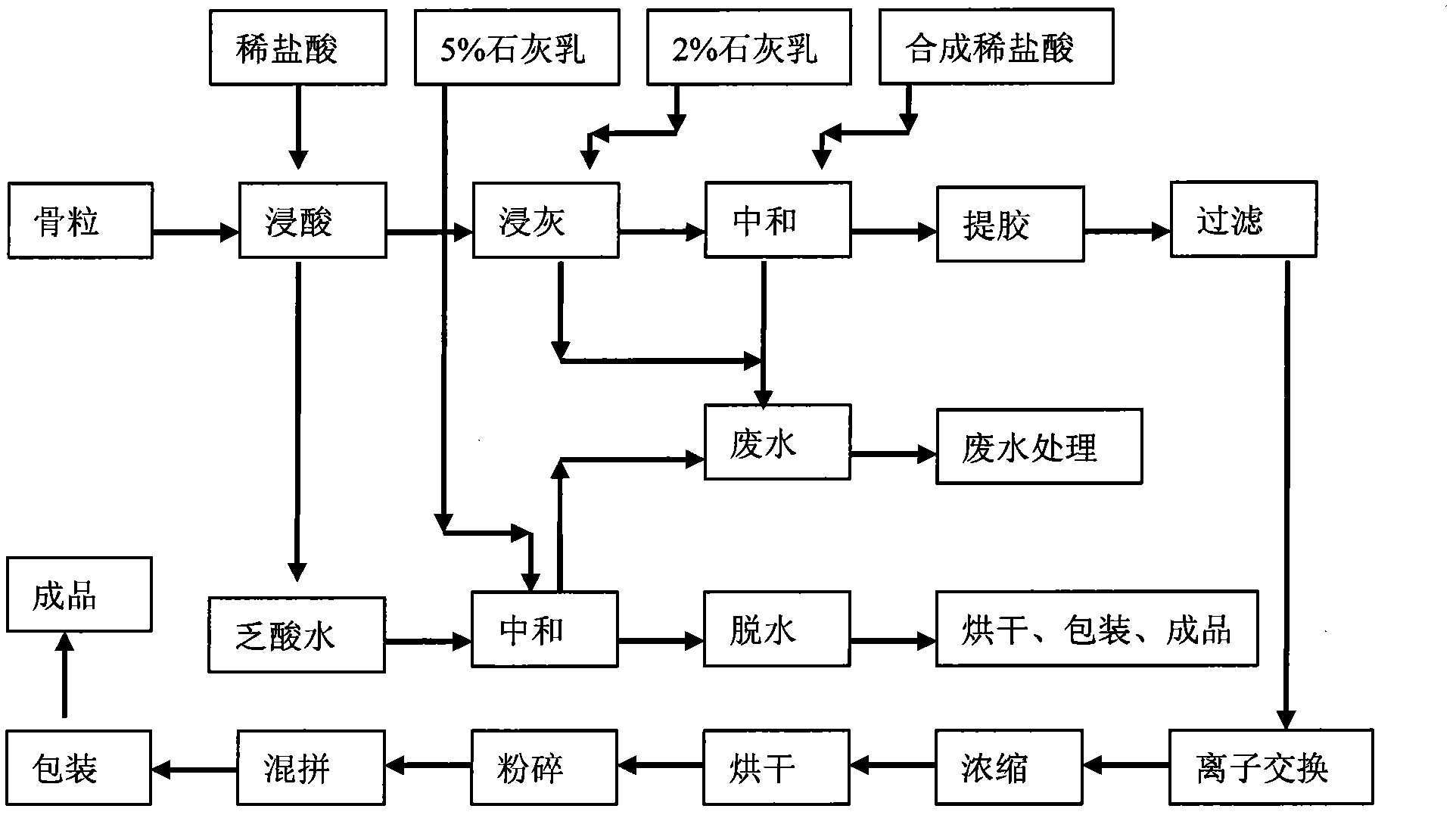
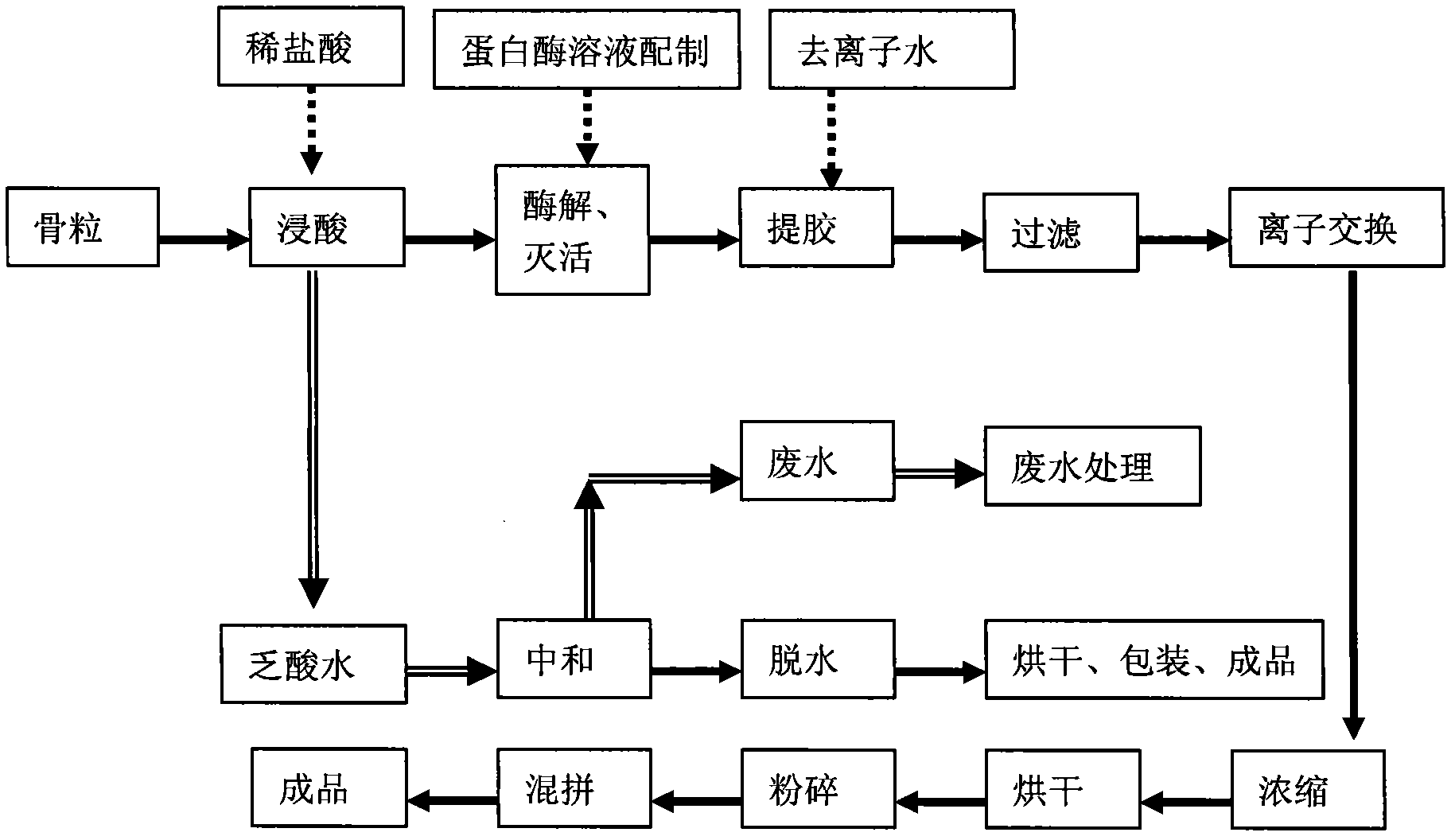
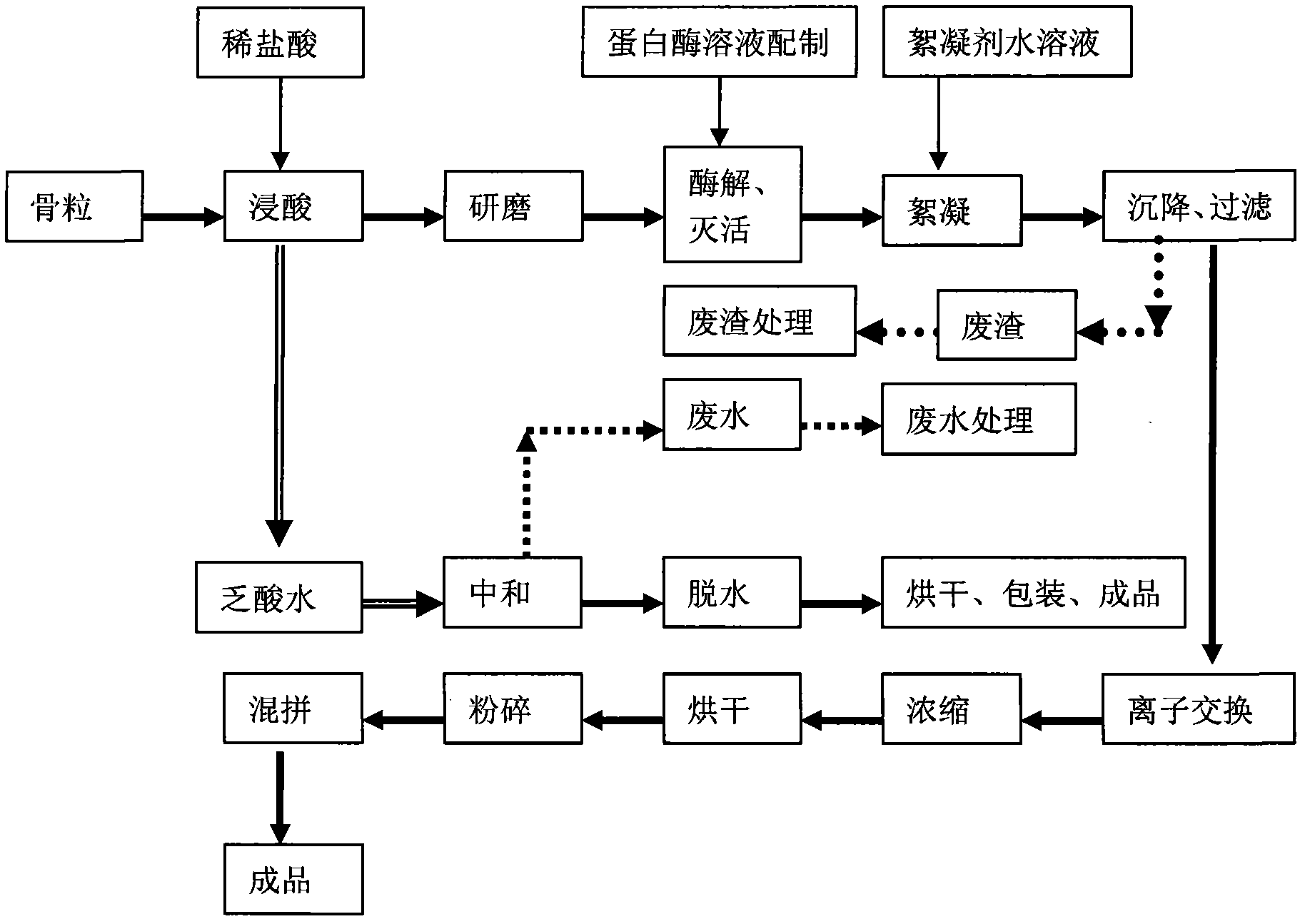
Enzyme method for preparing gelatin
A technology for enzymatic preparation of gelatin, applied in the field of enzymatic preparation of bone gelatin, which can solve the problems of high extraction temperature, destruction of quality indicators, non-property, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0116] Embodiment 1: enzymatic method gets bone gelatin
[0117] 1) Preparation and beating of bone meal:
[0118] Dry bone grains (water content≤10%, oil content≤4%), remove bone grains larger than 15cm, and then put the bone grains into a coarse grinder to grind them into bone powder with a particle size of ≤3mm (wherein bone powder with a particle size of ≤2mm accounts for 90%);
[0119] Add drinking tap water to the bone meal mixing tank G1 (self-designed, paddle agitator), add the measured bone powder into the bone meal mixing tank, and fully stir, according to the weight ratio of bone meal and water is 1:3.5 to make 22 % bone meal slurry;
