Preparation method and application of autologous mesenchymal stem cell-loaded human amniotic membrane cornea paster
A bone marrow mesenchymal and stem cell technology, applied in the field of regenerative medicine, can solve the problems of less treatment opportunities, increased risk of disease in healthy eyes, and limited source of materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1. Evaluation of ocular surface epithelial recovery
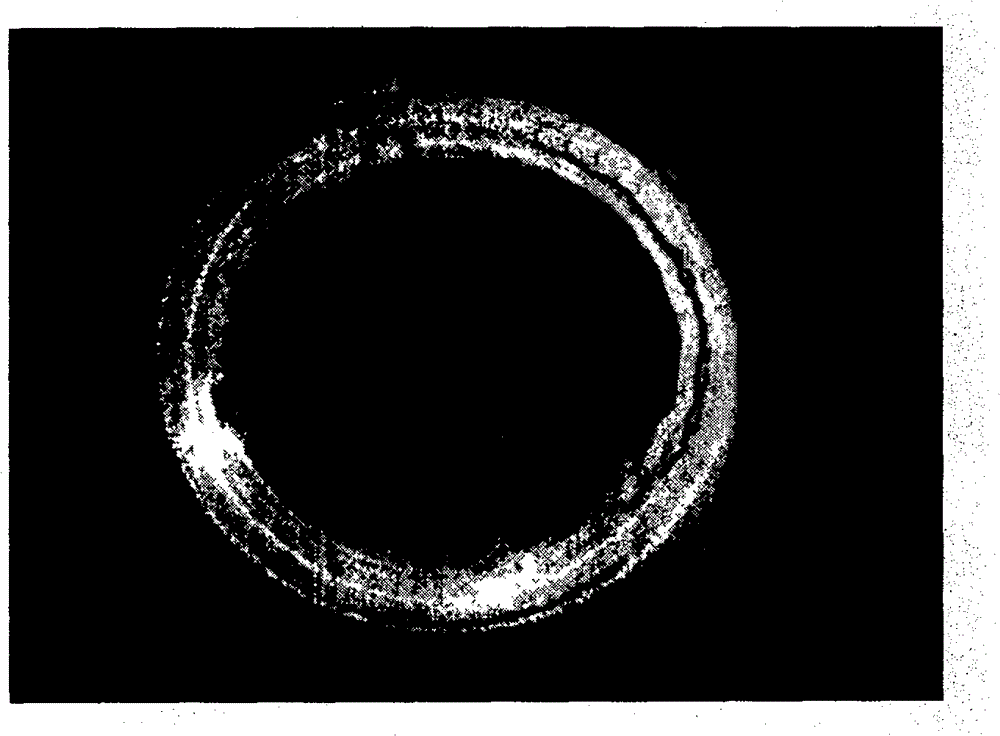
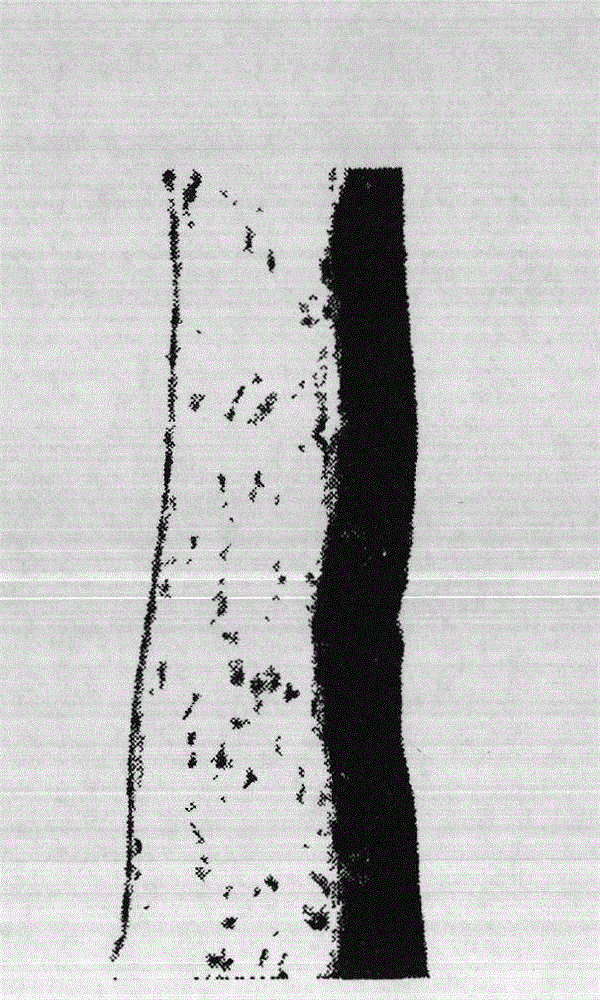
[0044] Severe corneal epithelial defects in rats after alkali burns (see Figure 3a , Figure 3b ), four weeks after the operation, the experimental animal cornea was observed, and each rat was evaluated from five aspects of corneal transparency, corneal turbidity, hyphema, hypopyon, and corneal perforation. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the corneal recovery effect after mesenchymal stem cell transplantation is basically the same as that after corneal limbal stem cell transplantation, and is better than simple amniotic membrane transplantation and fibroblast transplantation. In addition, through slit lamp photography, it can be seen that the new blood vessels in the burnt cornea transplanted with mesenchymal stem cells are significantly reduced, the epithelium is basically restored, and the cornea is transparent. The effect is basically the same as that of tran...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment two, the recovery of burnt rat visual acuity
[0048] By optokinetic tracker to the tracking of experimental rat's vision reflex state, the total distance of motion and the trajectory of the single eye before the burn, the single eye before the burn, and the single eye after the burn are compared (see Figure 6a , Figure 6b , Figure 6c , Figure 6d , Figure 6e , Figure 6f ), it can be seen that there is a significant difference in the visual tracker tracking the visual status of rats, and the optokinetic tracker works normally. After the burn, different types of cells were transplanted, and the data of each group were compared horizontally, and the P values were compared through the optokinetic responses of different gratings (see Table 2). There is a significant improvement. MSC: transplanted mesenchymal stem cells; LSC: transplanted limbal stem cells; AM: transplanted amniotic membrane alone; FB: transplanted fibroblasts; CON: negative control. ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3. Response of inflammatory factors
[0058] MMP-2 (matrix metalloproteinase 2) uses basement membrane collagen as a specific substrate, and its tissue-type inhibitor can directly regulate the enzyme activity in vivo, so MMP-2 can respond to the changes of its new blood vessels in corneal injury. It can be seen from the figure (see Figure 7a , Figure 7b ), the cornea transplanted with mesenchymal stem cells ( Figure 7b ) than the cornea with simple amniotic membrane transplantation ( Figure 7a ) stromal activity is low, indicating that mesenchymal stem cells play a decisive role in inhibiting the regeneration of new blood vessels, showing that the inflammatory response of the corneal stroma of rats transplanted with mesenchymal stem cells is weaker than that of other cells transplanted.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com