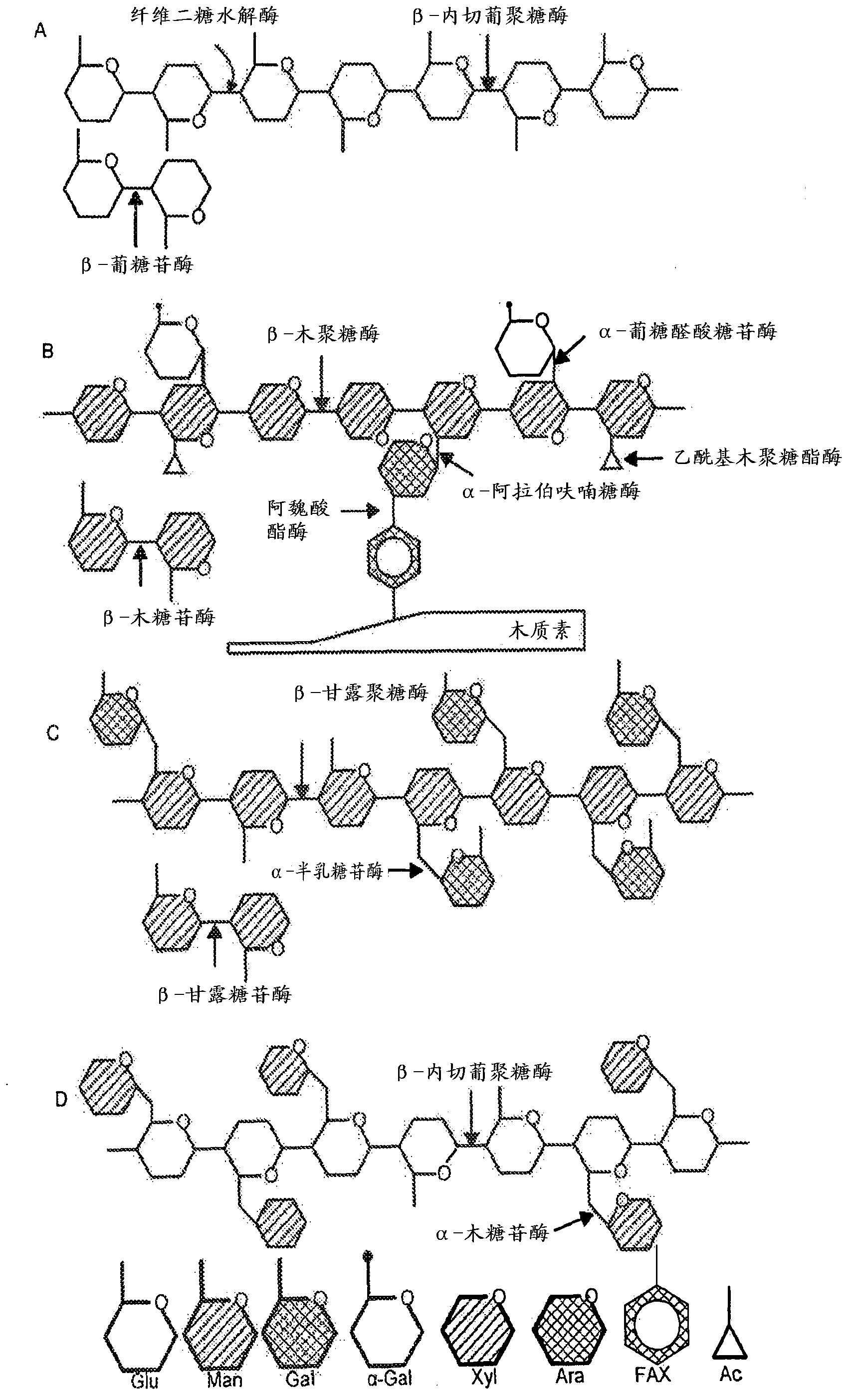
Yeast expressing saccharolytic enzymes for consolidated bioprocessing using starch and cellulose
A technology of cellobiose and hydrolase, which is applied in the direction of introducing foreign genetic material, hydrolase, biofuel, etc. through the use of vectors, and can solve the problems of lack of efficient utilization of pentose and undisclosed ethanol commercially relevant potency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0371] Embodiment 1: the expression of fungal lignocellulosic enzyme system component in yeast
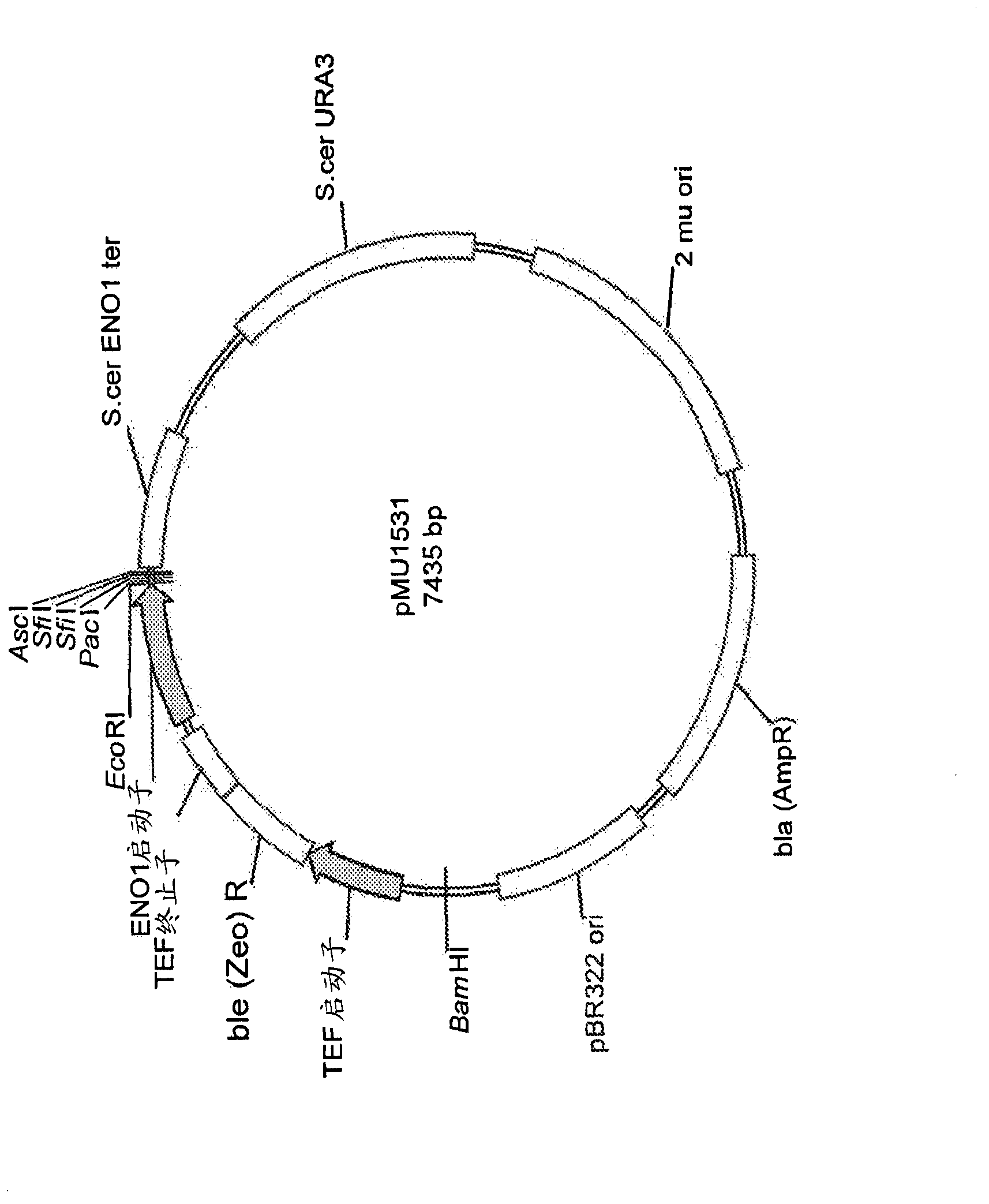
[0372] In order to generate strains expressing these different enzymes and expected to co-express them, several promoter and terminator pairs were generated for use as expression vectors. The promoter-terminator pairs and the enzyme types tested under their control are listed in Table 3. Genes encoding the various enzymatic activities were cloned into vector pMU1531 using standard molecular biology methods (see, eg, Maniatis, "Molecular Cloning" Cold Spring Harbor Press). figure 2 A schematic diagram of pMU1531 as the backbone cloning vector used is given. This vector contains the ENO1 promoter and terminator from S. cerevisiae and the URA3 and zeocin markers for use in yeast. It was subsequently modified to have various promoter / terminator combinations listed in Table 3.
[0373] Table 3. Promoters and terminators used to express fungal and bacterial genes
[0374]
[0375...
