Bioabsorbable polymer scaffold matrix as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for absorbing polymers and biology, applied in stents, prostheses, medicines and other directions, can solve the problems of increasing the processing and manufacturing costs of stent bases, complicated preparation process steps, and inability to resist blood flow scouring, and is conducive to large-scale The effect of the production and promotion of the drug, the improvement of the drug load, and the improvement of the supporting force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
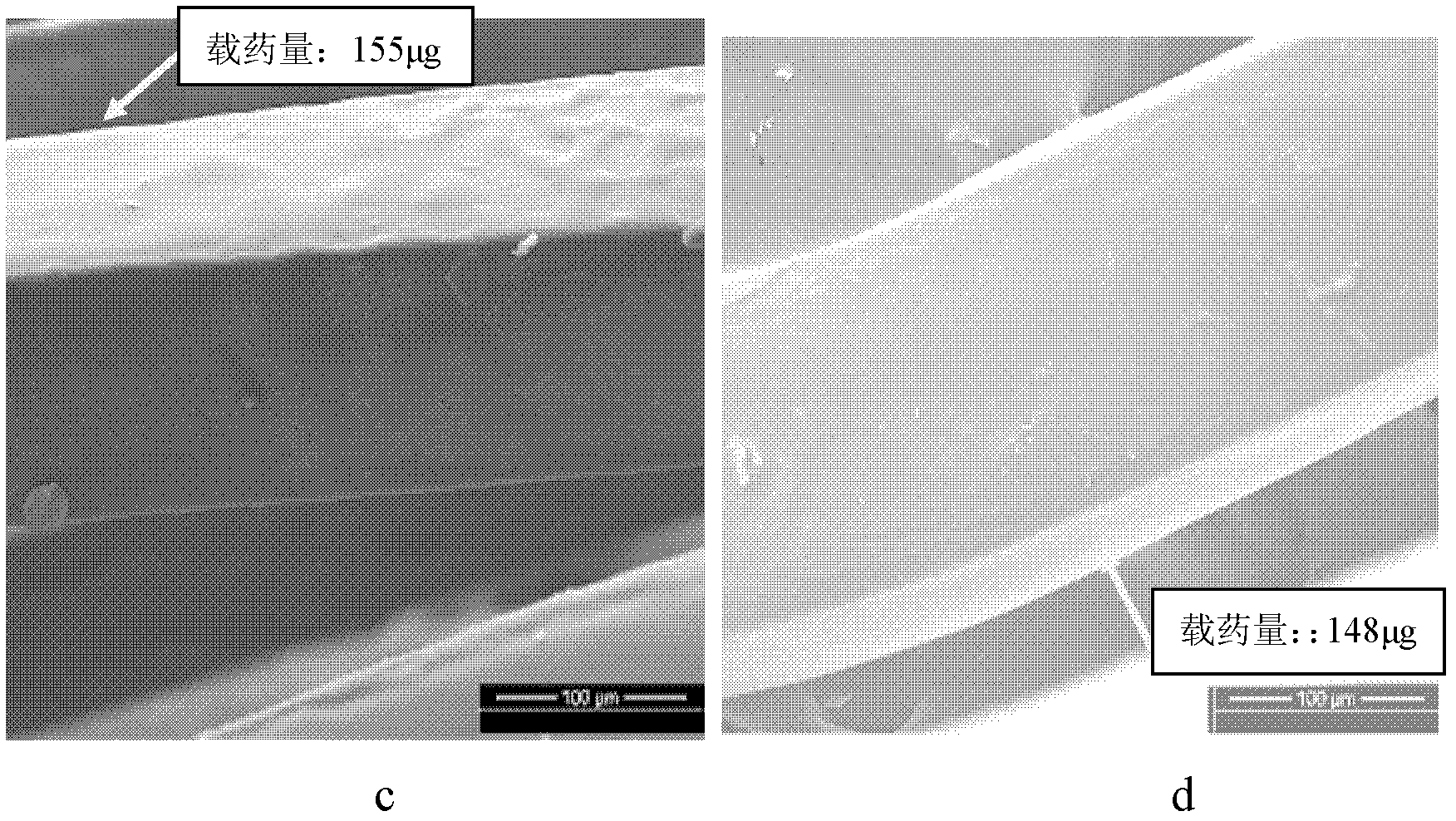
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] (1) Extrude L-polylactic acid with an intrinsic viscosity of 5.0dl / g into a pipe with an outer diameter of 4.0mm and a wall thickness of 0.5mm, and use a laser engraving method to carve the pipe into a stent structure.
[0060] (2) Surface treatment of the engraved stent structure: using a laser etching method to drill holes on the surface of the polymer stent structure. The size of the holes is 20 microns in diameter and 20 microns in depth to obtain a non-surface-activated stent matrix.
Embodiment 2
[0062] (1) Form a polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (polylactic acid: glycolic acid = 85:15) with an intrinsic viscosity of 2.00dl / g into a pipe with an outer diameter of 3.0mm and a wall thickness of 0.3mm with an extruder, and engrave it with a laser The method carves the tubing into a scaffolding structure.
[0063] (2) Carry out surface treatment to the engraved support structure: use chemical corrosion method to place holes on the surface of the polymer support structure, that is, immerse the support structure in a concentrated sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 98%, and use ultrasonic oscillation with an oscillation frequency of 30kHz. After 10 minutes, holes are placed on the surface of the support structure. The size distribution range of the pores is 1-50 microns in diameter and 1-50 microns in depth, so as to obtain a non-surface-activated support matrix.
Embodiment 3
[0065] (1) Extrude the polylactic acid-caprolactone copolymer (polylactic acid:polycaprolactone=50:50) with an intrinsic viscosity of 2.0dl / g with an extruder to form an outer diameter of 2.0mm and a wall thickness of 0.5mm. Tubing, the tubing is engraved into a stent structure by laser engraving.
[0066] (2) Surface treatment of the engraved support structure: use a pinhole processing method to punch holes on the surface of the polymer support structure, the diameter of the punching pin is 30 microns, and the size of the surface holes obtained is 30 microns in diameter and 30 microns in depth non-surface-activated scaffold matrix.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wall thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com