Method for preparing fermentable sugar and lignosulfonate from furfural residues
A technology of lignosulfonate and furfural slag, which is applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve problems such as the decrease of enzyme hydrolysis efficiency, and achieve the effects of reduced dosage, easy implementation, and good compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
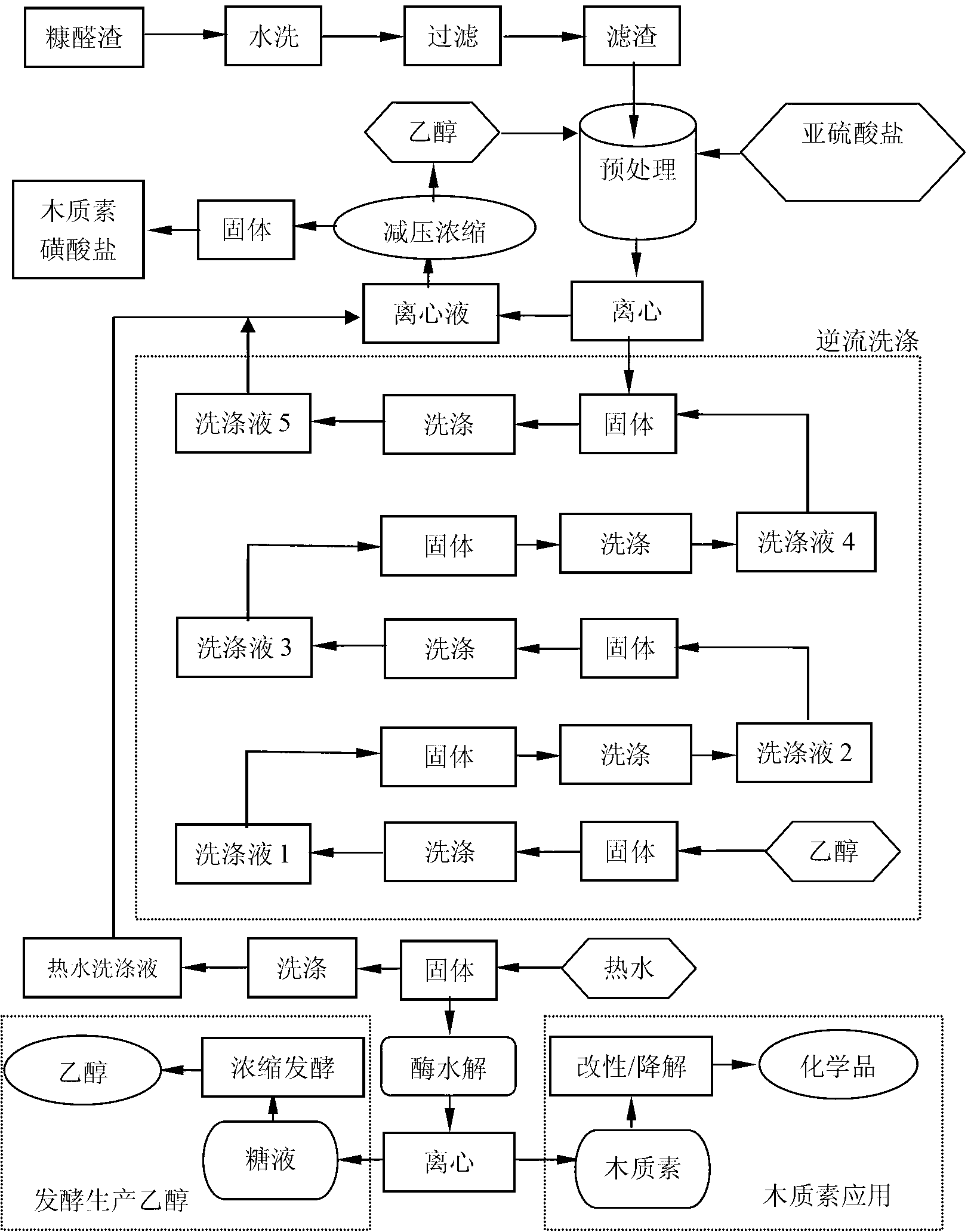
[0031] Take 10kg of furfural slag (industrial furfural slag) and adjust it to a solid content of 10% with water, soak for 24 hours, stir at regular intervals, filter, and rinse the filter residue with tap water 5 times until the pH of the rinse water is 7. Wash the obtained furfural slag for later use.
[0032] see figure 1 . Take 100g of furfural slag (furfural slag obtained by washing with water, the same below) and 80% ethanol solution, the solid content of the mixture is 100g / L, then add sodium sulfite (sodium sulfite concentration is 2g / L), and place in a 60°C 100rpm React in a constant temperature water bath shaker for 2.5 hours, then centrifuge the sample, the separated solid is used for countercurrent washing, and the separated liquid is retained.
[0033] The pretreatment steps were repeated to obtain five batches of solids, which were subjected to multistage countercurrent washing with 95% industrial ethanol. The first batch of solids was washed three times with 9...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Take 100g of furfural slag and use 80% ethanol solution to adjust the solid content to 100g / L, then add sodium sulfite (sodium sulfite concentration is 2g / L), place it in a constant temperature water bath shaker at 60°C and 100rpm for 2.5h, and then The sample was subjected to centrifugation, and the separated solids were sequentially countercurrent washed with detergent 4, detergent 3, detergent 2, detergent 1 and 95% ethanol solution of Example 1.
[0038] The samples after counter-current washing were washed with deionized water at 50°C, and then enzymatically hydrolyzed using an acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer system with a pH of 4.8. The enzymatic hydrolysis conditions were substrate concentration of 25g / L, and the amount of cellulase was 15FPU / ( g cellulose), the enzymatic hydrolysis temperature is 50℃, and the hydrolysis time is 68h.
[0039] The saccharification rate reached 84.1%. The lignosulfonate yield was 14.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Take 100g of furfural slag and adjust it to a solid concentration of 100g / L with 75% ethanol solution, then add sodium sulfite (the concentration of sodium sulfite reaches 5g / L), put it in a constant temperature water bath shaker at 60°C and 100rpm for 3h, and then carry out the sample Centrifugal separation, the solid that separates obtains uses the washing agent 4 of embodiment 1, washing agent 3, washing agent 2, washing agent 1 and 95% ethanol solution countercurrent washing successively.
[0042] The samples after countercurrent washing were washed with deionized water at 50°C, and then subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis. , using acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer system with a pH of 4.8, the enzymatic hydrolysis conditions were substrate concentration 25g / L, cellulase dosage 15FPU / (g cellulose), enzymatic hydrolysis temperature 50°C, and hydrolysis time 65h.
[0043] The saccharification rate reached 83.5%. Lignosulfonate yield was 15.6%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com