Method for preparing artemisinin for malaria
An artemisinin and anti-malarial technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of unfavorable environmental protection and industrial production, difficulty in realizing industrial production, long artemisinin synthesis route, etc., and achieve easy large-scale production, cheap reagents, and high yield high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
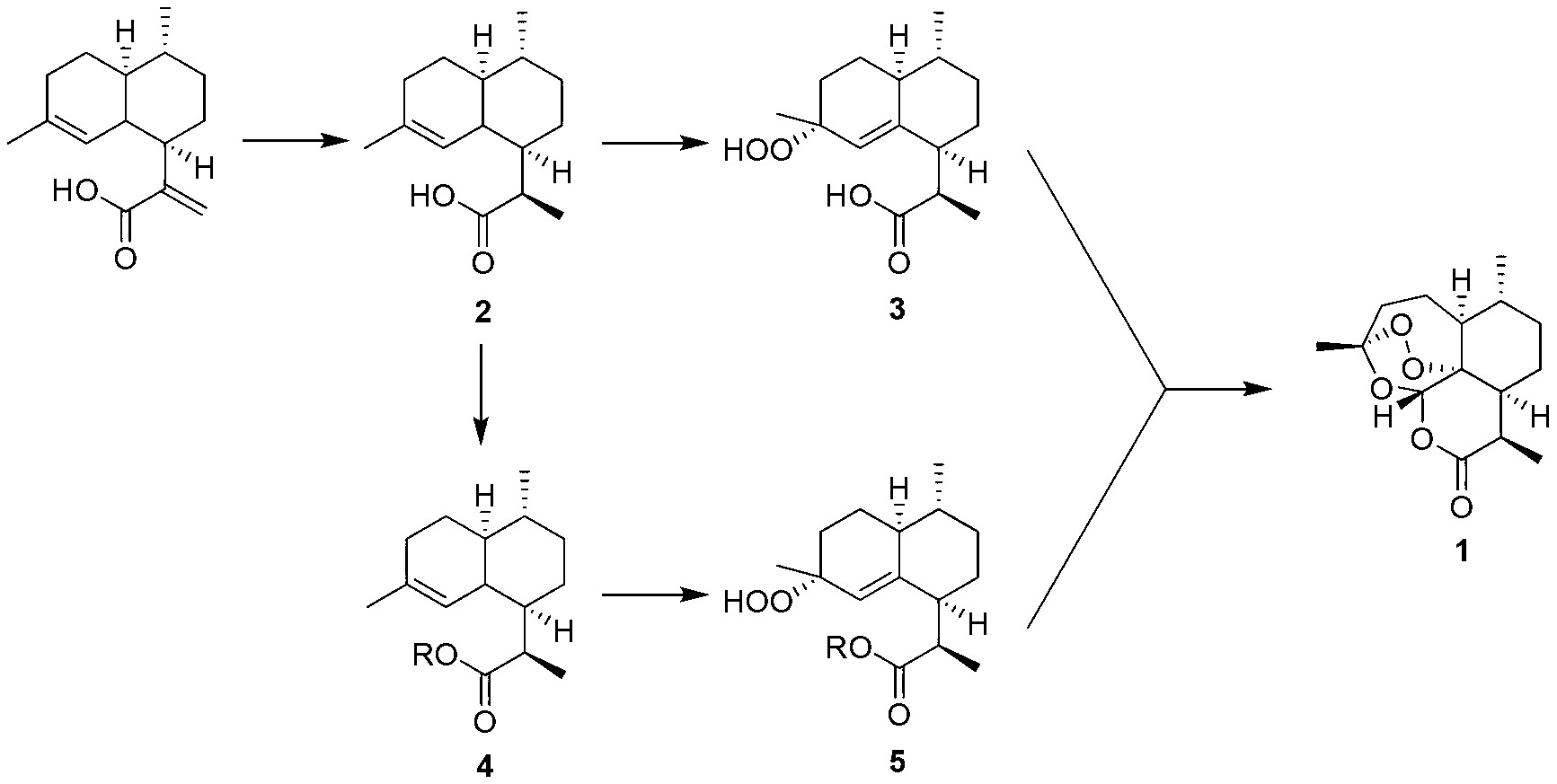
[0044] (1) Synthesis of dihydroartemisinic acid 2
[0045] Artemisinic acid (100 g, 427 mmol) and 10% Pd / C (4.3 mmol) were added to 1000 mL of methanol, and reacted at -50 °C in a hydrogen atmosphere (1 bar) for 24 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite, and the organic solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a white solid (99 g, 98%).
[0046] (2) Synthesis of dihydroartemisinic acid 3 peroxide
[0047] Dihydroartemisinic acid (99 g, 420 mmol), potassium dichromate (4.2 mmol), potassium carbonate (4.2 mmol) were added to 1000 mL of acetonitrile. At -78°C, slowly add 30% hydrogen peroxide (420 mmol) dropwise to the system, and react overnight. The organic solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, the residual phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (500mL×3), the combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered by suction, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the product was directly put into the next react...
Embodiment 2
[0051] (1) Synthesis of dihydroartemisinic acid 2
[0052] Artemisinic acid (100 g, 427 mmol) and 10% Pd / C (427 mmol) were added to 1000 mL of isopropanol, and reacted at 25 °C in a hydrogen atmosphere (1 bar) for 12 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite, and the organic solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a white solid (100 g, 99%).
[0053] (2) Synthesis of dihydroartemisinic acid 3 peroxide
[0054] Dihydroartemisinic acid (100 g, 424 mmol), sodium perchlorate (424 mmol), and pyridine (424 mmol) were added to 1000 mL of acetone. At -78°C, 30% hydrogen peroxide (4.2 mol) was slowly added dropwise to the reaction mixture and reacted overnight. The organic solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, the residual phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (500mL×3), the combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered by suction, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the product was directly put into the next...
Embodiment 3
[0058] (1) Synthesis of dihydroartemisinic acid 2
[0059] Artemisinic acid (100g, 427mmol), Al 2 o 3 / Rh (4.3mmol) was added into 1000mL of methanol, and reacted at -50°C in a hydrogen atmosphere (1 bar) for 24 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite, and the organic solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a white solid (99 g, 98%).
[0060] (2) Synthesis of dihydroartemisinic acid 3 peroxide
[0061] Dihydroartemisinic acid (99 g, 420 mmol), sodium hypochlorite (4.2 mmol), sodium hydroxide (4.2 mmol) were added to 1000 mL of acetonitrile. At -40°C, 30% hydrogen peroxide (420 mmol) was slowly added dropwise to the system, and reacted overnight. The organic solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, the residual phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (500mL×3), the combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered by suction, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the product was directly put into the next re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com