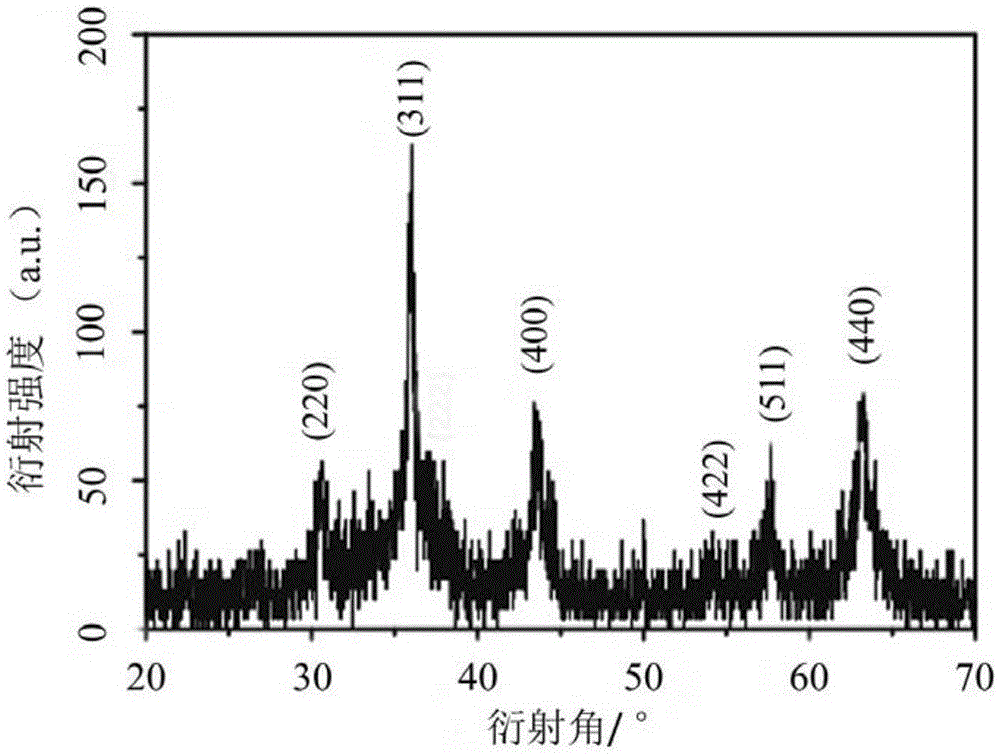
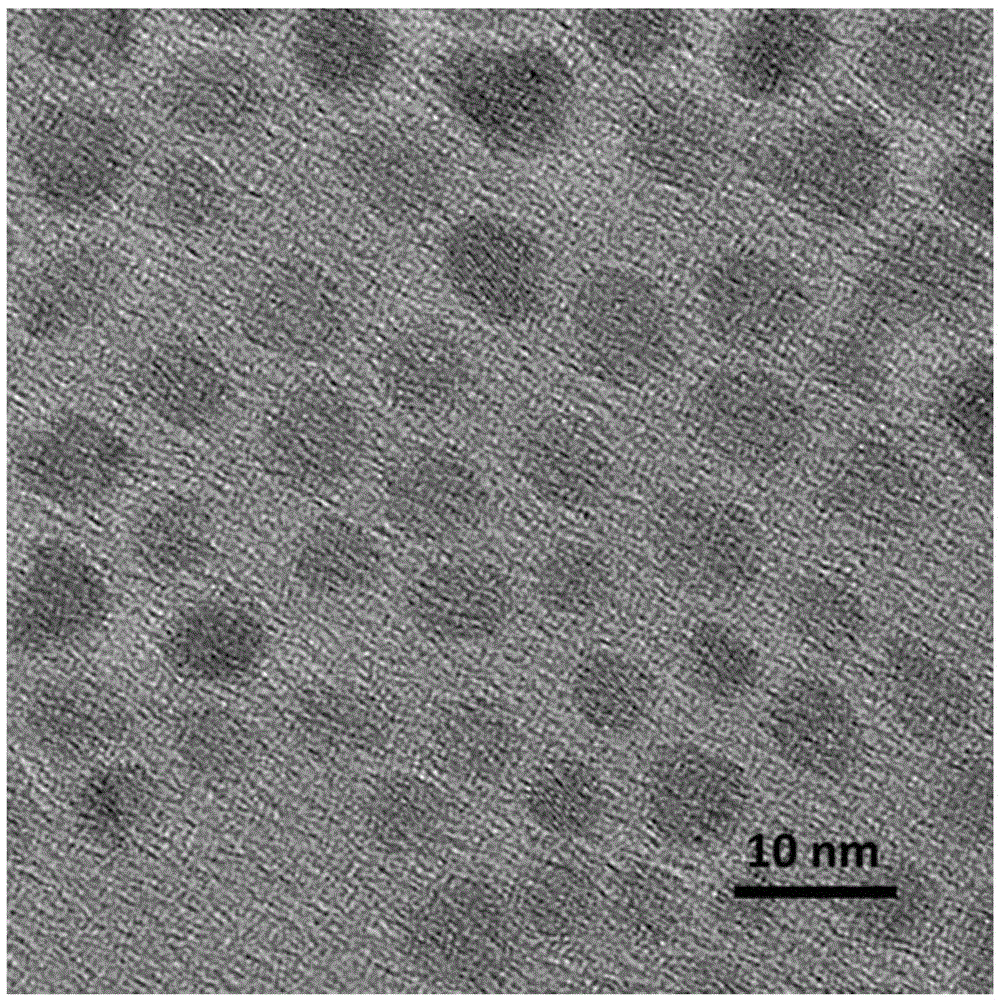
A kind of preparation method of superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticle
A nanoparticle and superparamagnetic technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve the problems of low purity of nanoparticles, uneven particle size distribution, and high energy consumption in the production process, and achieve good product performance, high saturation magnetization, and high energy efficiency. The effect of utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (a) Weigh 0.4g NaOH and dissolve in 1mLH 2 O, and then mixed with 6mL oleic acid and 3mL absolute ethanol in the process of stirring to obtain a homogeneous transparent solution A.
