Pyrethroid pesticide residue degradation bacteria as well as bacteria agent and application
A technology for the degradation of pyrethroids and pesticide residues, applied in the directions of bacteria, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of no degrading bacteria biological agents, complex mechanism, long half-life, etc., to promote coordinated and unified pest control. The effect of drug and food safety, good degradation effect and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The acquisition of embodiment 1 degrading bacteria DG-02
[0028] In June 2010, the inventor isolated a degrading bacteria strain DG-02 from the soil of Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China through a conventional enrichment culture method, and it was preserved in the China Type Culture Collection Center on November 8, 2011 ( The address is Luojia Mountain, Wuchang, Wuhan City, Hubei Province), the strain preservation number is CCTCC M 2011382, and it has been identified as Bacillus ( Bacillus sp.), the cells are rod-shaped, arranged in a chain, with spores; the colonies are white, opaque, with rough surfaces, large colonies, and irregular edges; contact enzyme test, methyl red test, acetylmethylmethanol test, nitrate Reduction test, starch hydrolysis test, gelatin liquefaction test, hydrogen sulfide test, casein hydrolysis test were positive; oxidase test, phenylalanine deaminase test, tyrosine hydrolysis test, indole test, glucose gas production test were negative;...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2 Preparation of degrading bacterial agent
[0030] The strain of pyrethroid pesticide residue degrading bacteria DG-02 of the present invention is activated on a solid plate, and its degradation performance is measured, and it is inoculated on the inclined surface of a test tube for later use. Inoculate the test tube seed of the pyrethroid pesticide residue-degrading bacteria DG-02 in a 1000 mL shake flask containing 250 mL of LB medium, shake at a constant temperature to the logarithmic phase, and prepare to inoculate the seed tank. The mass percentage of the LB medium consists of For: yeast extract 0.5%, peptone 1%, NaCl 1%; seed tank 100 L, feeding volume 80 L, medium formula: yeast extract 0.5%, peptone 1%, NaCl 1%, pH value 7.2-7.5. At 1.1 Kg / cm2 after feeding 3 Under the pressure of 121 ℃, high-pressure damp heat sterilization, after cooling to 30 ℃, inoculate the above cultured shake flask strains into 100 L seed tanks according to the inoculum amoun...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 Degradation experiment on pyrethroid pesticide residues
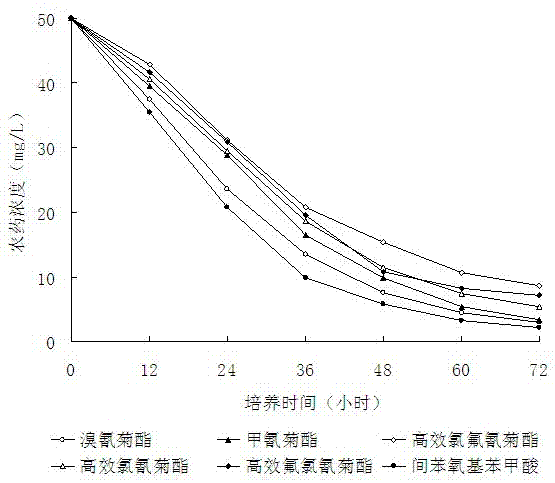
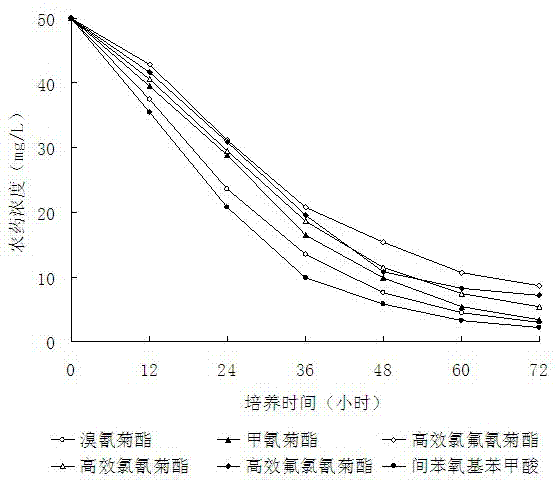
[0033] In basal salt medium (components: NH 4 NO 3 1.0 g, NaCl 0.5 g, K 2 HPO 4 1.5 g, KH2 PO 4 0.5 g, MgSO 4 . 7H 2 O 0.5 g, water 1000 mL, pH value 7.5) were added deltamethrin, fenpropathrin, lambda-cyhalothrin, lambda-cypermethrin, lambda-cyfluthrin and m-phenoxybenzoic acid to make the final The concentration was 50 mg / L; the concentration of the inoculated degrading bacteria DG-02 was 1.0×10 8 CFU / mL bacterial liquid, and the culture medium without inoculation was used as the control, cultured on a shaking table for 0-72 hours, samples were taken regularly, and the residual amount of pesticides was detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The results are shown in Table 1. The degradation curve is attached figure 1 shown.
[0034]
[0035] Table 1 Degradation effect of degrading bacteria DG-02 on pyrethroid pesticides and m-phenoxybenzoic acid
[0036]
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com