Method for analyzing and dissociating lipid molecules by laser-induced electron capture mass spectrum
A laser desorption and dissociation technology, applied in the field of laser desorption dissociation mass spectrometry, can solve the problems of difficulty in generating low-energy electrons, increase manufacturing difficulty, and complicated operation, and achieve the effects of fast analysis speed, simple and easy control of the process, and high product purity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
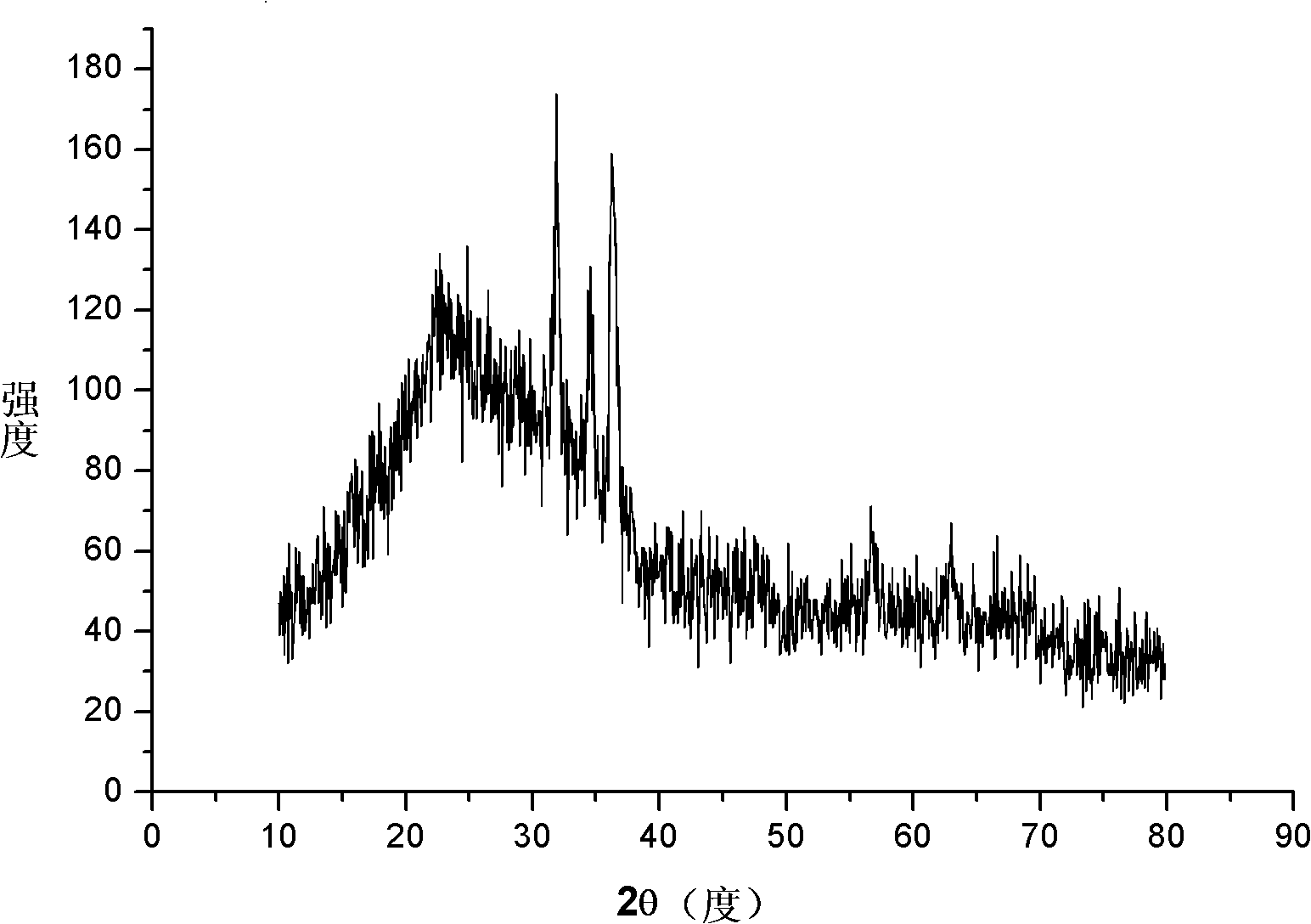
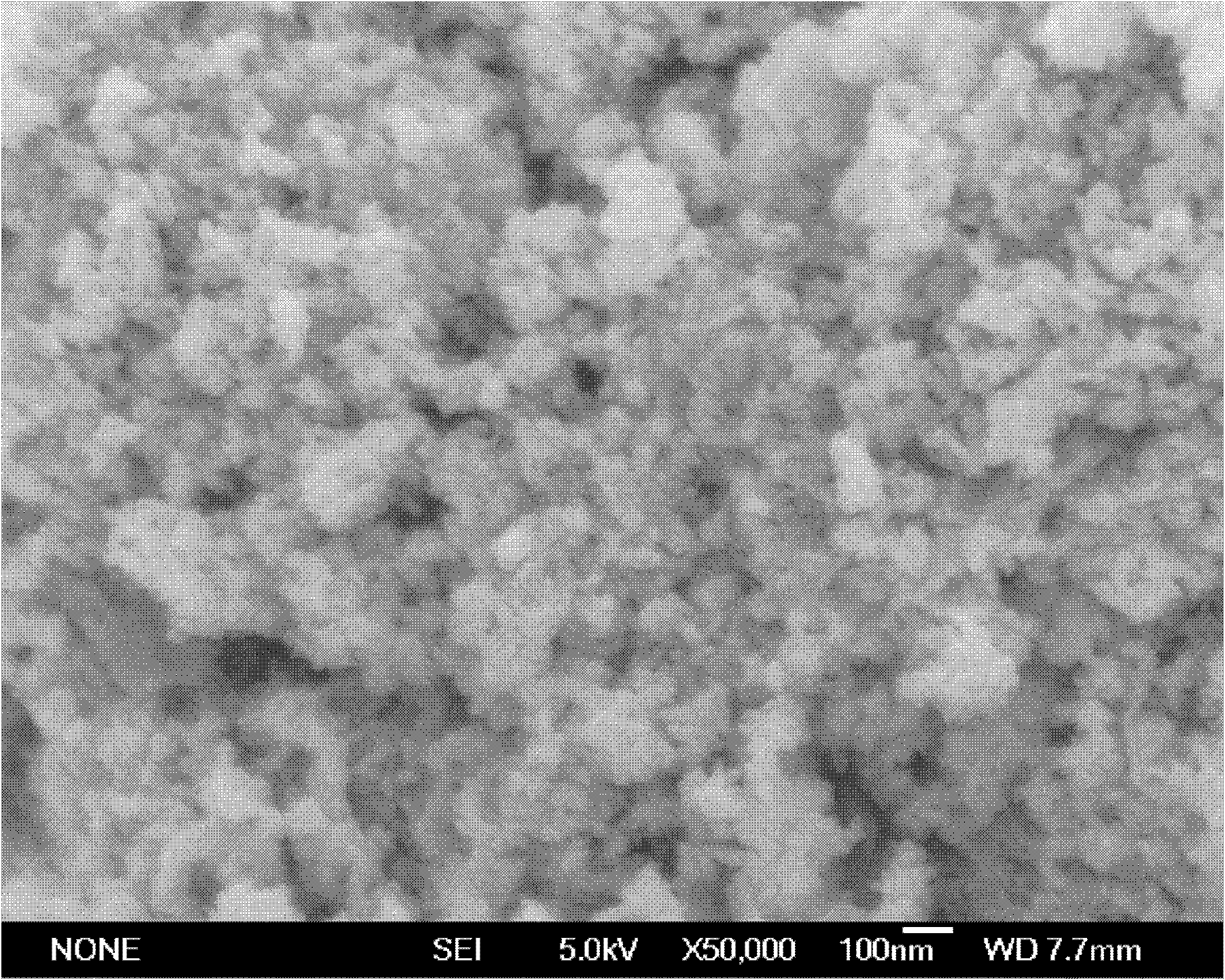
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Preparation of Nano-ZnO Matrix and Sample Target
[0042] The preparation steps are as follows:
[0043] 1. Stir and heat 15ml of zinc sulfate solution with a concentration of 1mol / L to 60°C, then dropwise add 30ml of ammonium bicarbonate solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, continue to stir for 2 hours after the dropwise addition and keep at 60°C;
[0044] 2. Centrifuge the material obtained in step 1) at 2000g (7722rpm) for 2 minutes, discard the supernatant, wash the solid with pure water until neutral, and bake at 100°C for 200 minutes;
[0045] 3. Take the dry solid obtained in step 2, put it into a muffle furnace, raise the temperature to 500°C, and calcinate for 2 hours to obtain white nano-zinc oxide matrix particles;
[0046] 4. Using an analytical balance, weigh the product obtained in step 3, suspend 1 mg of the product obtained in step 3 in 150 μl isopropanol solution, and sonicate for 10 minutes to obtain a white suspension. Using a pipette, add 1 μl o...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The nano-zinc oxide matrix and mass spectrometer sample target prepared in Example 1 were used for the analysis of free fatty acid, fatty acid methyl ester and triglyceride standard.