Embodiment 2
[0383] Example 2: Characterization of expression and activity of accessory cellulases
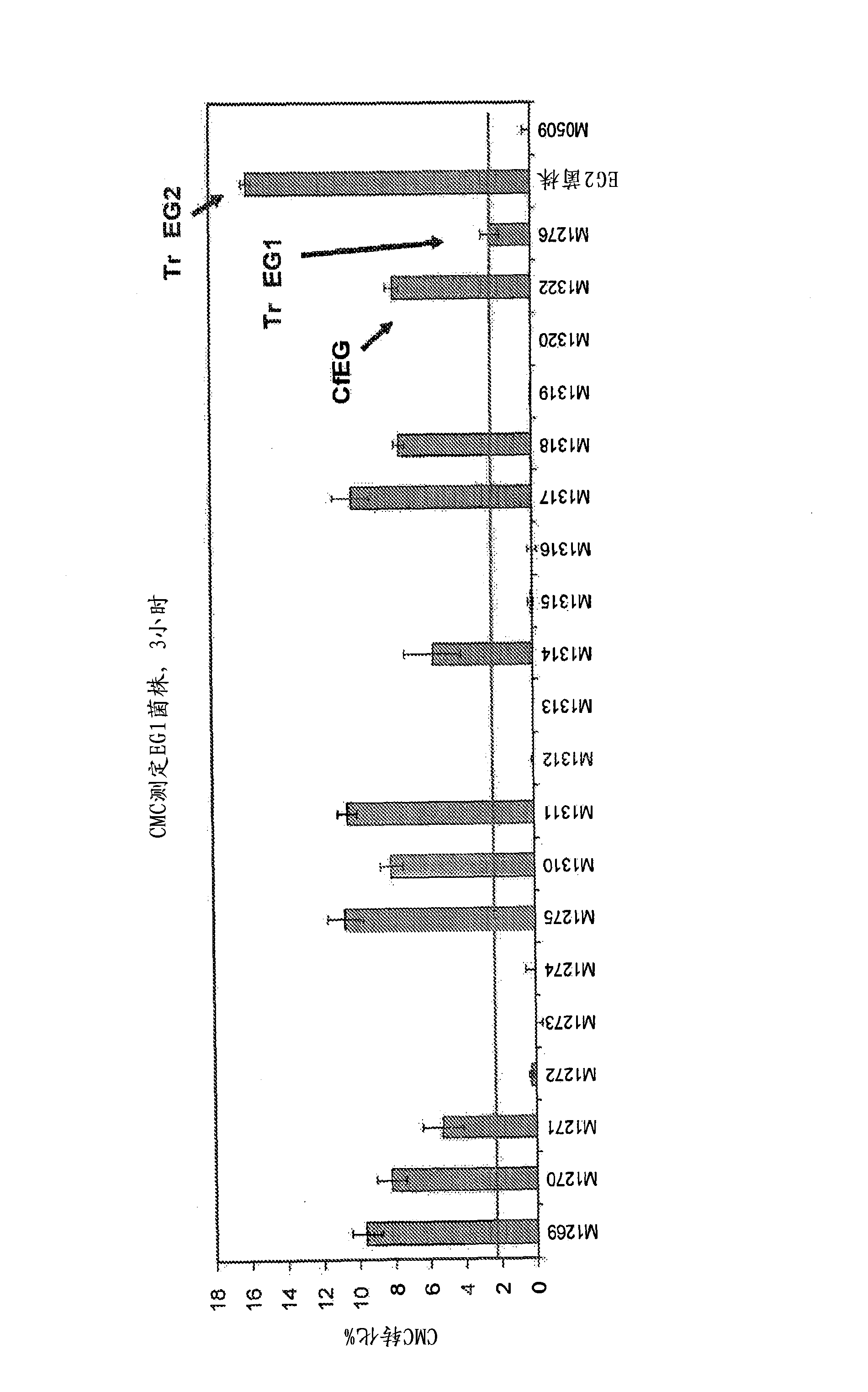
[0384] After strain construction, strains expressing fungal EG1 candidates were grown in 50 mL shake flask cultures with 100 ug / mL zeocin and tested for activity against CMC and Avicel. Figure 3 shows that several active EG1s were found and that several EG1s outperformed a previously used comparable enzyme (T. reesei EG1, M1276) in activity. Based on these data, the best top 6 candidates were selected based on activity against Avicel for further testing on PHW ( Figure 4 and 5 ).
[0385] PHW assays were performed using a pretreated wood substrate (MS149) in the presence and absence of purified yeast-produced CBH1 and CBH2 (2 mg / g each) and Novozyme 188BGL. 2 mL of supernatant from each EG1 expressing strain was used in the assay. A strain expressing TrEG2 from the same plasmid was again used as a control. Results from such assays can be found in Figure 4 and 5 middle. Several EG1...
Embodiment 3
[0398] Embodiment 3: cloning and expression of 5 kinds of synthetic xylanases and 5 kinds of synthetic xylosidases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0399] Expression of xylanases and xylosidases in yeast was examined to broaden the spectrum of enzymatic activity of yeast-produced lignocellulosic systems. Xylanases were selected from public databases and tested for functional expression in yeast on substituted xylans. Xylosidases were selected based on homology to Aspergillus niger xlnD (GH family 3 enzymes), which includes xylosidases from GH family 43. Table 5 (condensed form of Table 4) shows the genes selected for synthesis and the nomenclature of the expression vectors. All genes were cloned under the control of the ENO1 promoter / terminator using the pMU1531 expression plasmid. All the plasmids were transformed into Saccharomyces cerevisiae M0509, and the transformants were confirmed by PCR.
[0400] Table 5. Genes encoding xylanases and xylosidases expressed in Saccharomy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com