[0120] 2) Colloid mill grinding (high-shear colloid mill, model HSC-100R; Shanghai Yilu Electromechanical Equipment Co., Ltd.): Add the prepared bone powder slurry into the colloid mill and grind it into a bone powder colloid solution with a particle size of 40 μm;
[0121] 3) Phosphoric acid acidification: add phosphoric acid with...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Embodiment 2: enzymatic method gets bone gelatin
[0136] Concrete steps are with embodiment 1, and following part is slightly different:
[0137] 1) Phosphoric acid acidification: start the acidification stirring, heat up the collagen colloid, and raise the temperature of the collagen colloid to 45°C;
[0138] 2) Protease hydrolysis: start stirring, and slowly add the prepared 5% acidic protease solution. The weight ratio of acid protease solution to bone powder is 0.0144:1, heat preservation, stirring, and enzymolysis for 1.5 hours.
[0139] Under the condition of constant stirring, add 0.75% hydrogen peroxide (concentration: 27.5%) of the weight of bone powder to oxidize for 8 hours, and add the same amount of hydrogen peroxide (concentration: 27.5%) for the second time to oxidize for 24 hours. If time permits, it should be extended as much as possible. oxidation time;
[0140] 3) Flocculation: start stirring, slowly add calcium hydroxide suspension, stop adding c...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Embodiment 3: enzymatic method gets bone gelatin
[0144] Concrete steps are with embodiment 1, and following part is slightly different:
[0145] 1) Phosphoric acid acidification: start the acidification stirring, heat up the collagen colloid, and raise the temperature of the collagen colloid to 50°C;
[0146] 2) Enzymatic hydrolysis and decolorization: start stirring, slowly add the prepared 5% acid protease solution, add the amount of acid protease solution according to the weight ratio of acid protease solution and bone meal is 0.027:1, keep warm, stir, enzymolysis 1 Hour;
[0147] Under the condition of constant stirring, add 0.75% hydrogen peroxide (concentration: 27.5%) of the weight of bone powder to oxidize for 8 hours, and add the same amount of hydrogen peroxide (concentration: 27.5%) for the second time to oxidize for 24 hours. If time permits, it should be extended as much as possible. oxidation time;
[0148] 3) Start stirring, slowly add the calcium hydr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com