[0050] 1. Weigh 1 mg of the obtained nano-zinc oxide matrix material;
[0051] 2. Suspend the nano-zinc oxide obtained in step 1 in 150 μl isopropanol solution, and sonicate for 10 minutes to obtain a white suspension;
[0052] 3. Using a pipette, drop 1 μl of the white suspension onto the sample target of the mass spectrometer, and let the solvent evaporate completely;
[0053] 4. Weigh standard products such as free fatty acids, fatty acid methyl esters and triglycerides, dissolve them in n-hexane, and prepare a 10 μg / μl sample solution;
[0054] 5. Pipette 1 μl of the sample solution in step 4 and add it dropwise to the sample target obtained in step 3;
[0055] 6. In the mass spectrometry experiment, put the target with the sample added dropwise into the mass spectrometer (SYNAPT G2...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The nano-zinc oxide matrix and mass spectrometer sample target prepared in Example 1 are used for the analysis of fatty acids in vegetable oil
[0058] 1. Weigh 1 mg of the obtained nano-zinc oxide matrix material;
[0059] 2. Suspend the nano-zinc oxide obtained in step 1 in 150 μl isopropanol solution, and sonicate for 10 minutes to obtain a white suspension;
[0060] 3. Using a pipette, drop 1 μl of the white suspension onto the sample target of the mass spectrometer, and let the solvent evaporate completely;
[0061] 4. Weigh 5 mg of vegetable oil (rapeseed oil or cottonseed oil), dissolve it with n-hexane, and prepare a sample solution of 50 μg / μl;
[0062] 5. Pipette 1 μl of the sample solution in step 4 and add it dropwise to the sample target obtained in step 3;
[0063] 6. In the mass spectrometry experiment, the target with the sample added dropwise was put into a mass spectrometer (SYNAPT G2 HDMS, WATERS, USA), and the frequency of the ultraviolet laser was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com