[0032] (b) Add 50 μL of 80% hydrazine hydrate to solution A, and continue stirring for 5 minutes to obtain homogeneous solution B.
[0033] (c) Prepare 0.5mM ferric ammonium sulfate aqueous solution C and 0.25mM ferrous sulfate aqueous solution D for later use.
[0034] (d) Add 1mL of LC solution and 1mL of LD solution to solution B in turn, and stir quickly to mix evenly to obtain solution E.
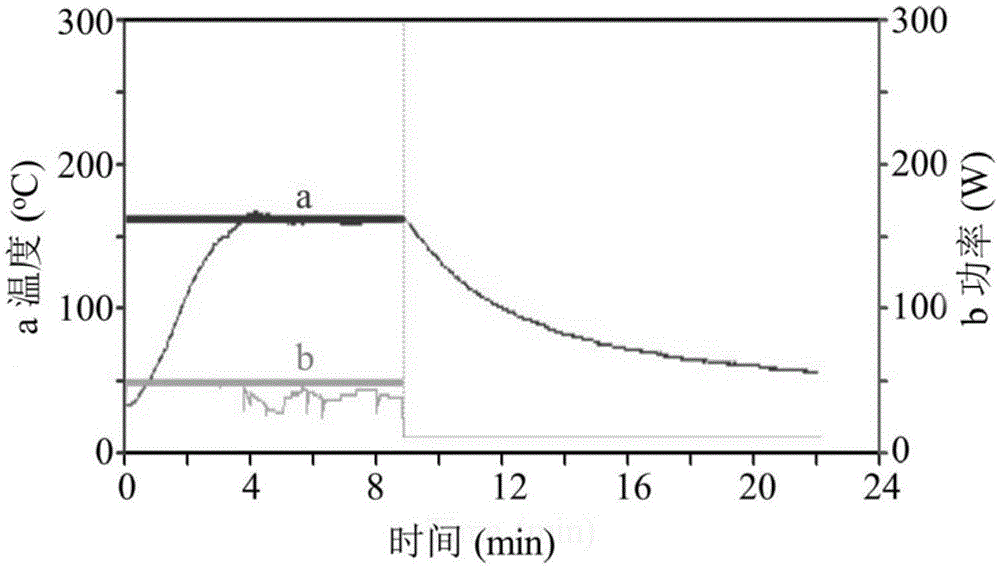
[0035] (e) Transfer the solution E into the quartz reaction tube of the microwave synthesizer, seal it with a matching rubber stopper, put it into the microwave synthesizer, and set the microwave synthesis parameters: power 40W, keep temperature 160°C, keep time 5min. Start the program for microwave synthesis.
[0036] (f) After the reaction stops, take out the reaction tube, add 10mL of absolute...
Embodiment 2
[0043] (a) Weigh 0.4g NaOH and dissolve in 1mLH 2 O, and then mixed with 6mL oleic acid and 3mL absolute ethanol in the process of stirring to obtain a homogeneous transparent solution A.
[0044] (b) Add 50 μL of 80% hydrazine hydrate to solution A, and continue stirring for 5 minutes to obtain homogeneous solution B.
[0045] (c) Prepare 0.5mM ferric chloride aqueous solution C and 0.25mM manganese acetate aqueous solution D for later use.
[0046] (d) Add 1mL of LC solution and 1mL of LD solution to solution B in turn, and stir quickly to mix evenly to obtain solution E.
[0047] (e) Transfer the solution E into the quartz reaction tube of the microwave synthesizer, seal it with the matching rubber stopper, put it into the microwave synthesizer, and set the microwave synthesis parameters: power 40W, keep temperature 160°C, keep time 1min. Start the program for microwave synthesis.
[0048] (f) After the reaction stops, take out the reaction tube, add 10mL of absolute eth...
Embodiment 3
[0053] (a) Weigh 0.4g NaOH and dissolve in 1mLH 2 O, and then mixed with 6mL oleic acid and 3mL absolute ethanol in the process of stirring to obtain a homogeneous transparent solution A.
[0054] (b) Add 100 μL of 80% hydrazine hydrate to solution A, and continue stirring for 5 minutes to obtain homogeneous solution B.
[0055] (c) Prepare 0.25mM ferric ammonium sulfate aqueous solution C and 0.125mM cobalt acetate aqueous solution D for later use.
[0056] (d) Add 1mL of LC solution and 1mL of LD solution to solution B in turn, and stir quickly to mix evenly to obtain solution E.
[0057] (e) Transfer the solution E into the quartz reaction tube of the microwave synthesizer, seal it with a matching rubber stopper, put it into the microwave synthesizer, and set the microwave synthesis parameters: power 20W, keep temperature 120°C, keep time 5min. Start the program for microwave synthesis.
[0058] (f) After the reaction stops, take out the reaction tube, add 10mL of absolu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com