Method for screening transgenic paddy plant by phosphomannose-isomerase (PMI) gene of yeast
A technology of mannose isomerase and isomerase, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, horticultural methods, genetic engineering, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1 Cloning of Saccharomyces cerevisiae phosphomannose isomerase PMI gene
[0064] From Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) HB52 (gifted by Professor Hao Bo, School of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural University, see: Kong Lin, Hao Bo, Yu Ziniu, Zinc-rich yeast selection and cultivation technology, Food and Biotechnology Journal , 2006, Volume 25, Issue 6) extracted genomic DNA and cloned the phosphomannose isomerase PMI gene. The specific steps are as follows: Inoculate a ring of fresh Saccharomyces cerevisiae into 20mL YPD liquid medium, YPD medium contains: 2% tryptone, 1% yeast extract, 2% glucose, 30°C, 180r / min shaking culture for 18~ 22h. The cells were collected by centrifugation, resuspended with normal saline, and the supernatant was discarded by centrifugation. Put the collected bacteria into a 5mL centrifuge tube, add 1mL of lysis buffer (50mmol / L Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 180mmol / L EDTA pH 8.0, 1% SDS, prepared now) for ever...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The construction of the pPMI carrier of embodiment 2 PMI gene
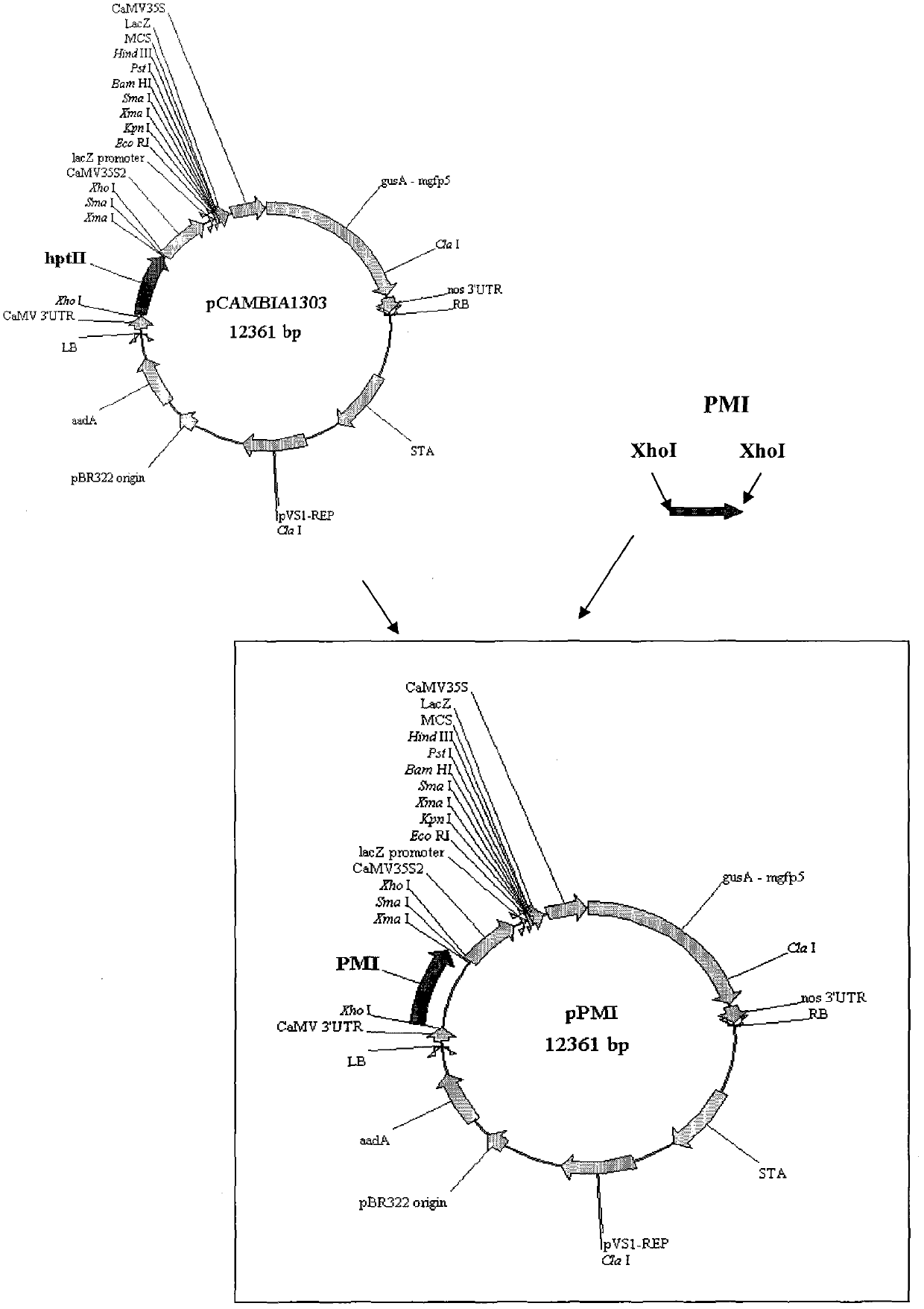
[0071] The transformation vector containing the PMI gene constructed by the applicant, which is named pPMI, is transformed from the plasmid pCAMBIA1303 (see the construction flow chart figure 2 ). pCAMBIA1303 contains a kanamycin resistance gene, a hygromycin resistance gene linked to a 35S promoter and a CaMV terminator, and a GUS-GFP fusion protein linked to a 35S promoter and a NOS terminator between the left and right T-DNA borders Gene. Escherichia coli containing the pCAMBIA1303 plasmid was inoculated in LB medium (10% tryptone, 5% yeast extract, 10% NaCl), cultivated overnight at 150 rpm at 37° C., extracted the plasmid, and used chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (volume ratio of 24 : 1) Purify the plasmid. Digest the purified plasmid overnight at 37°C to excise the hygromycin resistance gene. The PCR product was also digested with Xho I overnight after purification. According to pCAMBIA1303 plasmid ...
Embodiment 3
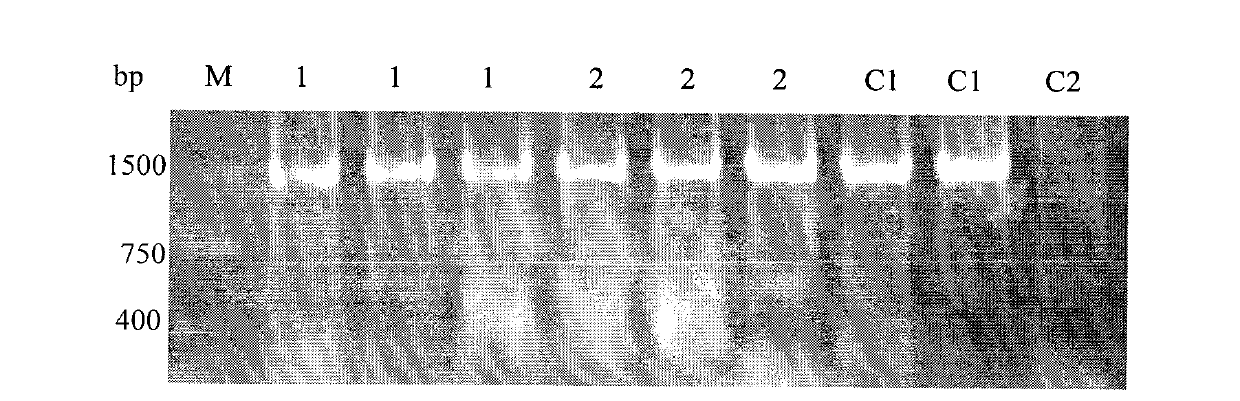
[0072] Example 3 Rice Genetic Transformation and Screening
[0073] The recipient plant of the present invention is rice (Oryza Sativa L) variety Mudanjiang No. 8, and the seeds of this variety are provided by Professor Lin Yongjun of the Rice Group of the State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement, Huazhong Agricultural University. The method of genetic transformation of the present embodiment is: first remove the chaff, soak with 70% ethanol for 1 min, then sterilize with 0.15% mercuric acid for 20 min, then wash with sterile water for 3-4 times and inoculate to the rice callus induction medium , 26 ℃ dark culture to induce callus. After 35-40 days, take the vigorous, light yellow granular callus and transfer it to the subculture medium, and subculture in the dark at 26°C. The embryogenic callus that has been subcultured for 1-2 times can be Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation experiments. The pale yellow callus granules with strong viability and dense text...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com